The medical term for ear pain is 'otalgia'. Many people regularly suffer from their ears... Pain in the ear can also be extremely intense and tormenting because the human ear is an extremely complex and vulnerable organ. Below we discuss:
- Acute or sudden ear pain
- Chronic ear complaints (remains continuous)
- Recurrent pain in the ear ( often, comes & goes)
In this post both ear complaints in adults and ear pain in children are discussed...
Causes of ear pain
Earpads are caused by internal ear infection or ear canal inflammation in the vast majority of cases. In case of an external ear infection, the ear canal is inflamed in front of the eardrum. When the middle ear or inner ear - or the part behind the eardrum - is inflamed, we speak of an actual ear infection: a middle ear infection or inner ear infection. The most important and most common causes of pain-related ear complaints are as follows:
- Internal ear infection (bacterial infection)
- Flu & cold
- Inflamed ear canal
- Whelk, abscess, fistula, polyp or tumor in the external auditory canal
- Accumulation of fluid behind the eardrum
- Fungal infection in the ear (candida albicans)
- Earbuds, headphones or hearing aid
- Irritation due to cosmetics or cleaning products (hairspray and others)
- Tapping with cotton swabs & matchsticks
- Blocked Eustachian tube
- Complication of 'tubes' or eardrum tubes
- Ear eczema & psoriasis
- Nerve inflammation in the face
- Excessive pressure on the ear due to height or depth
- Perforation of the eardrum (hole or tear)
- Inflamed eardrum ('myringitis')
- Cholesteatoma (cyst of skin cells & earwax) in the ear
- Inflamed balance organ ('labyrinthitis')
- Infection of jawbone or carotid tissue
- Allergy (hay fever and others)
- Slap on the head (head trauma)
- Excessive use of alcohol
- Viral infection (measles, mumps, red dog or herpes)
- Swimming underwater in chlorine baths
- As a radiance of jaw pain or toothache
- Inflamed tonsils: throat malignant inflammation
Ear pain is nine out of ten times the result of an ear infection. Many people with an ear infection stay there for too long. When an ear infection is not addressed in time, the inflammation can spread to other head and face cavities and even lead to life-threatening meningitis. In adults, pain in the ear usually indicates irritation or infection of the ear canal (in front of the eardrum). In children with ear pain, almost always the middle ear (directly behind the eardrum) is ignited.
Image Source
Additional complaints with ear pain
Earache is essentially a moderate to very severe pain deep into the ear. In many of the aforementioned causes of pain in the ear, however, there are usually also additional complaints and symptoms. The main symptoms that accompany ear pain are as follows:
- Itching in the ear
- Increase or fever
- Wounds on the earcups & ears
- Running (outflow of fluid, pus or blood)
- Swollen earcups & ears
- Hearing reduction and tinnitus
- Redness (earlobe, ear rim & ear entry)
- Mounted lymph nodes in the neck
- Narrowing of the ear canal
- Flakes & scabs in the ear
- "Full" feeling in the ear
- Twisting & dizziness
- Flu-like complaints
- Problems with balance & orientation
- Nausea & vomiting
- Acute hearing loss & temporary deafness
- Jaw pain & sore throat
- Irritation of the facial nerves
- Diarrhea
And so there are many more complaints that can accompany ear pain, depending on the exact underlying cause of the ear complaints.
Handling ear pain...
Advice on the treatment of ear pain is probably more practical than the information about the possible causes of ear complaints. That is why we discuss below how you can treat ear problems in children and then the treatment of pain in the ear in adults ...
1. Treating adult carrots...
In adults ear pain is often caused by infection or irritation of the ear canal. Your doctor can look into your ear with an otoscope to determine if there is something wrong with the ear canal. In many cases, the ear canal:
- Too dry
- Injured by cotton swabs or earplugs
- Too full of earwax
- Infected by bacteria or fungi
- Affected by eczema or psoriasis
If your ear canal is not in order, it should be treated with ear drops, ear cream, ear tampons or an ear toilet. With mild ear pain, itching and irritation, acid ear drops are usually the first choice. These ear drops contain acetic acid or aluminum acetate tartrate. Panotile® or Otosporin® is often prescribed for severe ear complaints and ear infections. These drugs contain antibiotics and corticosteroids.
