Hi friends, greetings, today I will talk about a topic that is very sensitive for this society. It is about the final battle, if that disease that kills millions of people every day that disease called HIV, what is HIV? How is HIV spread? Types Risks Stages Signs and symptoms Handling Symptoms Tests Prevention Safe sex Is there a vaccine against HIV? Vaccines to get if you have HIV Frequently asked questions about HIV / AIDS, I invite you to observe this interesting article.
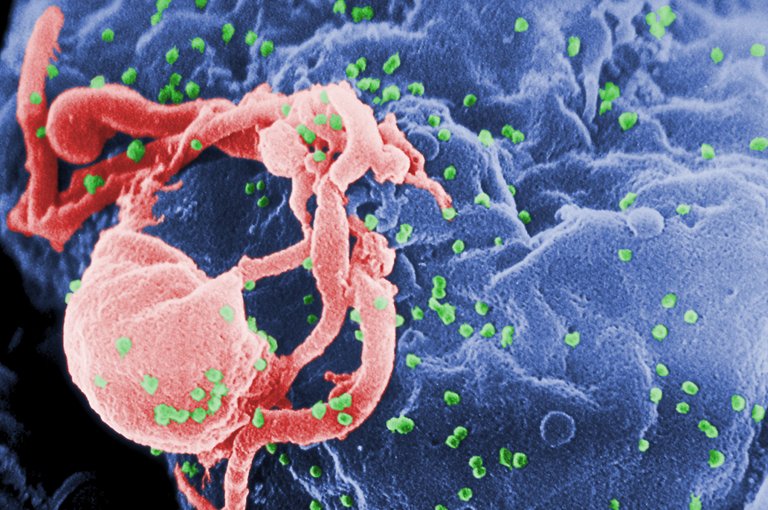
image fuentewikimedia
HIV is a virus that lives in human blood, sexual fluids and breast milk. It weakens your immune system, so your body has difficulty fighting common germs, viruses, fungi and other invaders. It spreads mainly through unprotected sexual contact and exchange of needles.
AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, is the condition that occurs when the immune system stops functioning and becomes sick from HIV.
Who gets it?
The infection is spread from person to person when certain body fluids are shared, usually during vaginal or anal sex, or when sharing medications that are injected. You can also go through dirty tattoo needles and body piercing. It can also be transmitted through oral sex, although the probability is small.
A mother can transmit HIV to her child during birth, when the baby is exposed to their infected blood or in their breast milk. But in some areas of the developing world, it is safer for a mother with HIV to breastfeed for a few months than to give a newborn baby. formula for potentially contaminated water, especially if you are receiving treatment for HIV (see below).
HIV does not live in saliva, tears, pee or sweat, so it can not be transmitted by casual contact with these body fluids.
HIV is not as easy to obtain as other infectious diseases. The virus can not survive for long outside the human body; It dies quickly when the body fluid dries. It is not transmitted by animals or insects. You will not find it on public surfaces such as door handles or toilet seats.
All blood products used today in the United States and Western Europe are tested for HIV. The blood banks get rid of any donation of blood that yields positive results, so it never enters the public supply. Someone who donates blood with HIV will be contacted so that the doctor can do the test and can not re-administer blood.
Where is it extended?
Sub-Saharan Africa (the southern part) has the highest number of people infected. The World Health Organization and the United Nations UNAIDS office estimate that more than a third of adults are infected with HIV in some areas of Africa. The number of people living with HIV in Eastern Europe and parts of Asia is growing due to the use of injectable drugs.
There are two main types of viruses: HIV-1 and HIV-2. HIV-2 is most commonly found in West Africa, although places in other parts of the world are seeing it too. HIV tests usually look for both types.
Types and varieties of HIV
There are two main types of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): HIV -1 and HIV-2. Both can lead to AIDS. However, they are very different from each other.
HIV-1 is the most common type. When you hear the term "HIV," it is probably HIV-1.
HIV-2 occurs in a much smaller number of people, mostly in West Africa. In the USA UU., Represents only 0.01% of all cases of HIV, and those are mainly people from West Africa. It is more difficult to transmit HIV-2 from person to person, and the infection takes longer to become AIDS.
