Hello dear steemians, this article is the second part of the series of (All about optics); in which we will learn about everything related to optics.
In the previous article All about optics [Part 1] we have seen that geometrical optics is the study of light as rays, and it is interested in the study of the geometrical properties of light, based on rectilinear propagation, limited speed, reflection and refraction of light.
Based on this definition we can determine the importance of geometrical optics in our daily lives and in the development of visual technologies. this science allows us to understand many phenomena, including reflection of images and light in mirrors and changes of dimensions of vision using lenses, understand light guiding aspects such as fiber optics, understand how optical instruments work (microscope, camera, tv, magnifying glass, telescope, jmelles ..... ect, geometric optics also allowed us to understand human vision and to correct its flaws.
Pixabay

Definition of the light:
Pixabay
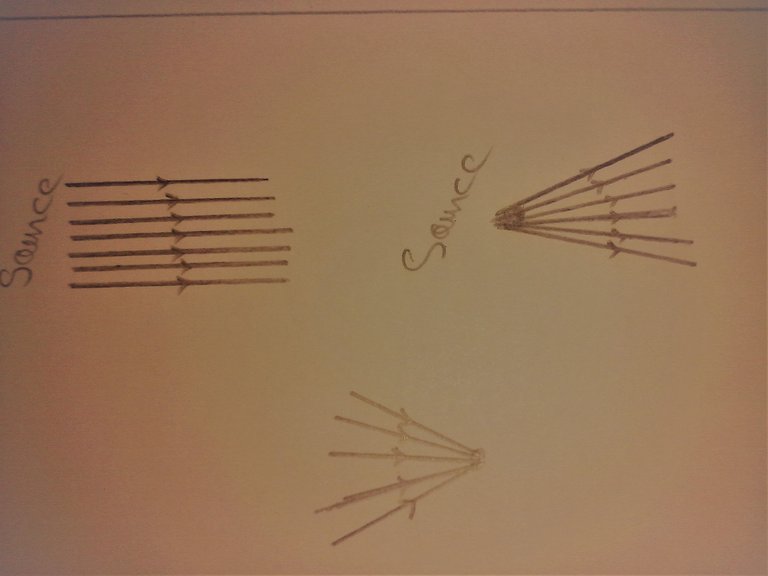
from a point of view of geometrical optics, a beam of light is a set of infinitely fine sub-beams, called 'light rays'; and these rays propagate in straight lines in a homogeneous and transparent medium or in a vacuum.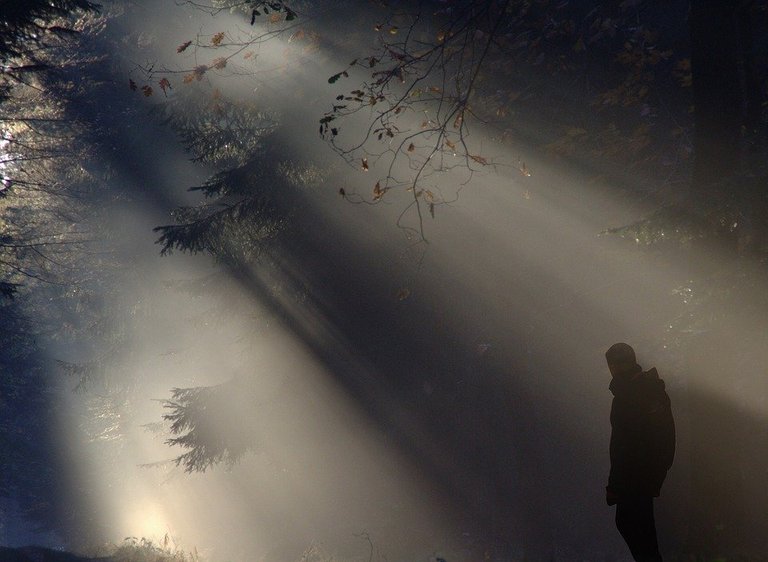
- light can't be seen:
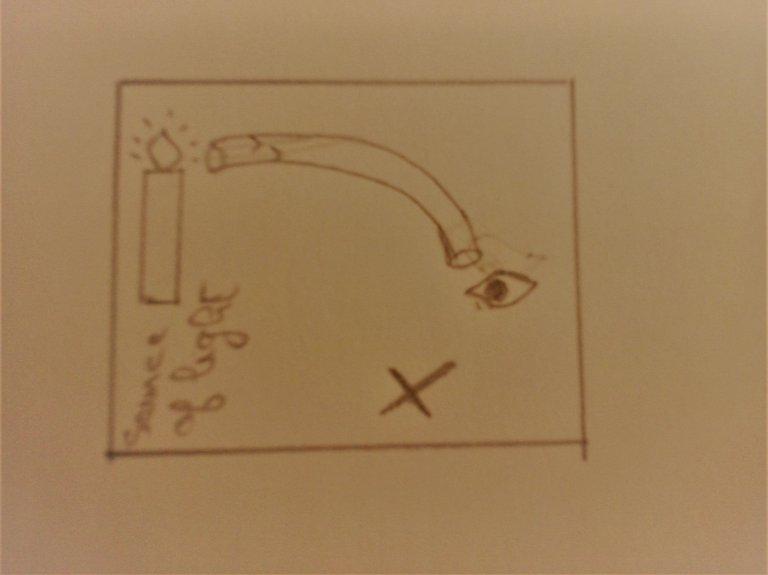
- light can be seen:
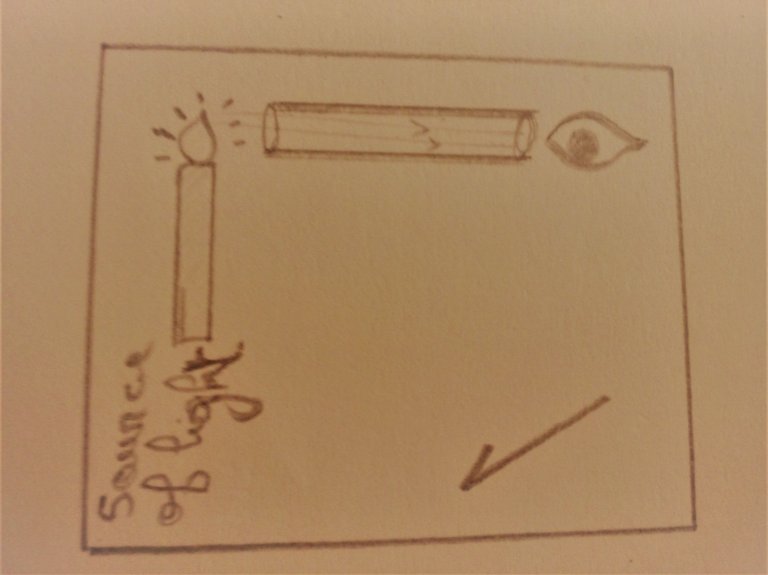
The speed of light:
When we hear the term (speed) it is obvious to think of the law of speed which equals distance divided by time, but it is not so simple when it comes to light because it is very fast, the speed of the light is 299 792 458 m / s, and this speed is fixed in the vacuum and never changes, and there is nothing that can move faster than this speed in the vacuum.
in other transparent media, the speed of light can be measured using the refractive index, where each medium has its own index n:
Vacuum: n= 1.
The air: n= 1,003.
Water: n= 1,33.
Alcohol: n= 1,36.
Glass: n= 1,52.
- 17 m/s is the lowest speed observed for light
Light source:
a light source is an object that emits light, this emission is due to several physical process (acceleration of electric charges, atomic transition .... ect).
- Types of light sources:
The light sources are divided into two parts, the primary light sources, which produce their own light, and the secondary sources (scattering objects) that reflect the light rays that they draw from other objects:
- Primary light sources:
a) Natural sources:
Nature provides large amounts of light, where the sun is the main source of light on earth (by thermonuclear fusion), as the star closest to the earth, all living organisms and others rely on energy luminous derivative of the sun. And other stars shining in the sky at night, where they are luminous balls that emit heat and light.
