
What is the nuclear energy?
Nuclear energy is one that is generated by a process in which the atoms of a material called uranium disintegrate. The energy that the uranium releases as its atoms disintegrate produces heat with which the water found in nuclear reactors is boiled. When boiling, the water generates steam with which the turbines inside the reactors move, thus producing electricity.
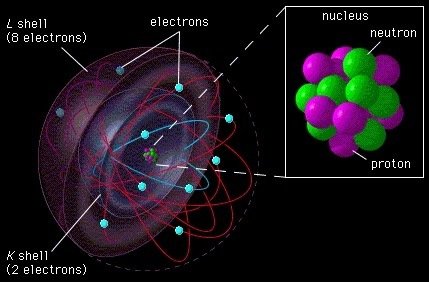
Where does nuclear power come from?
To explain where the nuclear energy comes from, it is necessary to remember Einstein and his famous equation E = mc2 (energy equal to mass by speed of light squared). Simplifying the process and making it more understandable, we could say that the key is the disintegration of atoms. Now, how is it possible to disintegrate these tiny particles? To understand it we must first remember that an atom is composed of a central nucleus with protons (with positive energy) and neutrons (without charge) attached, around which the electrons orbit (with negative energy).

Well, the disintegration of an atom is achieved by releasing the energy of its heavy nucleus and that is possible by bombarding it literally with neutrons, so that it decomposes into two lighter nuclei and that process, called fission, generates energy. In fission two or three neutrons are emitted that can continue interacting with other nuclei reproducing the same process. It is what is commonly known as "chain reaction".
Explained in this way, one could think of an uncontrollable and, therefore, dangerous chain reaction. The basic principle of a nuclear reactor lies in controlling that only one of the neutrons released produces a subsequent fission. If no neutron continues, the reaction is lost, and if there are more than two, the control is lost and the nuclear explosion occurs.
How is nuclear energy produced?
Nuclear energy is the energy that is released during the process of fusion or fission of the nucleus of atomic nuclei as a product of a nuclear reaction.
The energy that can be obtained through these processes are much greater than what any other process can develop.
The inequality of matter at the time of the reaction between the elements is what produces the energy.
A small amount of mass can provide a lot of energy, for example, the amount of energy that 1 kg of uranium can produce is equivalent to the energy that would provide 200 tons of coal.
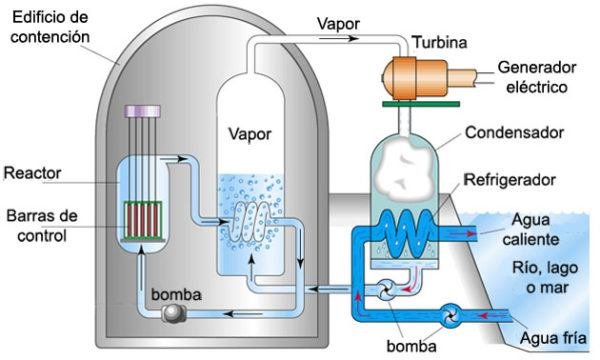
Nuclear energy is one of the cheapest forms of energy to manufacture, but also contains certain risks.
Atoms are small, energy-filled particles whose basic composition is limited to the union of protons and neutrons and their union is what liberates the energy they have inside and through which they work, when they face separation or when they see themselves wrapped in a forced union with other neutrons.
Nuclear energy is produced by fission, a process in which an atom is taken and divided into equal parts, in order to extract it. Also, through fusion, it is possible to achieve nuclear energy. They are totally different processes, but from both we get the energy we need, starting from the atoms.
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction that occurs in the nucleus of the atom that consists in breaking the nucleus by means of the impact of a neutron.
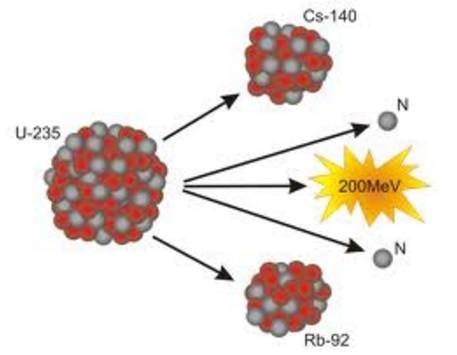
The core contains a large amount of energy stored, thanks to which both protons and neutrons remain together, with fission this energy is partly released and transformed into heat and radiation. These radiations are very harmful and harmful to living beings.
In fission, we divide the nucleus of an atom. In this division, the atom is divided into smaller particles, but not less than half the original mass, plus it has two or three more neutrons. When separated, the energy that keeps the neutrons and the protons together is released. When a chain reaction occurs, because one of the parts joins other neutrons, a nuclear fission once again occurs, releasing energy again.
