.jpg)
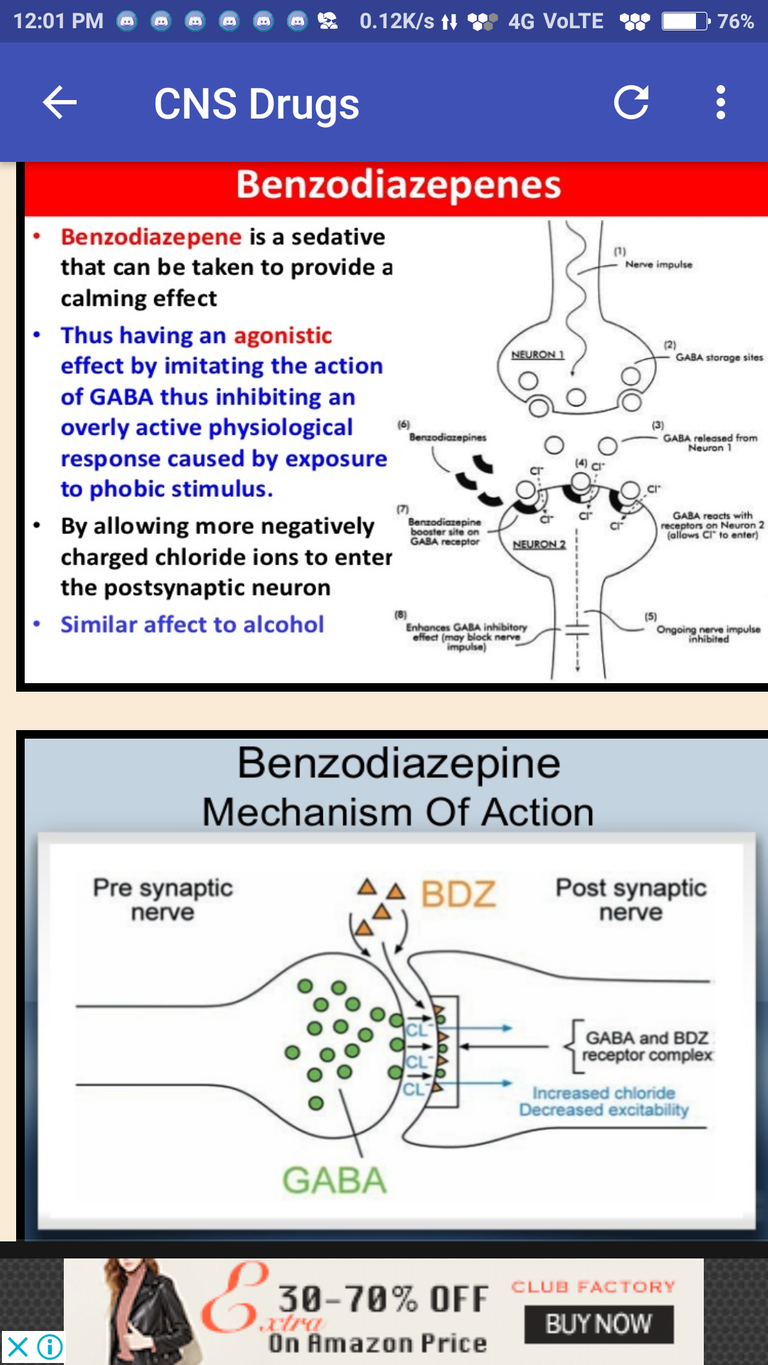
Benzodiazepines: actions
"Ben SCAMs Pam into seduction not by brain but by muscle":
Sedation
anti-Convulsant
anti-Anxiety
Muscle relaxant
Benzodiazepenes: antidote
"Ben is off with the flu":
Benzodiazepine effects off with Flumazenil.
Benzodiazepenes: drugs which decrease their metabolism
"I'm Overly Calm":
Isoniazid
Oral contraceptive pills
Cimetidine
*These drugs increase calming effect of BZDs by retarding metabolism.