Pixabay
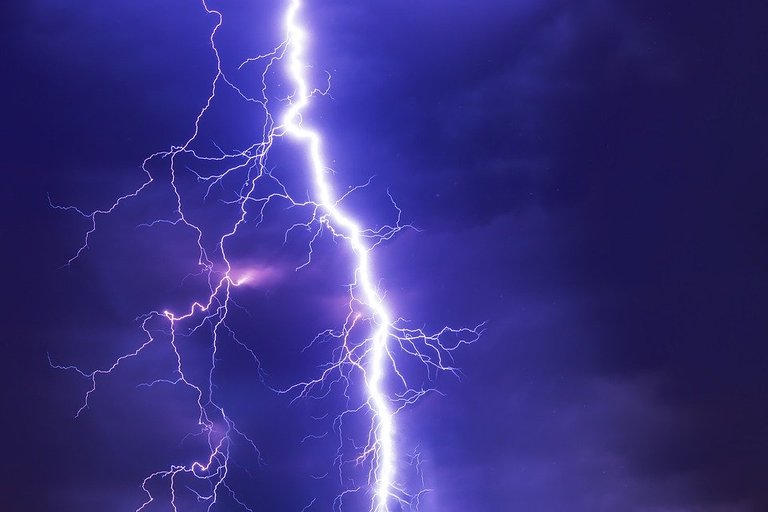
Lightning is also a natural source, because the collision of two clouds together (one carrying a negative charge and the other a positive charge) suddenly causes the appearance of light, and because the light is faster than the sound we see the light and then we hear the thunder.
Pixabay

b) Artificial sources:
they are the sources of light created by the human, which are numerous and constantly developed, we mention some of them:
Pixabay
bulbs (by electric heating), candles, spectral lamps (sodium or mercury vapor lamps), semiconductor sources (light-emitting diodes (LED or LED)), lasers ..... ect

- Secondary sources:
they are objects that draw their light from others, and are also divided into two parts:
a) Natural:
like the moon, wich is a non-luminous object in itself, where it draws its light by inverting the rays of the sun towards the earth.
Pixabay
b) Artificial:
they are objects made by humans, which absorb and reflect the light rays, where these objects are seen when the irradiated radiation on its side reaches the eye, example: mirror, book, wall ..... ect.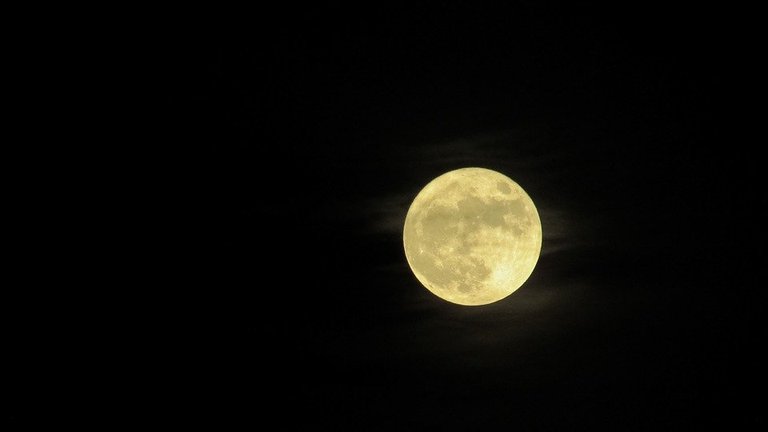
Angular size (apparent diameter):
When we see things, the eye does not see the objects in their real dimensions, they see them in the prespective, and the dimensions vary because of the changing angles of view that the eye sees through them.
The angle of view is the angle between the radius from the highest point of the object, and the radius from the lowest point of the object.