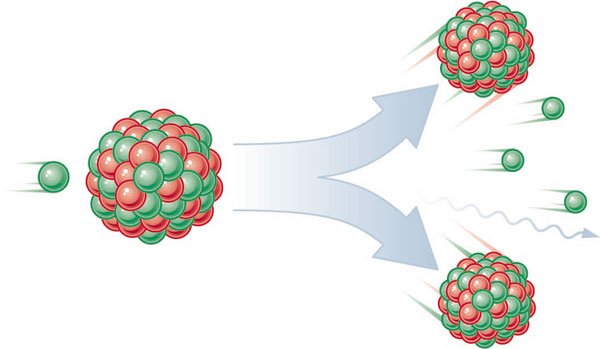
This is achieved by making them collide with Plutonium or Uranium, so that in each crash, nuclear fission occurs, the energy is released and a chain reaction that generates heat begins to awaken. This heat rises and begins to feed the turbines. These same, formed by shovels, begin to spin at such a speed that they begin to generate an energy that feeds a generator. This generator is the one that distributes the energy to all the houses.
Nuclear fusion
Many people talk about fusion and fission, as if they were talking about the same thing, but nothing is further from reality. In this case, we do not separate the atoms here. What is done is to unite them, to create a heavier one.
For nuclear fusion to take place, it is necessary that there be a very high temperature that causes the atoms to separate from the electrons and approach others, overcoming the electrostatic repulsive forces.
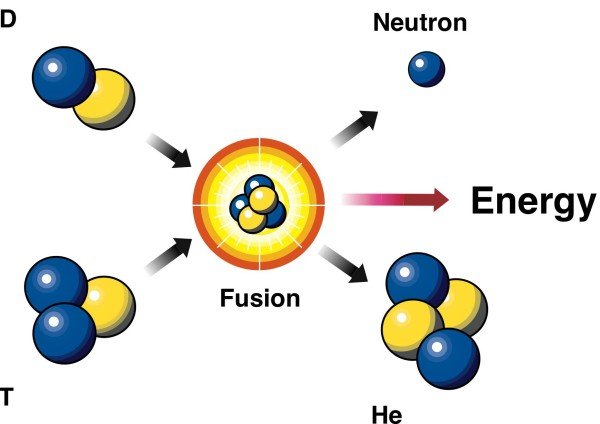
Normally, light atoms tend to be used to obtain the nuclear reaction in which the nuclei unite. Hydrogen atoms and their isotopes (deuterium and tritium) are often used, which bind hydrogen to create a heavier molecule. This union generates a reaction, emits energy and a series of particles that emit kinetic energy. Due to the amount of energy that is concentrated and released in the form of gamma rays, we find the energy from nuclear fusion, in the plasma state, which becomes a mass so dense, that allows it to generate reactions of nuclear fusion.
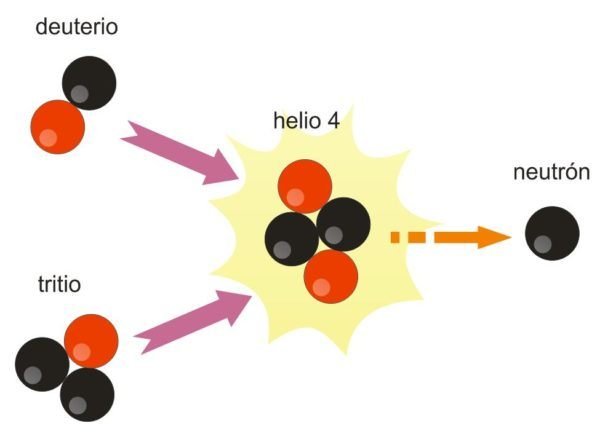
It must be borne in mind that when light atoms are fused, of weight less than iron, the energy emits it. In the opposite case, if the elements that merge are much heavier, the energy absorbs it.
Advantages of nuclear energy.
- Does not produce CO2
- Reduces dependence on oil producers.
- Generates a large part of the electrical energy that we consume every day.
- Its use guarantees less damage to the environment, avoiding the use of fossil fuels
Disadvantages of nuclear energy
- Produces radioactive waste very difficult elimination.
- Accidents, although rare, are very, very dangerous.
- It hinders the control of nuclear weapons
- Increased dependence on Uranium producers and manufacturers of enriched uranium.
- Nuclear power plants demand a high cost of construction and maintenance
Environmental impact of nuclear energy
<div class "text-justify">The environmental impact of nuclear energy is a result of the nuclear fuel cycle, the operation of nuclear power plants and the effects of nuclear accidents.

The routine risks to health and greenhouse gas emissions caused by nuclear fission are small in relation to those associated with the use of coal, but additionally there are catastrophic risks: the possibility that fuel overheating will release amounts Massive fission products to the environment, and the proliferation of nuclear weapons. The population is sensitive to those risks and there has been considerable public opposition to nuclear energy.
Support web pages:
https://twenergy.com/energia/energia-nuclear
https://erenovable.com/energia-nuclear/#Como_se_produce_la_energia_nuclear
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Impacto_ambiental_de_la_energ%C3%ADa_nuclear
That's good info. Thanks for sharing.
Great! congratulations.