School exams were approaching here in Olabisi Onabanjo Unversity, Ogun State. Student all over their dorms were reading vigorously; no one had anytime to spare for bullshit. Just then, a day before the exams, some group of guys in my hall decided to play some football. It's been long since they played and what's wrong with relaxing from the all week and all night reading. Unfortunately, within an hour, the game had to stop because one of them while trying to catch a ball landed with his right fore-arm and shouted out of pain, his hand was numb and flaccid. Cutting a long story short, his parent came to take him the next day, he had a fracture in his right forearm and wont be able to participate in the exam starting that same day.
The skeletal system provide the framework for which our posses is built on
What is a Skeleton?
The skeleton is divided into three major, although other forms also exist

Exoskeleton is found majorly among invertebrates animals. These includes insects and crustaceans such as flies, beetles, ants, mosquitoes, crabs, lobsters, shrimps, woodlouse etc. They form the external surface of the body of these animal. Some larger kinds of exoskeleton is seen in snails and tortoise as shells. Exoskeletons are made of chitin and variation in amount of calcium carbonate determines how hard and strong it will be. Exoskeleton is essential for protection, shape, excretion, sensing, support and defense against predators as seen in snails. Exoskeleton also provide attachment for muscles.
Endoskeleton is an internal support system containing mineralized tissues. They are found majorly in vertebrates as bones and cartilages. This skeleton perform various function such as protection of internal delicate tissues and organs, giving shape and rigidity to body, providing attachment for muscles and aiding locomotion.
The other forms of skeleton are found in lower animals and also provide the protection and rigidity to the animal. Some animals however posses more than one form or type of skeleton; example is the tortoise which posses an exoskeleton (in form of its shell) and an endoskeleton (which are its bones).
The Human Skeletal System
Classification of skeletal system
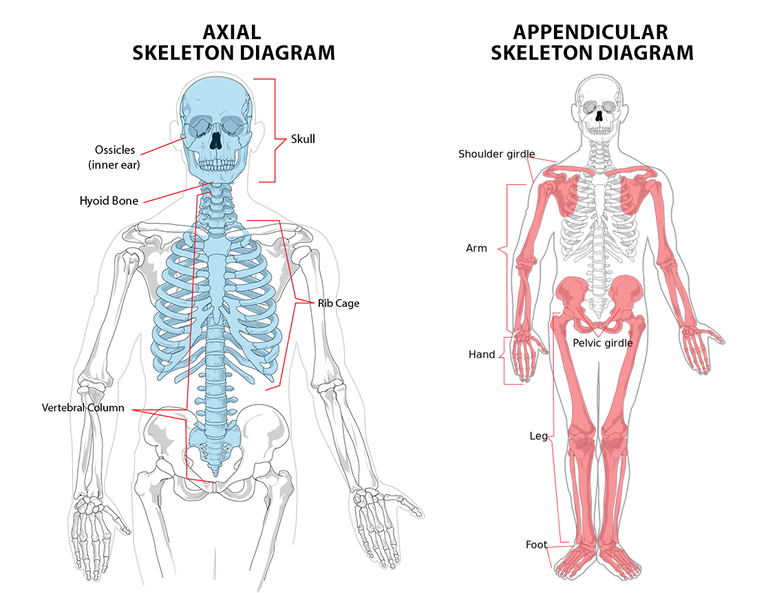
- Axial Skeleton
- Appendicular Skeleton
The axial skeleton is formed by the bones of the head, the neck and the trunk while the appendicular skeleton is formed by bones of the upper and lower limbs. There are about 270 bones in the human body at birth and this number reduces to around 206 at adulthood, this is due to fusion of some bones together. The bones are not just a continuous structure, different bones meet at a point called a joint. The joint is a point of articulation between two or more bones; this enable movements.
The other fundamental organ of the human skeletal system along with the bones are the cartilages. A cartilage is a smooth, resilient, semi-rigid, and avascular connective tissue. They are found serving as padding of long bones at joint, in the ear, nose, bronchial tubes as well as between the bones of our vertebral column. Because of their rrigdity and elasticity, they are often found in structures that need to be kept open or that need minimal movements. The ribs of the body connect anteriorly to the sternum with the aid of coastal cartilages, this is to provide required rigidity and yet allow movement of ribs during breathing. Cartilages do not have blood vessels as well as nerve supply, they simply get their required nutrient by simple diffusion. The cartilages are covered by a thin membrane called the perichondrium with exception of the cartilages padding long bones in joints. The perichondrium functions in repair and growth of the cartilage it covers. At birth, a significant amount of the bones in a baby are actually cartilage, as the child grows up, the cartilage is deposited with calcium which hardens it to become a bone.