Benzodiazapines: ones not metabolized by the liver (safe to use in liver failure)
LOT:
Lorazepam
Oxazepam
Temazepam
Benzodiazepins: 3 members that undergo extrahepatic metabolism
"Outside The Liver":
Oxazepam
Temazepam
Lorazepam
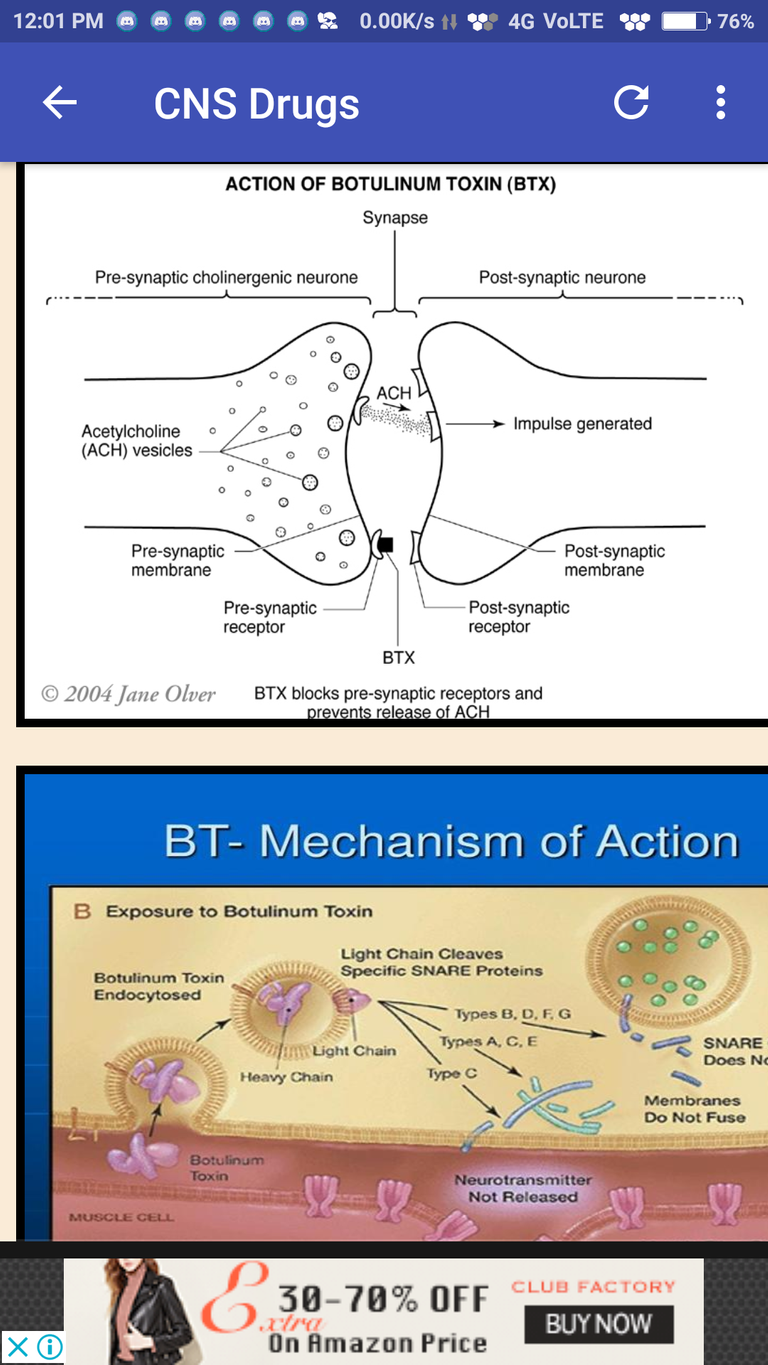
Botulism toxin: action, related bungarotoxin
Action: "Botulism Bottles up the Ach so it can't be the released":
Related bungarotoxin: "Botulism is related to Beta Bungarotoxin (beta-, not alpha-bungarotoxin--alpha has different mechanism).
Bromocriptine (for USA gang members)
The CRYPTS are an LA street gang that likes to smoke DOPE.