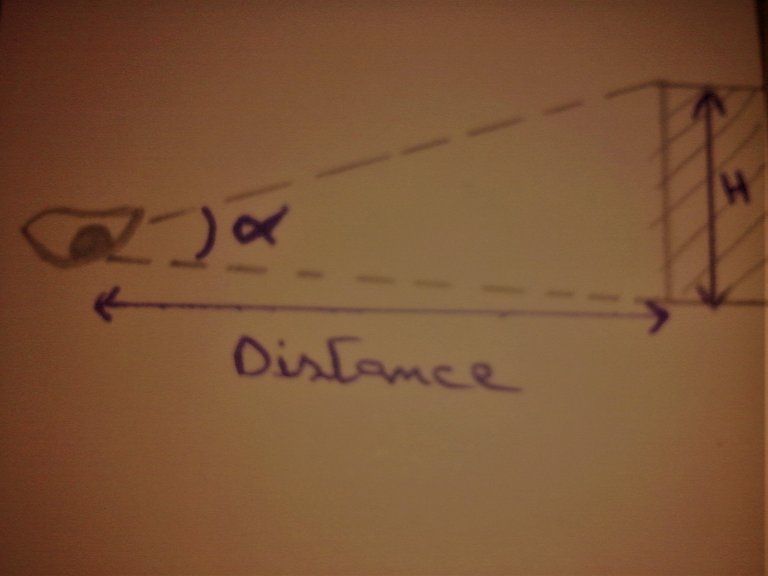
- How to measure the angle of view?
Using thales theory, we can calculate the dimensions of an object and its position, or calculate the angle of view:
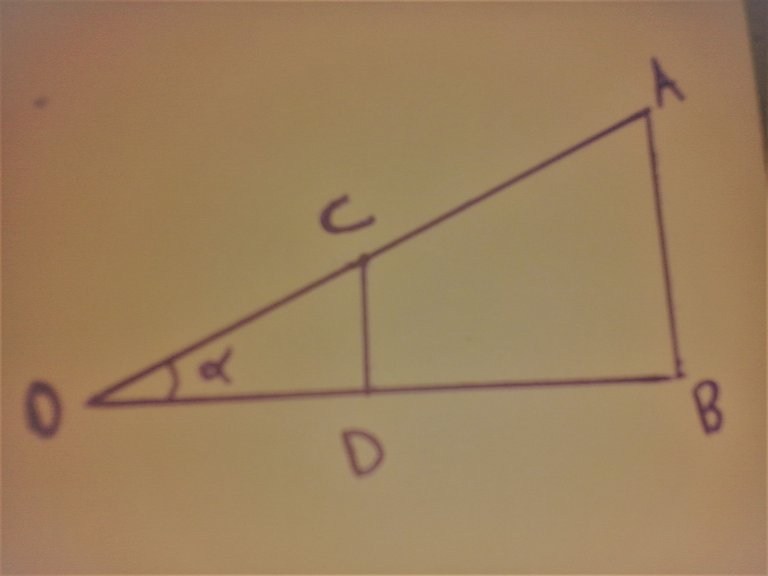
We have two triangles, OCD and OBA:
(OC / OA) = (OD / OB) = (CD / AB)
therefore: Tan (alpha) = AB / OB
180°=3,14rad
then if AB in this example is a height of an object, we can calculate this height:
AB = (OB.CD) / OD
Example:
we want to calculate the angle of view of a person for a building:
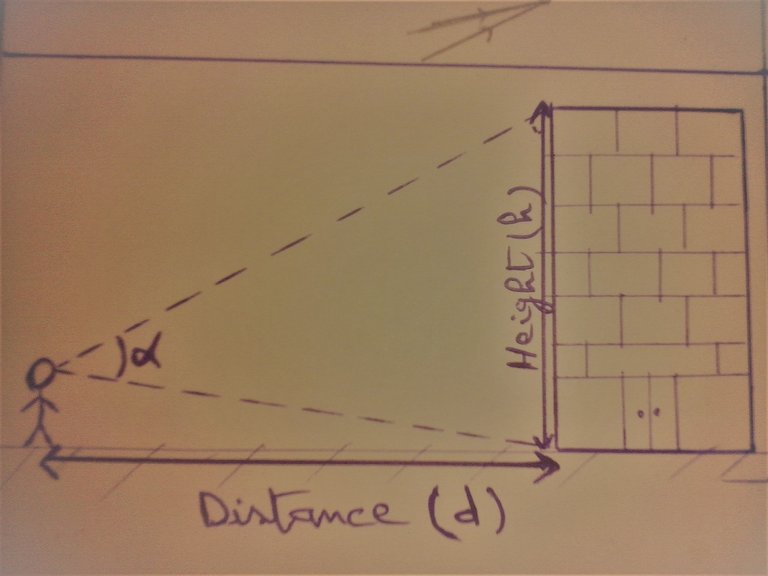
height of the building: h = 60m
distance between the observer and the building: d = 4500m
Alpha = h / d = 60/4500 = 0.0133 rad
Light sensor:
light has a great importance in physics, and for things to be seen it is necessary for an organ to detect this light, like the eye; with technology there are also many other light sensors:
Optical Sensors:
It is a kind of digital sensors, where optical sensors use light to sense objects. These sensors work almost the same way, Where there is a light source (transmitter) and a detector (receiver) to sense the presence or absence of light. This technology is used in smart homes, where it controls the house light and automatically opens the curtains with the sunrise.