The bones in the human body are layered exteriorly by a thin membrane called periosteum. It is similar to the perichondrium of the cartilages. This periosteum is involved in providing nourishment to the external aspect of the bones, laying down more bone which causes elongation and growth and as well provide attachment for the tendons of muscles and ligaments.
Types of bone
Classification of bone based on structure
The spongy bone is less dense compared to the solid strong compact bone
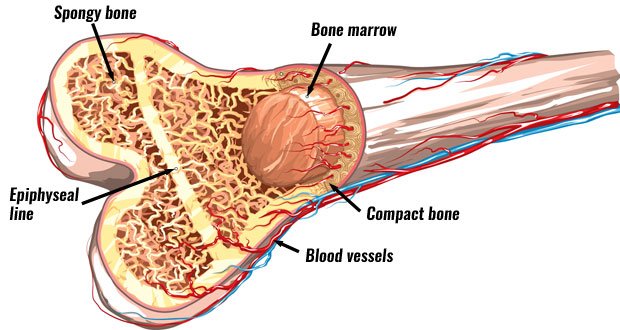
The spongy bone also called the cancellous bone or trabercular bone is a more porous, less rigid tissue found interior of the bone. It is weaker and more flexible than the compact bone. They are more in the end of long bones. It contains a lot of blood vessels along with bone marrows. These bone marrow can be yellow, red or both. The red bone marrow is involved in hematopoiesis (production of red, especially red blood cells). The proportion and architecture of compact bone to spongy bone is dependent on the intended function of the bone. Bones needed to support weight have more compact bone compared to other bones necessary to protect some internal structure, like the ribs.
Classification of bones based on shape
Types of bone based on their different shapes
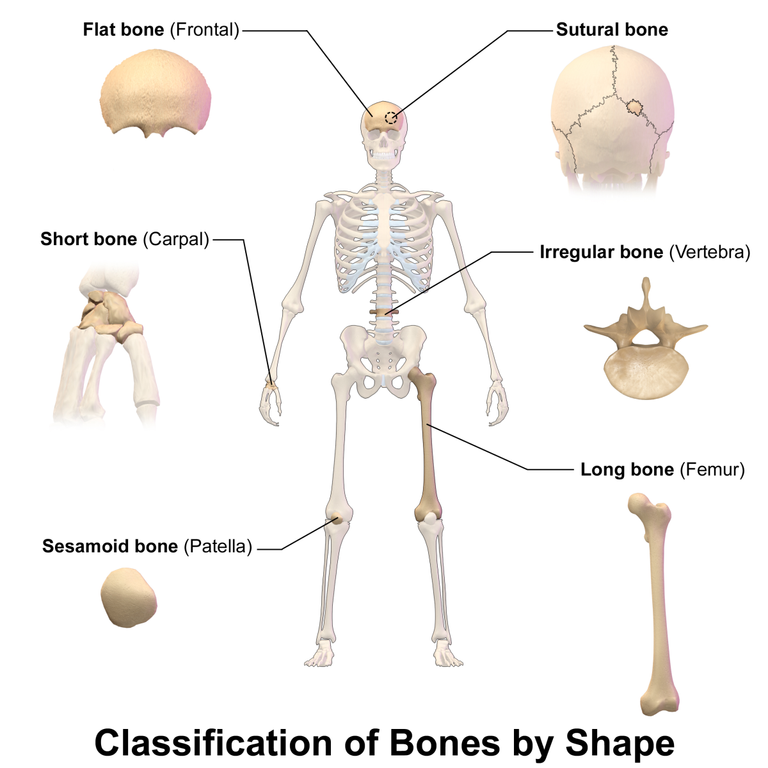
There are about 4 types of bone based on shape classification. They include:
- Long bones e.g humerus of the arm, femur of the thigh, phalanges of the fingers etc.
- Short bones e.g tarsal and capal bones of the feet and hand respectively.
- Flat bones e.g ribs, sternum of the chest, cranium of the head etc
- Irregular bones e.g bones of the face, vertebral bones etc
- Sesamoid e.g patella.