BromoCRYPTine is a DOPamine agonist.
Delerium-causing drugs
ACUTE CHANGE IN MS:
Antibiotics (biaxin, penicillin, ciprofloxacin)
Cardiac drugs (digoxin, lidocaine)
Urinary incontinence drugs (anticholinergics)
Theophylline
Ethanol
Corticosteroids
H2 blockers
Antiparkinsonian drugs
Narcotics (esp. mepridine)
Geriatric psychiatric drugs
ENT drugs
Insomnia drugs
NSAIDs (eg indomethacin, naproxin)
Muscle relaxants
Seizure medicines

Depression: 5 drugs causing it
PROMS:
Propranolol
Reserpine
Oral contraceptives
Methyldopa
Steroids
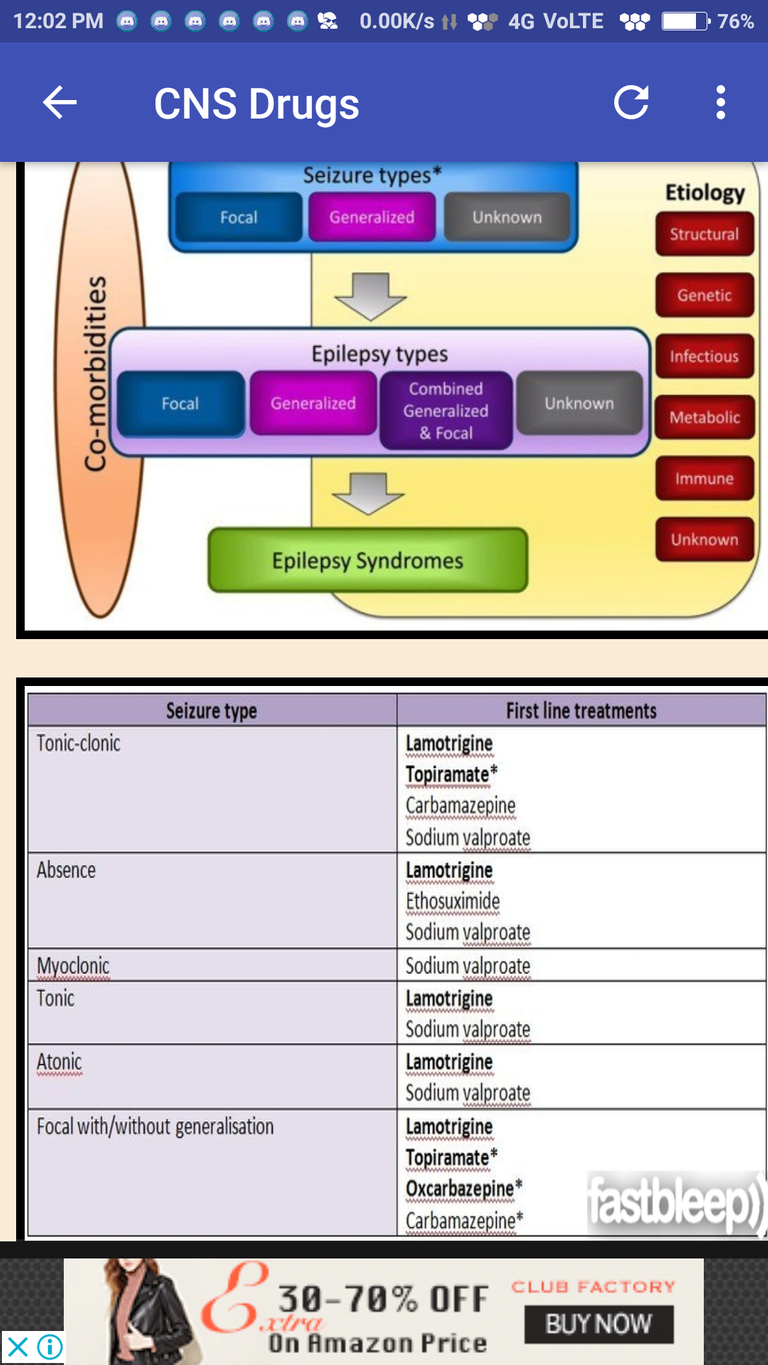
Epilepsy: types, drugs of choice
"Military General Attacked Weary Fighters Pronouncing 'Veni Vedi Veci' After Crushing Enemies":
*Epilepsy types:
Myoclonic
Grand mal
Atonic
West syndrome
Focal
Petit mal (absence)
*Respective drugsy:
Valproate
Valproate
Valproate
ACTH
Carbamazepine
Ethosuximide
Migraine: prophylaxis drugs
"Very Volatile Pharmacotherapeutic Agents For Migraine Prophylaxis":
Verpamil
Valproic acid
Pizotifen
Amitriptyline
Flunarizine
Methysergide
Propranolol
*Bare bones version [eg Lippincott's two], just Migraine Prophylaxis, as above.
