I am a BS-Mechanical Engineering student incoming 5th year and currently taking a summer class which is the"On-The-Job Training". I am hired in a private company which manufacture, produce and distribute semiconductor materials which is the transistor.
Intro
Transistors are widely used electronic components that perform the function of a switch or an amplifier. The semiconductor material used in transistors is generally silicon, germanium or gallium arsenide. Impurities are added to them in order to create electrically positive (P) or electrically negative (N) behavior.
When these layers are joined together the contact potential creates a potential barrier across the PN or NP junction. This potential barrier maintains electrons on the N side and holes on the P side. This property of transistor allows it to be used as a rectifier i.e. allow current to flow in only one direction.
When the P side is made positive by an applied field, the barrier height is lowered and most of the electrons from the N side flow to the P side and most of the holes flow to the N side. The transistor is said to be forward biased in this case. When the applied field makes the P side negative, the barrier height is increased and only a leakage current can flow through the transistor. The transistor is said to be reverse biased in this case.
The design of a transistor allows it to function as an amplifier or a switch. This is accomplished by using a small amount of electricity to control a gate on a much larger supply of electricity, much like turning a valve to control a supply of water.
Transistor as an Amplifier
When a small input current is applied to the base-emitter of a PNP transistor, it gets amplified and a larger current results in the collector-emitter circuit. A typical application of a transistor as a vital electronic component is in a radio wherein weak radio signals from an antenna are amplified into stronger signals identifiable by human ear by a transistor.
The Three Terminal Device
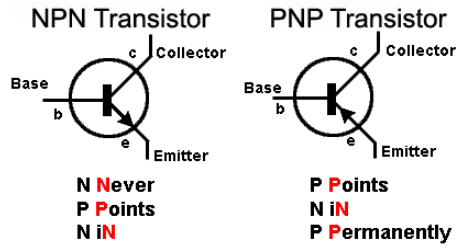
A transistor is a three terminal device consisting of three layers of semiconductor material. Two of them are one type of semiconductor and the third, a different type. For example, a PNP transistor consists of 2 layers of P type semiconductor and a layer of N type semiconductor. We can also have NPN type transistor. The three terminals are respectively referred to as emitter, base and collector.
The 3 terminal device namely are of the following with its characteristics :

| Collector | Base | Emitter |
|---|---|---|
| Positive lead | Lead responsible For Activating The Transistor | Negative Lead |
| Widest and Moderately Doped | Narrowest and Lightly Doped | Moderate and Heavily Doped |
Note : The common transistor has two faces (The curve one and the flat one), to determine which side the emitter or the collector on the transistor is to face the flat side upfront and the emitter side is usually on the left side.
2 Main Types Of Transistors
There are two main types of transistors, the junction transistors and field effect transistors. Each works in a different way. But the usefulness of any transistor comes from its ability to control a strong current with a weak voltage.
JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
A junction transistor consists of a thin piece of one type of semiconductor material between two thicker layers of the opposite type. For example, if the middle layer is p-type, the outside layers must be n-type. Such a transistor is an NPN transistor. One of the outside layers is called the emitter, and the other is known as the collector. The middle layer is the base. The places where the emitter joins the base and the base joins the collector are called junctions.
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS

A field effect transistor has only two layers of semiconductor material, one on top of the other. Electricity flows through one of the layers, called the channel. A voltage connected to the other layer, called the gate, interferes with the current flowing in the channel. Thus, the voltage connected to the gate controls the strength of the current in the channel. There are two basic varieties of field effect transistors-the junction field effect transistor(JFET) and the metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET). Most of the transistors contained in today's integrated circuits are MOSFETS's.
If you happen to reach until the end of this blog, I sincerely thank you for sharing your time on reading. If you have some concerns and thoughts about this please do not hesitate to leave a comment and I will surely be glad to respond :)
Ciao! @thonnavares
Join our discord channel and be a part of our growing community where people around the world are dynamic and oh so friendly! @dynamicsteemians. Help us grow each day by joining us!

Woah very informative post about Transistor, our Electronics class was amazing. Our group final project was the best mwahahaha <3.
Yes sir! You bet. It was one of the most memorable class that I am in. I definitely learned a alot!
Even though our final project was extremely time consuming but I had alot of fun and also learned alot :D !
Transistor: the wonderful three-legged component. Its applications are numerous
Nice post
Yes and It is used worldwide on every electronic device you can see :)
My mechanical engineering friends hated electronics. You are an exception in mechanical engineers I guess.
haha, I also hated it but as time goes by I learn to appreciate things like these because it is a necessity nowadays as a engineer :)
You have been upvoted by the @sndbox-alpha! Our curation team is currently formed by @jeffbernst, @bitrocker2020, @jrswab & @teachblogger . We are seeking posts of the highest quality and we deem your endeavour as one of them. If you want to get to know more, feel free to check our blog.
The transistor, a groundbreaking invention, transformed electronics by enabling compact, efficient circuits. In my projects, especially when working with power electronics, I often rely on the 25n120 igbt for high-performance switching. Its efficiency and reliability make it a go-to choice for handling larger currents and voltages seamlessly.