How bones are formed
Endochondrial Ossification

Intramembranous Ossification
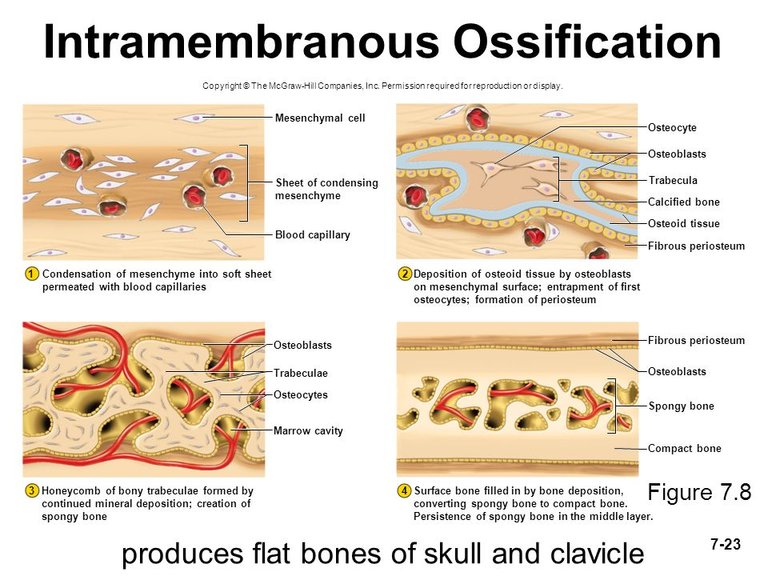
Bone formation is a process known as ossification. Bones are formed from the third month of life, in the wonb and will be completed in late adolescence where there will no longer be increase in mass or length of the individual's bone. The individual has attain his highest possible height at this point. There are information online guiding people into exercise and food to eat to gain extra inches to their height, this is not true if your bones are fully formed.
As stated earlier, offification of human bones begins within the eight weeks of intra-uterine life (life in the womb) and ends towards the age of 20 and 25. All bones are derivd directly or indirectly from mesenchyme. Mesenchyme is a differentiation from the mesodermal cells of an embryo. There are two processes or methods involved in ossification:
- Intramembranous Ossification
- Endochondral Ossification
Intra-membranous ossification is a bone formation process whereby the bone is formed directly from the mesenchymal cells. It is an essential process in bone healing. Endochondral ossification on the other hand doesn't start as a bone, it starts as a cartilage which is also a derivative of the mesenchymal cells. The cartilage is the deposited with salts such as calcium which makes it hard. Majority of bone healing process uses this method of bone generation. My hall mate whom I introduced in the beginning of this post will undergo this type of bone generation process. Endochondral ossification is the method adopted that causes lengthening of the bones over time from childhood to adulthood, till we reach our highest height peak. At the end of bone formation, there is no difference between a bone formed through intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification.
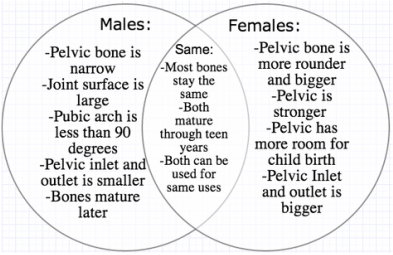
Differences between the male and female skeleton
Differences between the male and female skeleton is not very obvious

- The male bones are more stronger than the female
- The male bones are more thicker than the female
- A female bones are shorter compared to the male
- The female jaws are more rounded.
Functions of the bones
- Movement
- Blood Production
- Protection of internal organs such as liver, brain, heart etc.
- Storage of mineral (Phosphorus and Calcium)
- Acid-base balance
- Fat Storage
Bone pathology
There are different pathologies associated with bones. Some of these pathologies also affect the blood because the bones are a great deal producer of blood. Some of bone pathologies include:
Osteomyelitis: This is an inflamation of bone tissue caused by infection, usually by staphylococcus aureus.
Bone death could occur in oseomyeletis which will require surgical removal of dead portion of the bone
Rickets: This disease affects children causing bone growth. It occurs as a result of Vitamin D deficiency.
Rickets can be treated with adminstration od vitamin D and Calcium into diet and surgery in severe cases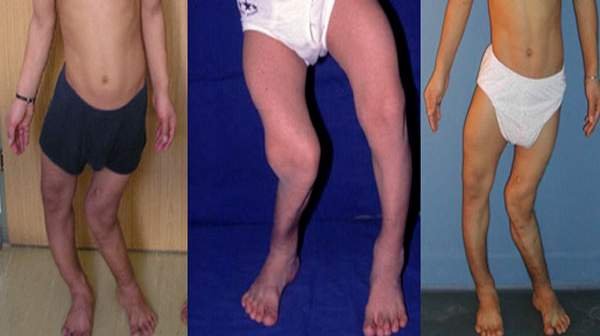
Osteogenesis Imperfecta: This is a rare connective tissue disease characterized by soft and brittle bones. This diseases is hereditary.
