
Image credit: Kaboompics/CC0 pixabay
What is NIHL?
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL ) is hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound . People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of
frequencies , impaired cognitive perception of sound including sensitivity to sound or
ringing in the ears. (Source) NIHL can also be caused by extremely loud bursts of sound, such as gunshots, explosions or sudden loud music which can rupture the eardrum or damage the bones in the middle ear.
In this case we shall be considering NIHL as a result of misuse of earphones. Simply putting, its a gradual loss of you hearing ability due to damage caused by loud sound.
Mechanism
Anatomy of the Human ear
Image credit: Chittka L, Brockmann/CC BY 2.5 ,wikicommons
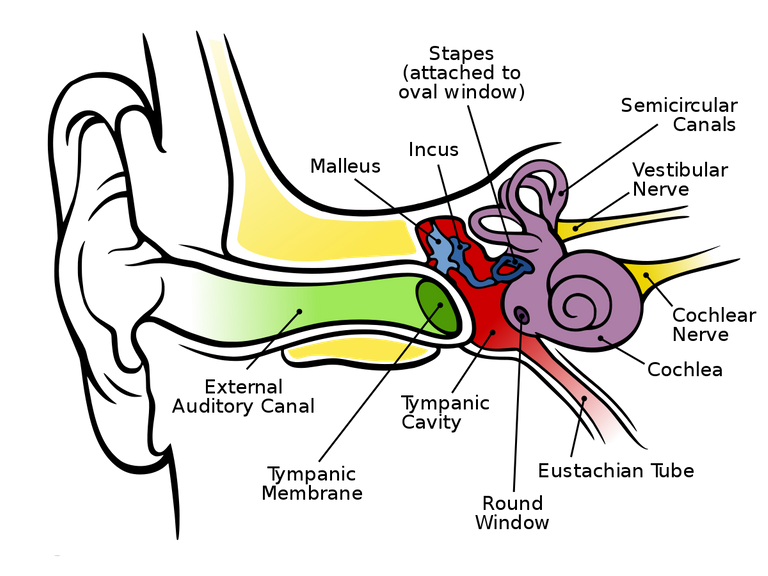
NIHL occurs when excess sound is transmitted into and through the auditory system. An acoustic signal from a sound source (the earphone in our case) enters into the external auditory canal (ear canal), and is funneled through to the tympanic membrane (eardrum), causing vibration. The vibration of the tympanic membrane drives the middle ear ossicles, the malleus, incus, and stapes into motion. The middle ear ossicles transfer mechanical energy to the cochlea by way of the stapes footplate hammering against the oval window of the cochlea. This hammering causes the fluid within the cochlea (perilymph and endolymph) to be displaced. Displacement of the fluid causes movement of the hair cells (sensory cells in the cochlea) and an electrical signal to be sent from the auditory nerve to the central auditory system within the brain. This is where sound is perceived. Different groups of hair cells are responsive to different frequencies. Hair cells at or near the base of the cochlea are most sensitive to higher frequency sounds while those at the apex are most sensitive to lower frequency sounds.source There are two known biological mechanisms of NIHL from excessive sound intensity:
- Damage to the hair cells and
- Damage to the myelination or synaptic regions of auditory nerves.
These might be discussed in another article.
Common signs
- Buzzing, ringing or roaring in your ears after hearing loud noise
- Hearing distorted or muffled sounds
It would be good to know that NIHL from using earphones might take a while to notice because it happens gradually. This makes it a huge problem because people might not know they have the problem until it's too late. Signs would begin to manifest when it has already become serious.
Difference between headphones earphones, canal phones
It is important to know the difference between these devices so as not to misuse any. People often tend to use these terms interchangeably. All these audio components have important differences and a substantial knowledge of these differences may help prevent NIHL.
What are headphones?