Both HIV-1 and HIV-2 have multiple groups within them. These groups branch further into subtypes or strains.
HIV constantly makes copies of itself. Some strains multiply faster and can be transmitted from person to person more easily than others.
Your doctor can treat your HIV better if you know what tension you have. A blood test can tell you. The same test can also indicate if certain anti-HIV drugs will not work well for you.
Groups of HIV-1
HIV-1 has four groups: one large and three much smaller.
This group is responsible for the HIV epidemic. Almost 90% of all cases of HIV-1 come from this group.
The group has nine strains with names: A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J and K. Some have sub-strains. Researchers find new strains all the time as they learn more about HIV-1 group M.
Strain B is the most common in the USA. UU Across the world, the most common HIV strain is C.
Scientists have not investigated much about strains other than B, so information about the rest is limited. Medications that treat strain B (antiretroviral drugs) also work in most others.
Groups N, O and P
The smallest groups of HIV-1 are rare outside West Central Africa, specifically Cameroon. They are:
- N (new group, not M or not O): this form of the virus has only been seen in a small group of people in Cameroon. Researchers have not named any strain for this group because there are very few cases of this disease.
- O (Atypical group): this group has almost as many variations as the M group. However, researchers have not yet identified their separate strains because it is very rare.
- Group P: this is the newest group of HIV-1. It was given its own name because of how different it is from the M, N and O strains.
What puts you at risk of contracting HIV?
What is HIV? How is HIV spread? Types Risks Stages Signs and symptoms Handling Symptoms Tests Prevention Safe sex Is there a vaccine against HIV? Vaccines to get if you have HIV Frequently asked questions about HIV / AIDS Find a doctor
HIV is passed from person to person in the blood, semen, pre-seminal fluid, fluids in the vagina and rectum, and breast milk. Therefore, it is at risk when the bodily fluids of someone infected can enter and mix with theirs.
Some things you do now may increase your chances of getting HIV, but you can not change the things you were born with or had in the past.
Unsafe sex
One of the most common ways to get HIV is to have vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV. It could also transmit HIV during oral sex, but that is less common. It is also risky when you do not know if your partner is HIV positive or not, because they could be. The more sexual partners you have, the more your chances of getting HIV will increase.
Using condoms, barriers and dental barriers will help a lot to keep you safe, but they are not perfect.
Your choice of partner also matters. Having sex with someone who is more likely to get (and, therefore, have) HIV, a sex worker, or an intravenous drug user, for example, also increases your chances.
Shared needles
The other big risk is reusing needles, syringes or other equipment that a person with HIV uses to inject drugs, whether it has been prescribed by a doctor or illegal. You should not even reuse yours.
CONTINUE READING BELOW
YOU MAY LIKE
You could also get HIV with a needle used to pierce or tattoo if you did not get sterilized after piercing or tattooing someone with HIV.
An accidental cane from a contaminated needle or medical device could cause HIV, but that is very rare.
Alcohol and recreational drugs
Because this can weaken your judgment, you are more likely to do other risky things, such as having unprotected sex.
- A sexually transmitted disease
An STD such as herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, or gonorrhea can cause changes in the tissue of the vagina or penis that make it easier for HIV to pass while having sex.
- From mother to son
A mother infected with HIV can transmit the virus to her baby before or during birth, or breastfeeding. This is one reason why pregnant women should get tested for HIV.
- Donated blood
It is possible if you had a blood transfusion or were given blood products before 1985. Since then, all blood in the United States and Western Europe has been tested for HIV.
- Your genes
Some people have fewer copies of a gene that helps fight HIV. We may one day have a test that can tell you if you are more likely to get HIV and develop AIDS, but there is not one yet.
leer mas aqui :
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/VIH/sida
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Usuario:Jmieres/SIDA
https://ast.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIDA
https://ast.wikipedia.org/wiki/SIDA
Congratulations @dialexandro! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Congratulations @dialexandro! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!