Very Large Array: Day trip to outer space

By Cindy Graff Cohen Southwest Senior source: National radio astronomy observation
What is Radio Astronomy?
We see the world around us, because our eyes detect visible light, a type of electromagnetic radiation. Objects on Earth and in space also emit other types of EM radiation that cannot be seen by the human eye, such as radio waves.
The study of celestial phenomena at radio wavelengths, radio astronomy came into being after the accidental discovery of cosmic radiation by radio engineer Karl Jansky in 1933. Honor Harger
USA.NM.VeryLargeArray

By user:Hajor [own work], from Wikimedia Commons
In 1959 the University recognized our work by appointing me to a new Chair of Radio Astronomy. Martin Ryle
For the greater part of us, the possibility of space science is something we specifically interface with "stargazing", telescopes and seeing superb shows in the sky. Furthermore, no doubt, that is the energizing zone of space science that records for its enormous fame. So to the uninitiated, "radio space science" appears to be bizarre. There are two explanations behind that. To start with is that people are much more visual than sound arranged. Furthermore, the second is that radio cosmology doesn't generally include "tuning in" to the universe but to the degree that researchers who utilize this complex type of "stargazing" don't depend on the visual investigation to direct their work.

Fornax A is a galaxy with a very active black hole in its core that is spraying radio waves out into enormous jets. Here, the white glow in the center is the visible galaxy NGC 1316 that you can see through the constellation of Fornax. Notice the wee spiral galaxy above it? These two galaxies are merging, and as gas and dust are stripped out of the small galaxy and poured into the center of NGC 1316, the black hole nestled there spins it up. How do we know this? The huge radio lobes to either side of this merger are the telltale signs that a black hole is being fed more than it can handle. These are the billowing ends of powerful jets shooting out spun-up, escaped material far into space.

In radio waves (blue), the Whirlpool Galaxy is a lot larger than it appears to optical telescopes (white).
To acknowledge what is extremely energizing about radio space science, first, we need to move how we see cosmology. That is on the grounds that to proficient space experts, contemplating the universe is more about frequencies than it is about visual documentation of marvel. This takes us back to Material science 101.
Light, clearly, is the physical marvel that enables our capacity to utilize our visual affirmation framework, e.g. our eyes to value something, for this situation the stars. So when we gaze toward the sky, we can see the light emanating from a star or reflect from a planet or moon. Much of the time, in the event that we see a distant star, we are really observing it hundreds or thousands of years back in light of the fact that that is to what extent it takes for that light to cross the universe and be noticeable in our sky. That by itself is a beautiful personality blowing thought.
The Essential material science of how radio discharge functions.
Standard in the discovery of radio signs from space is the Hydrogen iota.
Hydrogen_emission1
Radio emanation. Picture: SKA Association
The hydrogen particle contains a proton and an electron. While not entirely little circles, both the electron and proton do have a property known as 'turn'. The twists of the two particles can be adjusted or against adjusted. On the off chance that twists of the electron and proton in a hydrogen iota are adjusted, the particle has somewhat more vitality than if the twists are hostile to adjusted.
A hydrogen iota can make a change from the adjusted state to the counter adjusted state. In doing as such, it emanates radio vitality at a wavelength of 21 cm or a recurrence of 1420 MHz.
Then again, all together for the particle to make the progress from against adjusted to adjusted, the iota must be presented to 21 cm wavelength radiation, from which it can assimilate radio vitality.
This 21cm line as it is known in radio space science is a key to radio stargazing and mapping it will be critical to the task of the SKA
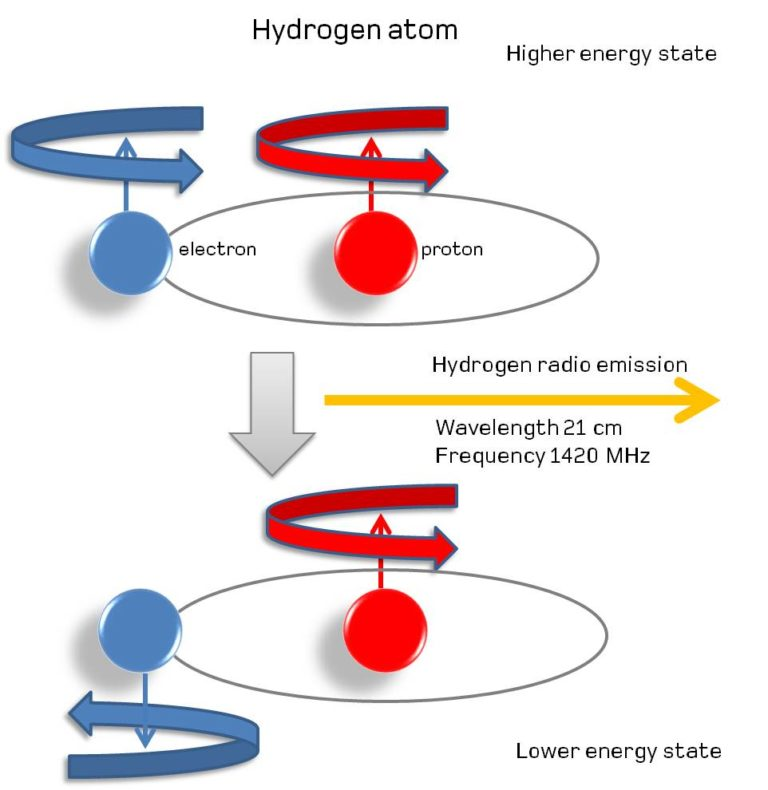
Radio emission. Image: SKA Organisation
Presently light itself is an entirely weird substance. However, to our space science researchers, light is simply one more vitality that exists in a specific recurrence. Presently, we tend to consider frequencies when we discuss sound waves. In logical terms light, vitality and sound are only a couple of types of a similar thing, frequencies of vitality that are copying from a source.
Presently we get to why radio space science is so vital. The scope of recurrence that light possesses in the huge range of frequencies is extremely entirely little. To put that all the more obtusely, we can just "see" a small piece of the universe that is quite. Presently when you turn upward in the night sky and it is so overpowering, when you then that we are seeing only a small measure of what is really going ahead up there, once more, our psyches can get pretty overpowered.
Computer science is no more about computers than astronomy is about telescopes. Edsger Dijkstra