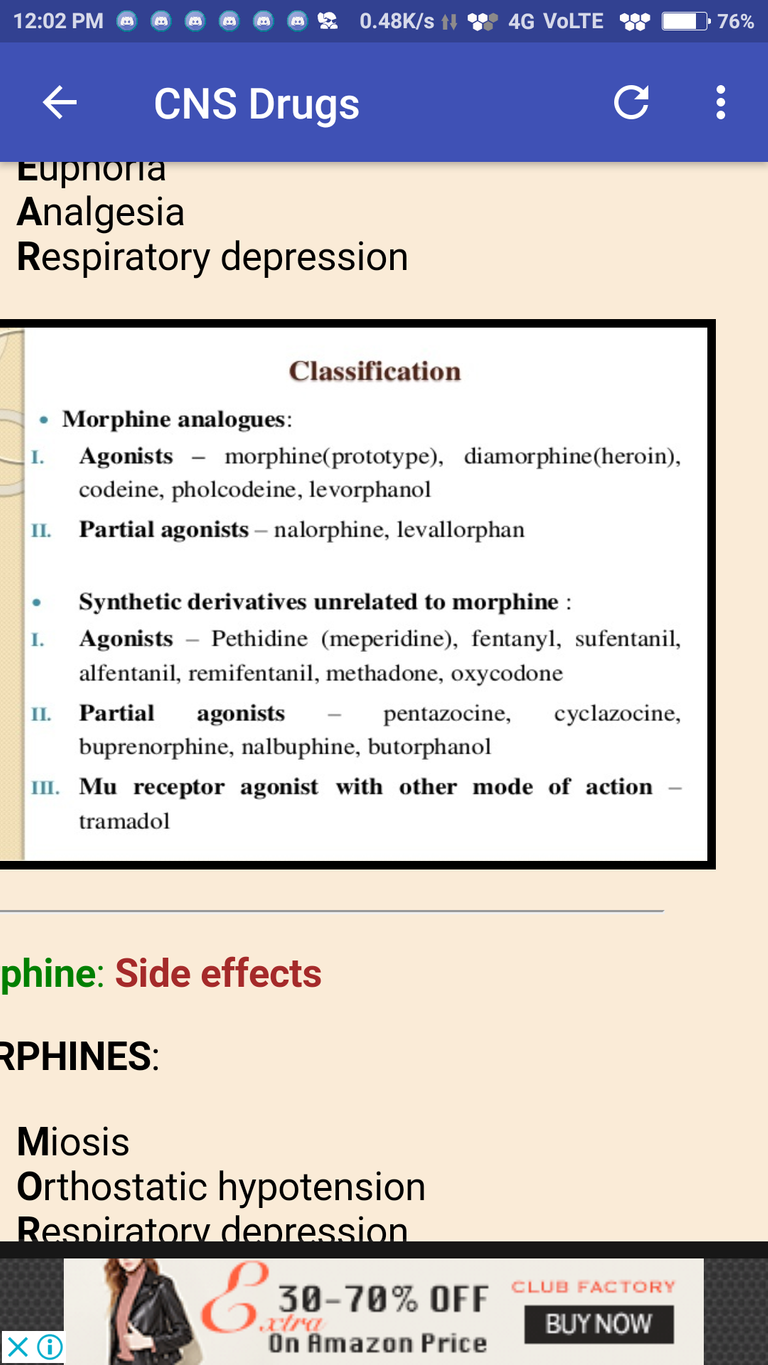
Morphine: effects at mu receptor
PEAR:
Physical dependence
Euphoria
Analgesia
Respiratory depression
Morphine: Side effects
MORPHINES:
Miosis
Orthostatic hypotension
Respiratory depression
Pain supression/Pneumonia (aspiration)
Histamine release/ Hormonal alterations/Hypotension
Increased ICT/Infrequency (Constipation, urinary retention)
Nausea
Euphoria/Euphoria
Sedation
Myasthenia gravis: edrophonium vs. pyridostigmine

eDrophonium is for Diagnosis.
