Plasmodium is causitive agent of malaria. wikemedia commons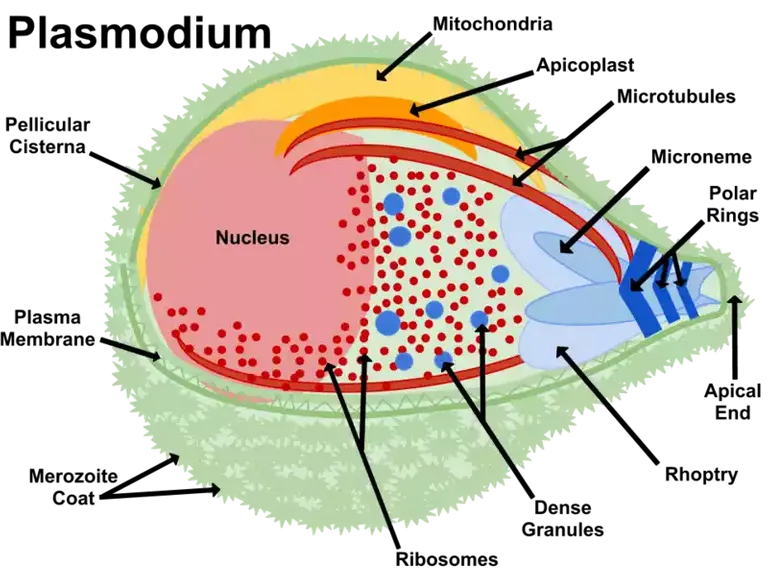
Malaria is a protozoan disease caused by parasite named plasmodium. it is transmitted via bite of female Anopheles Mosquito containing sporozoites of plasmodium parasite in their saliva.
Male anopheles do not cause malaria because they do not feed on human blood

Female anopheles is vextor of malaria. public domain
Anopheles mosquito is carrier of a disease and not the causative agent of the disease.
Four species of genus plasmodium infect humans and they are as following.
- Plasmodium falciparum
- Plasmodium ovale.
- Plasmodium malariae.
- Plasmodium vivax
Life cycle of malarial parasite-wikimedia commons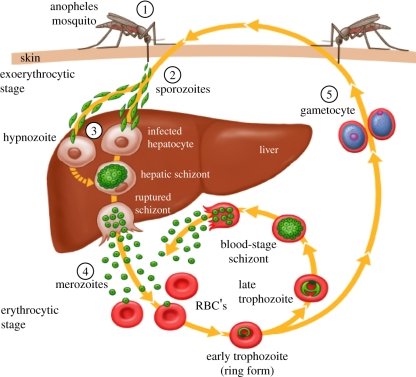
CLINICAL SPECTRUM OF MALARIA
Malaria signs and symptoms -public domain
Of all the species the most severe form of malaria is causes by P. falciparum.So I will discuss clinical spectrum under two headings. First one is severe malaria due to P. falciparum and sexond heading will include manifestations of other three species .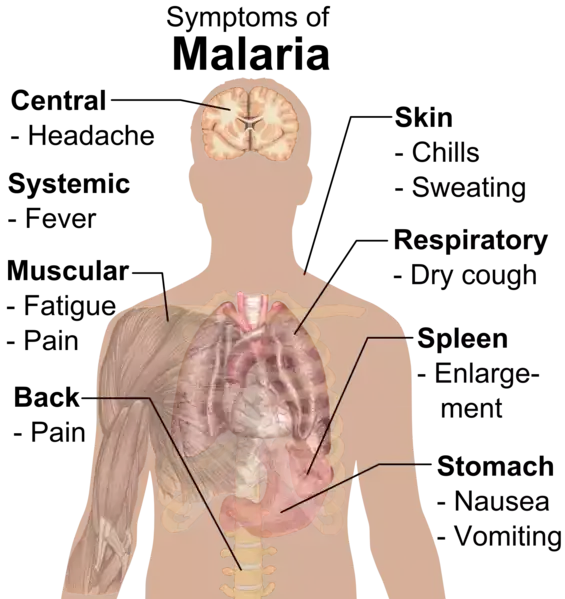
FALCIPARUM MALARIA
For sake of understanding it better, I will divide its manifestations into two phases.
A. Prodromal Phase=During this phase patient will experiance
- Mild fever.
- Malaise and anorexia.
- Headache.