Image credit:Florian Fuchs/CC-BY-SA 3.0:wikicommons
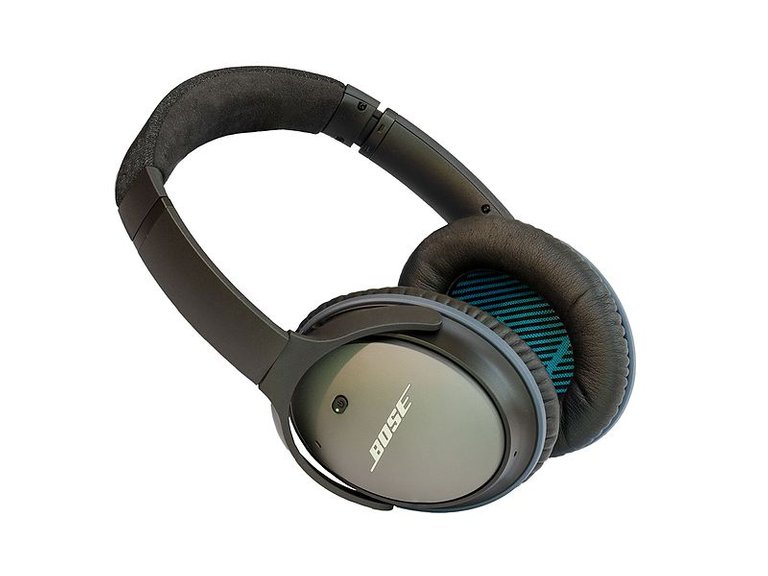

The word has been used to describe devices worn over, or in the ears. It is also used to describe a pair of small speakers joined by a band placed over the head. The types commonly used are the circumaural and Supra aural It is shaped to help block out external noise while listening to music. It's always a great choice for music producers and radio personnel.
What are earphones?
Image credit:Liam Dunn/ CC BY 2.0
wikicommons
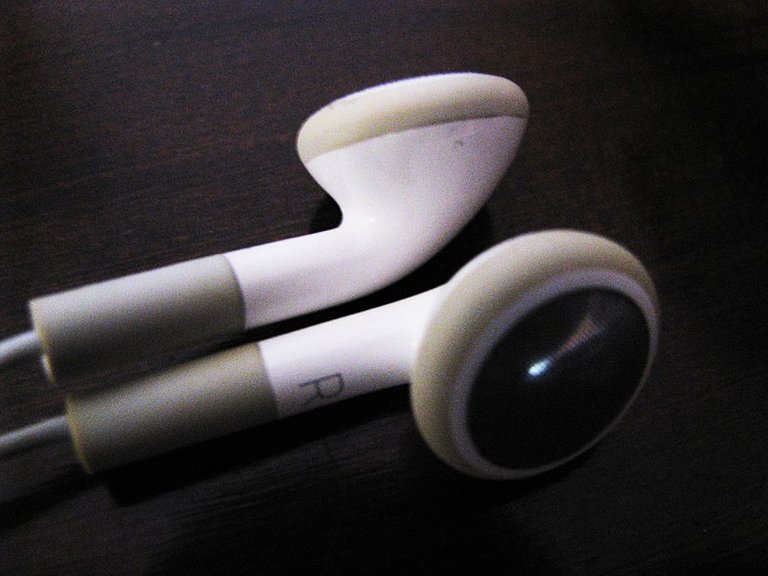

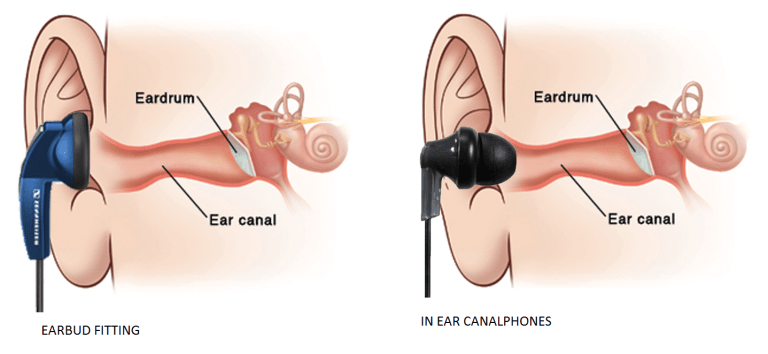
Earphones(sometimes called 'earbuds'), are very small headphones that are fitted directly in the outer ear, facing but not inserted in the ear canal.