Reflective Sensors:
It is one of the common types of optical sensors of reflective type. Where the sensor sends the light to the product and then the reflected light returns from the product.
These sensors have less sensitivity than other optical types because they rely on reflected light from the product.
Laser Sensors:
Laser sensors are used to obtain high accuracy in the scan.
Specific color sensor:
This type of sensor can distinguish between colors, especially between color spectra.
still existe many other sensors, like: Sensor type Rebound, Fiber-optic sensors, Intra-ray sensors......ect
The Darkroom, the first camera!
One day Aristotle was in a room where there was a shadow, and saw a picture of the solar eclipse upside down on the wall caused by a light beam passing from the narrow aperture of the door, from here began the idea of the dark room, which knew great developments by other scientists after Aristotle, where all these developments led to the invention of the camera.
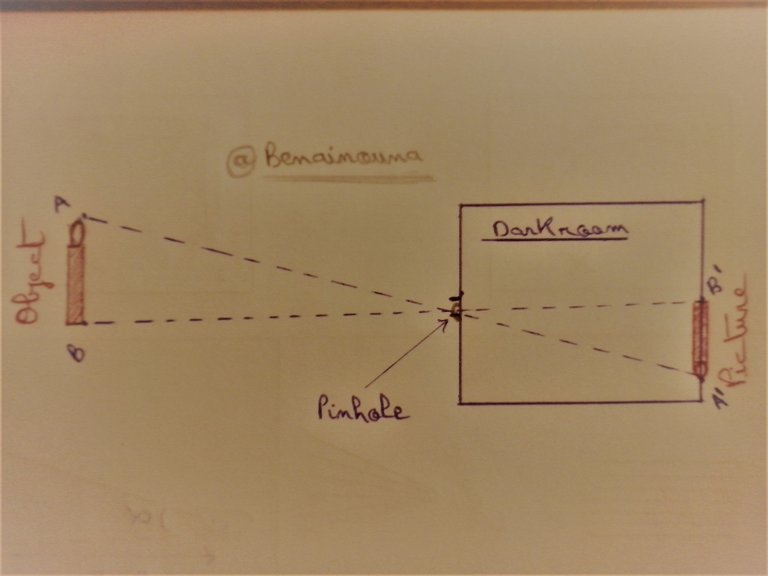
In the dark room we note the following:
- ُThe picture of the object in each case is inverted.
- The picture is clear whenever the diameter of the pinhole is small.
- The picture grows as we close the object from the dark room.
- For a more clear image we add a rounded lens
...............................................................TO BE CONTINUED
References list:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Optique géométrique, richard taillet
Physique generale, Nour eddine hakiki
الغرفة المظلمة
Dear steemians:
- thank you for reading.
- If you like this post upvote and follow To be informed of upcoming posts.
- If there is any comment, criticism or additional information, please write it down.
@Benainouna
Interesting posts. Keep up the good work!
thank you :)
thank you freind
you welcom, thank you for the support :)
This post has received a 1.73 % upvote from @speedvoter thanks to: @benainouna.
This post has received a 1.60 % upvote from @booster thanks to: @benainouna.
You got a 3.19% upvote from @upmewhale courtesy of @benainouna!
Earn 100% earning payout by delegating SP to @upmewhale. Visit http://www.upmewhale.com for details!