In our everyday life, we interact with different forms of matter that we have we've defined 'as any substance that has weight or mass and occupies space by means of its volume'. Everything we can see and interact with on a daily basis is made up of atoms, which themselves are composed of engaging subatomic particles. Hence, matter is everything you see and interact with daily.
Now, there is another form of matter that we can’t interact with, even scientists are having a hard time understanding it’s intricacies. And this is the Dark side of the universe
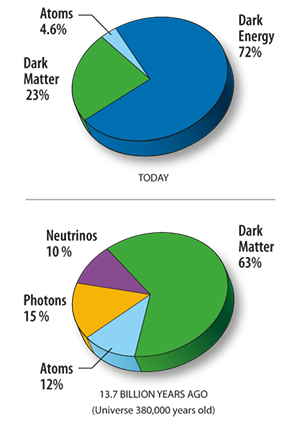
Everything imaginable around us, your phone, the planets, trees, the bus etc, only account for less than 5% of the known universe, about 23% is dark matter, the outstanding 72% is dark energy. Dark energy and dark matter, (which are both invisible to the human eye) both accounts for the 95% mass of the universe that scientists, till today, have not been able to observe.
source: Wikimedia Commons
An estimated energy division in the universe into dark energy, dark matter
Places with a high concentration of dark matter, have the ability to bend light passing nearby, which indicates that there’s something present that interacts with gravity
We will be discussing the Dark side of the universe, which consists of both Dark matter and Dark energy. In this post, we will explore the world of Dark matter, and in the subsequent post, we will talk about dark energy.

What is Dark Matter?
After the Big Bang that occurred 150 million years, the universe was void and without form, no planets or stars - there was nothing. With the passage of time, stars started to form, together they started forming galaxies. The cluster of these galaxies consists of material, which was a collection of matter smashed together, and the planets in our universe started forming around the sun.

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Strong gravitational lensing as observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in Abell 1689
Gravity was the glue that held the galaxies, solar system and the clusters of galaxies altogether. In the case of some the clusters, the vacuum between galaxies is filled with intensely hot gases, which can’t be seen with the use of the visible light telescope. These gases can only be seen with the use of gamma and x-rays, and upon measurement to ascertain their quantity between galaxies clusters. A discovery was made which proves the existence of materials that are 5 times more in the cluster than what can be normally detected.
The invisible material in space that can’t be detected is what is known as “Dark Matter”
Much is known of what dark matter isn’t that what it actually is, scientists have been able to peg that an estimate of 27% of the entire universe is made of dark matter. In 1930, Fritz Zwicky, a Swiss astronomer was the first person to use the term “Dark Matter”; he studied how fast this galaxy cluster revolves.

What Dark Matter “Probably” is
Dark Matter could possibly be brown dwarfs, stars that failed to ignite due to the lack of mass required to start burning.
Dark matter may also be white dwarfs, the remains of cores that belonged to dead stars of small to medium size
They also can be black holes, neutron stars which are also the remains of large stars after they explode
A major number of scientists believe dark matter is made up a matter that is non-baryonic. The major candidate which is WIMPS have more mass than protons (ten-to-a-hundred times more) but they are difficult to detect due to their frail interactions with regular matter.
- Other candidates include; Neutralinos, Sterile neutrinos, and scientists have a significant amount of evidence that none of them is made up of dark matter
These suggestions, however, come with some challenges, scientists and astronomers have provided strong evidence that there aren’t enough white dwarfs or brown dwarfs to account for all the universe’s dark matter. Also, neutrons, black holes and stars are all too rare.
Dark matter is most likely made up of materials we are not too familiar with, they could be a lot different than we thought they are. And we may be using wrong theories to observe its particles, probably new theorise will need to be enacted in order to better understand dark matter and what they represent.
As mentioned earlier, scientists are certain of what dark matter isn’t, rather than what they actually are. There are some of the things that dark matter is “not”
- Dark matter is not clouds of ordinary matter that lack stars because they would discharge particles we could be easily observe They are not antimatter, this is because antimatter creates distinct gamma rays when they react with normal matter
Dark matter does not consist of black holes, which are dense objects that aggressively affect their immediate environment

Where are we with Dark Matter?
Due to scientists inability to directly see and observe dark matter, they are exploring other means of carrying out an adequate investigation. The indirect way of studying something seems viable, this can be achieved by looking at a shadow, and making an informed guess about the object that casts the shadow. Applying this scenario to investigating dark matter, scientists by the use of gravitational lensing, are indirectly studying dark matter.
.jpg)
Dark matter map by Kilo-Degree Survey Collaboration/H. Hildebrandt & B. Giblin/ESO with creative commons Attribution 4.0 International licenseDark matter map for a patch of sky based on gravitational lensing analysis.
Light passing across a gravitational lens is alike to light passing through an optical lens, the light gets bent. When light rays from faraway stars progress through a cluster or a galaxy, the gravity of the available matter in the cluster or galaxy forces the light to bend. This results in making the source of the light seem it's coming from somewhere else, rather than the actual source. The degree of bending enables scientists to understand the dark matter present. NASA scientists utilize the Hubble Space Telescope to detect gravitational lensing.
In addition, NASA scientist believes they have devised a direct means of observing dark matter with the use of Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope. This device looks at gamma rays, which are the highest energy form of light. In the event of a collision between two dark matter particles, there is a possibility of the release of a gamma ray. The Telescope theoretically could observe such collisions, which will appear in the form of a burst of gamma rays.
Dark matter is still one of the mysteries of science.

REFERENCES
SPACE | Dark Matter and Dark Energy Explained
NASA | Dark Energy, Dark Matter
YouTube | What is Dark Matter and Dark Energy?


I guess explaining dark matter is something what we couldn't reach yet..!
I agree with this analogy more..!
Btw, good informative article..!
Best regards..!🙌
Many thanks for gracing my post with your presence...Really appreciate the amazing feedback!
Thanks for sharing this scientific knowledge with us but i would to adk a question about this dark matter.
What really bought about this dsrk matter, i mean how is it form