They are held in place by your concha ridge at the centre of your outer ear. They are often shaped in a one-size-fits-all, making it uncomfortable for some to wear.
Most Earphones(Earbuds) make room for ambient noise enabling the wearer to hear what is going on around him or her.
What are Canal phones/in-ear headphones/IEMs(internal earphone monitor)
Image credit:user:Julo • CC-BY-SA-3.0
wikicommons
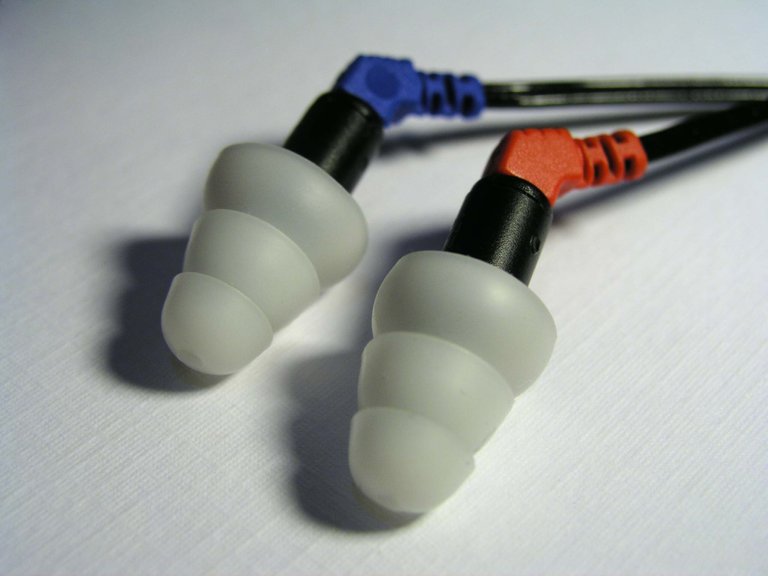

As the name implies, canal phones fit snuggly inside your ear canal. Most of them use comfortable rubber tips for superior isolation from ambient noise. They were originally developed for use in stage monitoring for live performers.

Image credit:DianaKat/CC BY-SA 3.0 wikicommons
Generic or custom fitting ear canal plugs are made from elastomer, silicone rubber or foam. Custom molded plugs are created by using castings of the ear canal to provide added comfort and noise isolation.
MX 365 and Panasonic RPHJE120K
Image credit:wearableinear.com
Looking at ambient noise reduction

Image credit:Lukas Hartmann/CC0,pexels
If your like me , you might hate external sound creeping into your ears while you listening to music. As I might have mentioned before this might lead to increasing the volume to cover the ambient sound. Unwanted sound from the environment can be safely reduced in two ways which are by excluding sound from the ear by passive noise isolation, or, by active noise cancellation.
Passive noise isolation is basically using the body of the earphone itself to block out sound. This is achieved with the earppho pine either over or in the ear, as a passive earplug that simply blocks out sound. The headphone types that provide most attenuation are in-ear canal headphones and closed-back headphones, both circumaural and supra aural. Open-back and earbud headphones provide some passive noise isolation, but much less than the others. Typical closed-back headphones block 8 to 12 dB, and in-ears anywhere from 10 to 15 dB. . Certain headphones claim to reduce ambient noise by around 25 dB. Some of such models have been specifically designed for drummers to facilitate the drummer monitoring the recorded sound while reducing sound directly from the drums as much as possible.