- Myalgia.
B. Classical Malarial Paroxysm=This phase represents the manifestations during which time the organism's activity is at peak. Patient looks severely ill. Manifestations include.
- Rigors and shaking chills are followed by fever (regularly spiking).
- Convulsions due to fever.
- Myalgia and arthalgias.
- Severe throbbing headache.
- Palpitation (hearing ones own heartbeats).
- Tachyapnea (fast breathing).
- Syncope (fainting attacks).
- Anemia.
- Hepatosplenomegaly (Enlarged liver and spleen).
- Jaundice.
Types of fever in malaria
Quotidian fever, a fever which recurs every 24 hours, typical of Plasmodium falciparum or Plasmodium knowlesi malaria
Tertian fever a fever that records after 48 hours, it is typical of Plasmodium vivax or Plasmodium ovale malaria
Quartan fever , recur after 72 hours and is typical of Plasmodium malariae malaria.
COMOLICATIONS OF FALCIPARUM MALARIA.
The patients with falciparum malaria are more likely to develop comolications involving multiple systems of body especially nervous system.These complications are more commom in non-immune people, children and pregnant female in endemic areas.Comolicatioms include-
a. Cerebral Malaria = Cerebral malaria is a name given to a barrage of signs and symptoms resulting from diffuse encephalopathy in a person with p. falciparum infection after ruling out other causes of encephalopathy.Features include
- Convulsions.
- Irritability.
- Retinal haemorrhages and pappliedema.
- Bruxism and pouting.
- Opisthotonus.
- Decerebrate and decorticate rigidity.
- Coma.
In cerebral malaria, CSF is clear and has normal pressure.But lactic acid and protein levels are elevated.
b. Anemia = Likely causes of anemia are
- Destruction of infected RBC'S.
- Sequestration of red cells in spleen.
- Depletion of folate stores.
c. Hypoglycemia = It is a frequennt compilation in malaria.Probable reaaons are
- Increased consumption of glucose by host and parasite.
- Size effect of quinine or quinidine.
- Failure of hepatic glucomeogenesis.
d. Fluid and acid base disturbance.
Manifests as low JVP, hhpovolemia, oliouria, renal failure and lactic acidosis.
e. Circulatory collapse It is seen in patients with gram negative septicemia and pulmonary edema, hypoglycemia , massive gastrointestinal bleed, lactic acidosis.
Itamifests are very low blopd preasure, cold clammy extremities, drowsy patient, cynosis, thready pulse etc.
f. Spontaneous Bleeding and DIC.
Bleeding from multiple sites manifest as gum bleeding, nose bleed, petechiae, subconjuctival bleeding, haemetemesis (Blood in vomitus), malena (Blood in stool) etc.
g. Haemoglobinuia (Black water fever) - it is a severe but rare complication of falciparum malaria. It is seen in patients with G6PD deficiency and other enymw defciencies. It manifest as mild fever and dark urine due to intravascular haemolysis.
There is no parasitemia in BWF.
h. Jaundice- it is due haemolysis and malarial hepatopathy. Haemolysis is due to destruction of infect d red cells in spleen. Malarial hepatopathy is due to clogging of hepatic microvasculature by infected red cells .
Severe inflammation is never seen in malarial hepatopathy*.
Manifestations due to P. vivax, P. ovale and p. malarae malaria.
| P. vivax. | P. ovale | P. malarae |
|---|
Fever type
| Tertian | Tertian | Quartan |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia. | do. | do |
| Thrombo- | do. | do |
| cyopenia | ||
| Mild | do. | do |
| jaundice | ||
| High Risk | low risk. | low risk |
| of spleniic rupture | ||
| No relapse | No relapse | Relapse seen |
Investigations
A. MICROSCOPY
a. It is the most common test done in case of Malaria patients.
Patient's blood is examined under microscope after preparing slides. Two types of slides are prepared l--thick and thin thin.
Thick slides are used to estimate the degree of parasitaemia, that is, the parasite load in patient's. blood.
Thin slides are used to identify the specie{s) of the plasmodium infecting the patient.
b. Quantative Buffy Coat examination. it is more sensitive then microscopy..The centrifuged buffy coat is stained qith flourochrome and examined under UV light. Plasmodium parasite lights up under UV light and is therefore easy to detect.
c. Bome Marrow Examination- in some cases despite severe parasitaemia, parasites are not detected in blood smear because of sequestration of parasitised cells in deep vascular beds.