X-ray showing severity of the disease in different patients of different ages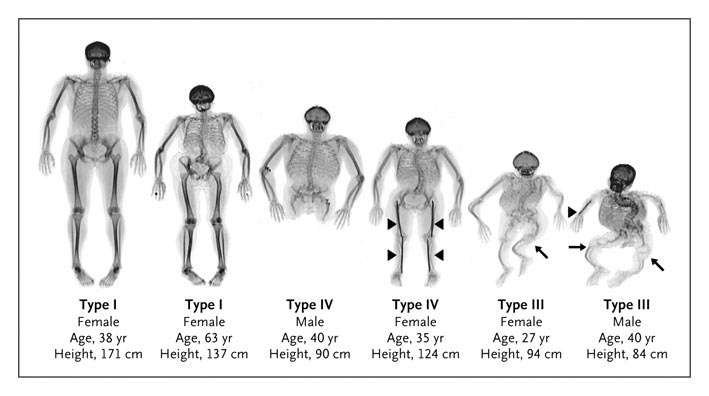
Fracture: This is a discontinuation in bone usually caused by having heavy object hit the bone.
Different types of fracture occur depending on the direction and amount of force suffered by the bone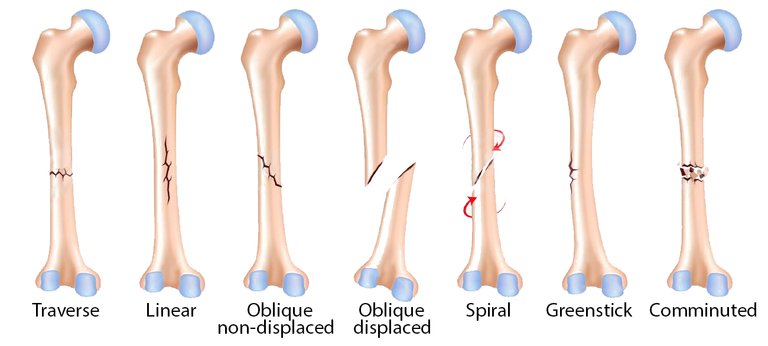
Osteoporosis: This is the reduction in the mass of a bone causing it to be liable to break in presence of minimal applied effort.
Reduced mass and density of bone in osteoporosis is the major cause of fracture in early people
Bone fracture and healing
Fracture occurs when bones break. It is caused by apply force to a brittle bone or apply enough force to cause a breakage in the bone. Fracture is common among children and old people. This is because they posses very fragile bones. There is a higher risk of fracture among smokers also because thy have low bone density. Low calcium intake can also cause low density of bone making you a topper in the risk of getting a fracture. The bone when they fracture can cause damage to internal organs; example is the fracture of a rib which in turn punctures the heart, lungs, spleen, stomach or liver. Or fracture of the skull which leads to damage of the brain tissues.
When fracture occurs, the bone would heal itself except in cases where by the bones will need to be arranged properly and bandaged together. The bones then uses the process of endochondral ossification to regain it's continuity. Depending on site of fracture healing can take up to 10 weeks.
There are ways we can take good care of our bones, these include participating in regular exercises, eating food rich in calcium and phosphorus and as well avoiding alcohol and smoking.
- Wikipedia: Skeleton
- Wikipedia: Exoskeleton
- Wikipedia: Endoskeleton
- Wikipedia: Skeleto
- Wikipedia: Cartilage
- Wikipedia: Musculoskeletal System
- Wikipedia: Ossification
- Differences between the male and the female skeleton
Thanks for taking your time to read this post on Skeleton System, I'm sure you learnt a lot from this article.
Do leave a comment on what you think about it and how I can improve on my posts.


Wow......that shows the guy will be having extra year or what?
It's possible but He should be able to register and do them with his final year courses in 400l. Final courses unit are not much and should accommodate his undone 300l courses.
physiology is awesome
It sure is!!
Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by Damzxyno from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Very nice!I followed you and I will vote as soon as my vote is not 0 :)
Don't give up, keep posting about science and you will grow! Also follow other people posting in the same tags, since common interests are what you seek in the community. Cheers!