In case of high fever, blood loss and / or recurring or rapidly worsening ear pain, it is advisable to consult a doctor. It may prescribe antibiotics or spray the ear.
2. Treat ear pain in children...
Oorpijn in children is usually the result of a 'normal' uncomplicated ear infection or middle ear infection. This type of pain in the ears of a child is usually caused by a cold virus or flu virus. The mucous membranes in the middle ear swell up due to the virus. This means that the "Eustachian tube" can no longer be opened properly. In children this happens extra often because the 'Eustachius tube' or 'tube of Eustachius' in them is smaller and shorter.
The blocking of the Eustachian tube causes moisture to accumulate behind the eardrum. In this fluid bacteria start to nest, causing a bacterial middle ear infection. The main symptoms of ear pain in children due to middle ear infection are as follows:
- Ear pain & pressure on eardrum
- Increase or fever
- Excretion of blood and / or fluid from the ear
If the pressure becomes too great, the eardrum breaks and a 'loopoor' arises. The inflammatory fluid then runs out, after which the ear pain immediately diminishes or even completely disappears. The eardrum will automatically recover. If ear infection-related ear problems regularly occur in children, however, 'tubes' or eardrum tubes must be placed in the eardrum.
Note:
children under the age of 2 should be examined directly by a doctor for ear pain. Older children and adults can first try paracetamol and nasal spray for earaches. When this does not work an anti-inflammatory analgesic such as:
- Ibuprofen or Advil
- Ascal or Diclofenac
- Femapirin
- Nurofen or Naproxen
- Or a different non-prescription NSAID analgesic
In small children an internal ear infection is often caused by colds, measles or chickenpox. In adults usually due to clogging of - or inadequate ventilation and / or discharge through the Eustachian tube: the connection between middle ear and esophageal head. Due to accumulation of pus and mucus, pressure is created on the eardrum. This is painful and can turn out to be a chronic ear infection.
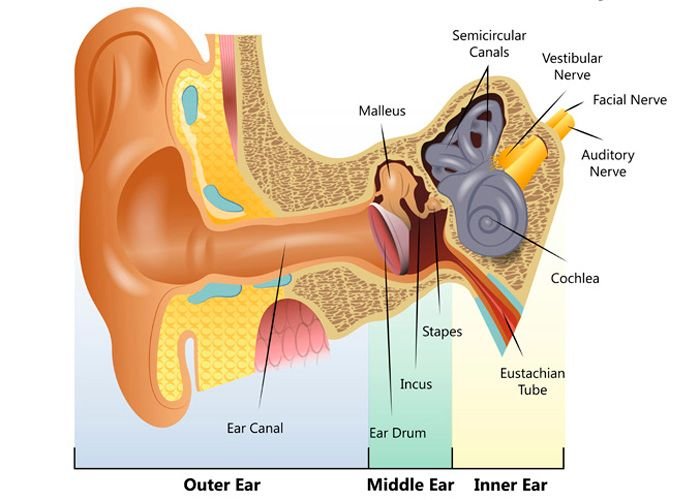
Image Source
Tips to prevent pain in the ear...
Here are some practical tips to prevent ear pains, whether or not due to an ear infection:
- Children up to 6 years and people with tubes or holes in the eardrums can better stay away from chlorine baths.
- Only clean the shell of the ear and only use water.
- Never use objects such as cotton swabs in the ear; certainly not deep into the ear canal.
Earache: finally
Children with earaches younger than 2 years should always be treated by a doctor. Older children and adults can be self-sufficient for three days (nasal drops, steaming, pain relief with ibuprofen, etc.). For pain in the ear that is accompanied by fever over 40ºC or ear pain that lasts for a long time, you can always consult a doctor as a precaution.
If you suffer from continuous, recurring or chronic ear complaints, the ear should usually be thoroughly cleaned with an ear toilet or by having your ears sprayed. Even 'doctoring' on or in the ears is also extremely risky and therefore anything but advisable.
Sources:
Thanks for your time on my post.


I've suffered an ear pain before. It later progresses to acute tonsillitis, and I have to take two weeks course of antibiotics. Ear pain can't be taken lightly.
We should not take it lightly... any ways thanks for ur comment on my post.
You're welcome.