By olafpictures, from Wikimedia Common
Detecting the invisible sky
Radio signals pass straight through the clouds and can be detected by these large antenna/dishes or receptors as the radio telescopes are known. The radio frequency range covers a vast swathe of the electromagnetic spectrum between around 30 MHz and 40 GHz, which is equivalent to, wavelengths from 10 m down to 7 mm. The SKA will observe at a frequency range from 50 MHz to 20 GHz which is equivalent to wavelengths of 4 m to 3 cm
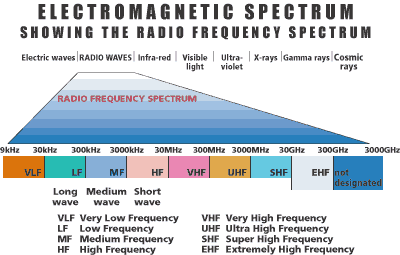
The Radio Spectrum – Image credit: CEPL
The history of astronomy is a history of receding horizons. Edwin Powell Hubble
Radio space science utilizes complex sensor hardware to think about The greater part of the frequencies of vitality coming to us from the universe. In that way, these researchers can "see" everything that is going ahead out there thus get an exact thought of how the stars look, act now and will carry on later on.
For a few of us who have caught wind of radio stargazing, we consider it regarding "tuning in" for indications of life in the universe. Also, truly, SETI, or "the Look for Additional Earthly Knowledge" is a piece of radio space science, but a minor part. Be that as it may, of substantially more noteworthy significance is the manner by which radio cosmology has enabled genuine space experts (that is the individuals who get paid to do it) to contemplate stars numerous light years away, to examine dark openings which we would never observe with our telescopes and to assemble research and information about the entire of the universe that generally would be difficult to know and get it.
Radio astronomy reflects our fascination with how audio can be used to understand information or ideas. Just as scientists visualize data through charts and pictures, we can use 'data sonification' to translate radio signals into a sound that help us better understand some of our most enigmatic planetary systems. Honor Harger
Karl Jansky: Father of Radio Astronomy

source
But when researchers at Bell Labs discovered that static tends to come from particular places in the sky, the whole field of radio astronomy opened up. Murray Gell-Mann
This is vital work that is always continuous in the realm of cosmology. It merits staying aware of and adapting more about as we have scarcely touched the most superficial layer in our short dialogue today. However, seeing how critical radio space science is will just develop and make more important your affection and handle of this enormous field of information known as stargazing.
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guideline here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on the proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here
Reference