In such cases bone marrow is aspirated and examined under microscope to detect parasites or their pigments.
B. IMMUNODIAGONOSIS
- Tests like ELISA ( enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) and IFT ( immuno fluorescent test) are used to detect antibodies against the malaria parasite but these tests are not specific and sensitive.
- Other sensitive test include detection of histidine rich protein 2 (HRP 2) and lactose dehydrogenase enzyme in a fingerprint blood sample of patient.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test detects mRNA or DNA of plasmodium parasite in patients blood. This is highly sensitive test.
C. Complete Blood Counts - Patients with Malaria may have normocytic normochromic anaemia and raised ESR. TLC is low but there may be neurophilic leucocytosis.
D. Other non-specific findings
Plasma viscosity may be increased. CRP may be elevated.
Electrolyte abnormalities like low sodium, magnesium and blood glucose. Low pH.
in severe cases performing time and partial thromboplastin time may be increased.
E. Neuroimaging
In cerebral malaria there may be brain edema, hyperintense white matter and cortical infarcts.
PREVENTION
MOsquito control measures
A. Anit-larval measures
- Environmental Control- it involves measures to render environment unfavorable for breeding of mosquitoes. Certain measures taken in this connection included:-
- Filling, levelling and drainage of breeding places.
- Avoid collection of water in and around our living places.
- Avoid development of aquatic plants in our surroundings.
Chemical Control -it invalid use of larvicidal agents like Mineral oil , Paris green , malathion etc.
Biological Control Use of fishes which feed on larvae and in this way serve as natural control measures. Examples includeGambiensis affenis, labester reticulate etc.
B. Anti-adult measures
Residual and Space spray- it includes insecticides which prevent development of mosquitoes in environment for longer period of time, for example, DDT has residual effect of 6 to 12 months and BHC has residual effect of 2 months.
Genetic control- it includes techniques to alter the genotype of the adult mosquitoes so as to render them non-infectious. Techniques like
- Gene replacement
- Chromosomal translocation
- Cytoplasmic incompatibility etc
Personal protection measures
Use of insecticide treated bad nets to avoid contact of mosquito and humans
Use of clothes like full sleeve shirts
Management
Only drugs given in malaria will be discussed. Dosage and schedules will not be discussed.
Treatment
UNCOMPLICATED MALARIA
| Plasmodium species | Drug |
|---|---|
| P. vivax | Cloloroquine |
| P. falciparum. | Artemesnin based combination therapy (ACT} |
| P. Falciparum in pregnancy | |
| First trimester | quinine |
| Second trimester | ACT |
| Third trimester | ACT |
| COMPLICATED MALARIA | |
| P. Falciparum | |
| Clloroquine sensetive | chloroquine |
| Resistant | Quinine or Artemesnin derrivatives |
Redical care of malaria dur to p. Vivax and p. Ovale- Primaquine is DOC (drug of choice).
Chemoprophylaxis of malaria -it is indicated in travellers to malaria endemic areas
Short term (<6 weeks} - doxycycline.
Long term (>6 weeks)- mefloquine.
Proud Member of @air-clinic
Join air-clinic's discord server here
Know everything related to health.
hereJoin the @steemSTEM
A community project to promote science technology engineering and mathematics postings on Steemit.
Please support @surpassinggoogle as a witness by voting him at https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type in "steemgigs" at the first search box.
If you want to give him witness voting decisions on your behalf, visit https://steemit.com/~witnesses again and type in "surpassinggoogle" in the second box as a proxy
Hello @drkamran,
Air-Clinic sends her greeting!
We are happy that you are creating amazing medical contents on Steemit using the #Air-Clinic tag.
This article was found as a result of #Air-Curie Initiative!We encourage you to keep it up!
Expect an upvote from @Air-Clinic soon!
If you haven't joined us on Discord please do so by clicking here
Cheers!
@drqamranbashir- Air-Clinic Curator!
Thank you @sir-clinic. I joined discord today.
Congrats @Drkamran
Your great article has been selected to feature in this week Air-Curation Round 16.
Expect an upvote from a supporter of this initiative.
Continue using the #Air-Cliniic tag.
Thanks.
Congratulations @drkamran! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Congratulations @drkamran! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Your next target is to reach 50 replies.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSupport the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!