pyRIDostigmine is to get RID of symptoms.
Narcotic antagonists
The Narcotic Antagonists are NAloxone and NAltrexone.
*Important clinically to treat narcotic overdose.
Narcotics: side effects

"SCRAM if you see a drug dealer":
Synergistic CNS depression with other drugs
Constipation
Respiratory depression
Addiction
Miosis
Nicotinic effects
MTWTF (days of week):
Mydriasis/ Muscle cramps
Tachycardia
Weakness
Twitching
Hypertension/ Hyperglycemia
Fasiculation
Opioids: effects
BAD AMERICANS:
Bradycardia & hypotension
Anorexia
Diminished pupilary size
Analgesics
Miosis
Euphoria
Respiratory depression
Increased smooth muscle activity (biliary tract constriction)
Constipation
Ameliorate cough reflex
Nausea and vomiting
Sedations
Opiods: mu receptor effects
"MD CARES":
Miosis
Dependency
Constipation
Analgesics
Respiratory depression
Euphoria
Sedation
Parkinsonism: drugs
SALAD:
Selegiline
Anticholinenergics (trihexyphenidyl, benzhexol, ophenadrine)
L-Dopa + peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor (carbidopa, benserazide)
Amantadine
Dopamine postsynaptic receptor agonists (bromocriptine, lisuride, pergolide)

Phenobarbitone: side effects
Children are annoying (hyperkinesia, irritability, insomnia, aggression).
Adults are dosy (sedation, dizziness, drowsiness).
Phenytoin: adverse effects
PHENYTOIN:
P-450 interactions
Hirsutism
Enlarged gums
Nystagmus
Yellow-browning of skin
Teratogenicity
Osteomalacia
Interference with B12 metabolism (hence anemia)
Neuropathies: vertigo, ataxia, headache

Physostigmine vs. neostigmine
LMNOP:
Lipid soluble
Miotic
Natural
Orally absorbed well
Physostigmine
*Neostigmine, on the contrary, is:
Water soluble
Used in myesthenia gravis
Synthetic
Poor oral absorption
Pupils in overdose: morphine vs. amphetamine
"MorPHINE: Fine. AmPHETamine: Fat":
Morphine overdose: pupils constricted (fine).
Amphetamine overdose: pupils dilated (fat).
Teratogenic drugs
"With TERATOgenic drugs":
Warfarin
Thalidomide
Epileptic drugs: phenytoin, valproate, carbamazepine
Retinoid
ACE inhibitor
Third element: lithium
OCP and other hormones (eg danazol)
Tricyclic antidepressants: members worth knowing
"I have to hide, the CIA is after me":
Clomipramine
Imipramine
Amitrptyline
- If want the next 3 worth knowing, the DNDis also after me:
Desipramine
Norrtriptyline
Doxepin
Tricyclic antidipressents (TCA): side effects
TCA'S:
Thrombocytopenia
Cardiac (arrhymia, MI, stroke)
Anticholinergic (tachycardia, urinary retention, etc)
Seizures
Vigabatrin: mechanism
Vi-GABA-Tr-In:
Via GABA Transferase Inhibition
any relation to @drqamranbashir ?
He is my younger brother.