Active noise-cancelling headphones use a microphone, amplifier, and speaker to pick up, amplify, and play ambient noise in phase-reversed form; this to some extent cancels out unwanted noise from the environment without affecting the desired sound source, which is not picked up and reversed by the microphone. The downside to me though is that they require a power source, usually a battery, to drive their circuitry. Active noise cancelling headphones can attenuate ambient noise by 20 dB or more, but the active circuitry is mainly effective on constant sounds and at lower frequencies, rather than sharp sounds and voices. Some noise cancelling headphones are designed mainly to reduce low-frequency engine and travel noise in aircraft, trains, and automobiles, and are less effective in environments with other types of noise.
What would be the right choice of head phone?
The answer would be whichever ones help you resist the temptation to turn the music up. Noise cancelling headphones which do the best work at this, help to block other noise, that way you do not have to strain to hear the sound coming from the speakers when you are in a noisy place.
To preserve your hearing, doctors recommend headphones, which sit on your head like earmuffs, rather than earbuds, which fit inside your ear. The main reason is earbuds naturally add about 9 dB of volume because they are closer to the ear canal.
Factors of importance As regarding earphone usage
Volume
Chainsaws and motorcycle engines create about 100 db of sound. Exposing yourself to that can begin to damage you're hearing after less than half an hour of exposure. It might interest you to know that an mp3 player at 70% of its top volume is about 85 db. Crank up the volume a bit more and you get really close to having a chainsaw or a motorcycle right in your ears.
The table contains some loudness/time facts to consider (the unit of measurement is decibel):
| 95 | Damage will occur after four hours of exposure per day. |
| 100 | Damage will occur after two hours of exposure per day |
| 105 | Damage will occur after one hour of exposure per day. |
| 110 | Damage will occur after 30 minutes of exposure per day. |
| 115 | Damage will occur after 15 minutes of exposure per day. |
| 120 | Damage occurs almost immediately. |
Most portable stereo music systems produce sound in the range of 95-108 dB at level four and in excess of 115 dB at level eight.
For comparison, a soft whisper is usually measured at 30dB; busy traffic at 75dB; a subway train at 90dB; a gunshot blast at 100 dB, a jet plane at 140 dB; and a rocket launching pad at 180 dB. Sounds above 140 dB usually cause pain.
Audiologists recommend that sound should not go above 55 to 65 dB to protect your hearing. This happens to be the volume of a standard conversation. How to easily achieve this is while using earphones, ensure that the person around cannot hear the sound from your earphone. If they do, that means its loud enough to cause permanent hearing loss.
Duration
The duration of time exposed to loud sounds is equally important as the volume. Natalie Johnson, Aud an audiologist with University of Utah healthcare says " very loud sounds such as gunshot, can damage hearing instantaneously. But listening to your ipod at moderately loud levels for a long time can do just as much damage". Watching the duration is equally as important as watching the volume coming out from the earphones. Why this is a factor is because unlike some other parts of our body, the ear never stops hearing. So long as there is something to hear or not the ear is open and willing to work the overtime. Johnson says "you have to think of your total daily 'noise' intake and try to give your ears a break.
In Conclusion
For headphone usage Doctors have recommended the 60/60 rule
- Limit the amount of time you spend with earphones to 60 minutes
- Listen to music, video games or movies at no more than 60% of the maximum volume
NIHL is a danger to many and because it might not hit the individual immediately, it might be overlooked all together. Earphones are a very helpful invention for music and sound enthusiasts. But we need to be careful of how we use them to avoid being victims of NIHL.
REFERENCES
Earbuds vs headphones, medicaldaily
Earphones,earbuds,canalphones, audiolinks
Congratulations @abeludotu! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard!
Participate in the SteemitBoard World Cup Contest!
Collect World Cup badges and win free SBD
Support the Gold Sponsors of the contest: @good-karma and @lukestokes
Congratulations @abeludotu! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @abeludotu! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!