Carbohydrates have been known to be of great importance to human, chiefly in form of energy.
We can find carbohydrates in food like rice, spaghetti, macaroni, yam, garri, wheat and so on.
Carbohydrates are food substances which when broken down releases energy inform of ATP(Adenosine triphosphate), water and carbon dioxide as a by product.
Well, in chemistry of Carbohydrates we don't define it that way. We define Carbohydrates as a polyhydroxyl of Ketone and Aldehyde (Hydrocarbon compounds) that can dissolve on hydrolysis.
Carbohydrates can be classified into two classifications;
Based on the number of Carbons
Based on the Functional Group
Based on number of Carbons
Monosaccharide - Carbohydrates made up of sugar molecule.
Diasaccharide. - Carbohydrates made up of two monosaccharide.
Oligosaccharide - Carbohydrates made up of 3-10 monosaccharide.
Polysaccharide - Carbohydrates made up of more than 10 sugar molecules.
Based on Functional Group
We have two types of carbohydrates based on the functional group which are;
Aldose Sugars - Sugars which have the -CHO carbonyl group.
Ketose Sugars - Sugars which have the -CO carbonyl group.
Today I would be talking about the Monosaccharide before I move to the others.
Monosaccharide
These are carbohydrates which are made up of one single molecule of sugar. They can be classified based on two properties which are ;
Based on functional/carbonyl group
Based on number of carbon atoms
Based on functional/carbonyl group
Monosaccharides are classified based on the carbonyl group in their structural or molecular formula. Remember I mentioned carbohydrates are polyhydroxyl of Aldehyde and Ketones, so Monosaccharides are now classified based on the carbonyl group they posses;
Aldose - Monosaccharides that have the aldehyde carbonyl compound present in their structure or molecular formula.
Ketoses - Monosaccharides that have the ketone carbonyl compound present in their structure or molecular formula.
Based on number of carbon atoms
Monosaccharides can also be classified based on the number of carbon atom molecules present.
Though, based on number of carbon atoms juxtaposes with the based on functional group classification.
| Number of carbon | Aldose | Ketose |
|---|---|---|
| Three /Triose | Glyceraldhyde | Dihydroxyl acetone |
| Four /Tetrose | Erthylose | Erythrulose |
| Five/Pentose | Ribose, Xylose, Albinose | Ribulose |
| Six/Hexose | Glucose | Fructose |
| Seven/Heptose | - | Sedoheptulose |
Properties of Monosaccharides
Three properties which are mostly seen together in Monosaccharides are ;
Mutarotation
Reducing Property
Osazone Formation
Reactions of Carbohydrates
Enediol Formation
Carbohydrates containing a free sugar group will tautomerise to form enediols when two hydroxyl is attached to double blinded carbon atom.
In mild alkaline condition glucose can be converted onto fructose and mannose sugar. Interconversion of sugars through enediol form is termed Lobry de Bruyn-Van Ekestein Transformation.
Benedict's Reaction
It is a reaction which is used to detect the presence of glucose in urine. A standard lab test usually used to diagnose diabetes mellitus. A reducing sugar test
Any sugar which has a free aldehyde/ketone group is a reducing sugar.
Osazone Formation
All reducing sugar would form osazone when reacted in excess phenlyhydrazine and kept at constant boiling temperature.
Osazones are insoluble in nature
Oxidation of Sugar
The aldehyde group of sugar is oxidised to form aldonic acid. Example Glucose forms Gluconic acid and Mannose forms Mannoic Acid.
Though when the aldehyde group of the sugar is protected its not a reducing sugar anymore, therefore the sugar oxidises to form Uronic acid. Example Glucose forms Glucouronic acid.
Under Strong Oxidative conditions(Nitric acid + heat ), the first and last carbon atom are simultaneously oxidized to form dicarboxylic acids known as Saccharic acids.
- Alcohol formation
Sugars can also form alcohols when they are reduced by compounds such as sodium, amalgam and hydrogen, they can reduce sugars.
Aldose sugars would yield their corresponding Alcohol while Ketose sugars would yield double alcohol.
Examples include Glucose yielding Sorbitol, Mannose yielding Mannitol for the Aldose sugars, while for the Ketose sugars Fructose yielding Mannitol and Sorbitol.
Structures of Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide has three structural representation. They are the Open Chain, Emil Fischer Projection, and the Haworth Structure.
Open Chain is a straight chained while Emil Fischer is a closed form of the open chain structure. Both structures are not really recommended by biochemist, they prefer using the Haworth Projection since its the way Monosaccharide looks like in nature.
Haworth Projections are chair-like and look like a ring structure at first look.
BioMedical Importance of Monosaccharide
They provide energy easily without being broken down easily
They are the building blocks of disaccharide and polysaccharides.
Fructose can be found in the sperm cells which provides energy to it during ejaculation.
They can be used as additives in juice and fruit drinks
They are used by athletes to gain instant energy since they are the monomers of carbohydrates.
When reduced to alcohols, they can be used to identify bacterial colonies and reduce intracranial tension by forced diuresis.
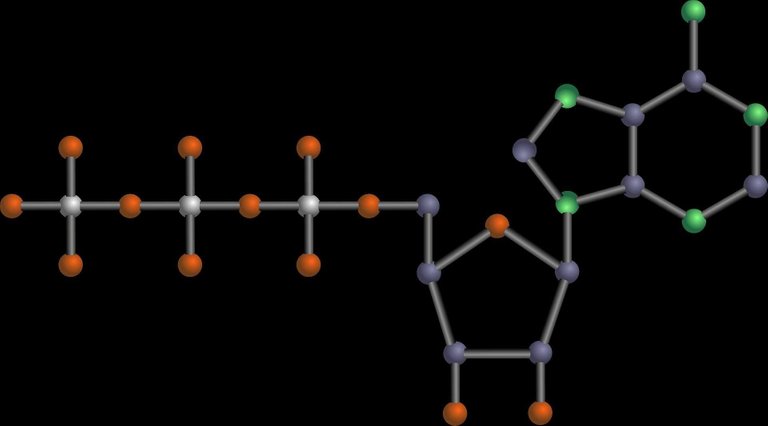
Ribose makes the backbone of RNA and DNA structures (genetics).
Where we can find Monosaccharide
GLUCOSE
glucose can be found in honey
FRUCTOSE
fructose can be found in berry
RIBOSE
Ribose in a RNA molecule



This is well articulated. Carbon is of great importance. One of its constituent is the first line of energy fuel for humans and animals. I learnt a great deal.
Carbohydrate a chief source of energy
This post is educative..carbohydrates form major parts of our dietWelldone @bcrafts
Welldone @bcrafts for analysing carbohydrate and its usefulness also its source