Today, I will be introducing this great topic useful for engineers particularly electrical engineering student. Electricity is the life we can't do without it. Have you ever see a person that said he don't need electricity? So electrical engineers are illuminance of the world.
"Electrical science has revealed to us the true nature of light, has provided us with innumerable appliances and instruments of precision and has thereby vastly added to the exactness of our knowledge" Nikola Tesla
Let's start with definitions of some terms.
What is an electric circuit?
An electric circuit is simply a closed path through which an electric current flows.
This is a simple circuit diagram below,
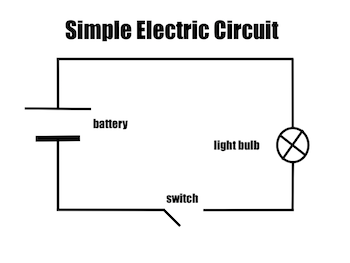
Image source
Electric current (I)
Electric current (I) is a flow of electric charge. This charge can be carried by electrons in wire and ion in an electrolyte.
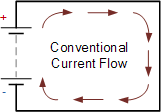
Image source
The Standard International SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere and it is denoted with A, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a measuring device called an ammeter.
Electric current is divided into two part which is Direct current (D.C) and Alternating current (A.C).
Let's discuss briefly on the two parts one another.
Direct current D.C
Direct current is the flow of charge moving in one direction.
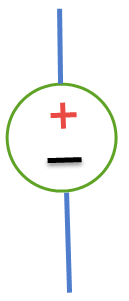.png)
Image source
The source of a direct current is produced by batteries, electrochemical, and photovoltaic cells. And it is rechargeable. A typical example of DC is a phone battery because it is rechargeable.
Alternating current.
Alternating current is the flow of charge moving in sinusoidal form or changes directions periodically.
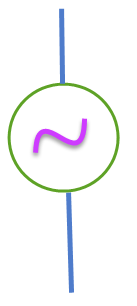
Image source
The main difference between A.C and D.C is thatA.C is not rechargeable while D.C is Rechargeable. Outlets at home or offices are using A.C because the appliances will be automatically switched off when there is no power supply.
I believed you have to know the difference between A.C and D.C now.
Resistance
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current.
The standard International SI unit is Ohms, which is denoted with Ω. The circuit components that perform this task is called a resistor.
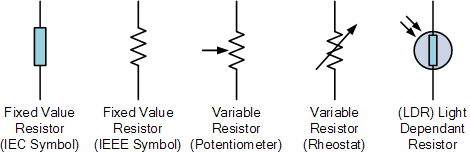
Image source
From the picture above, you can see that there are three types of the resistor which are fixed value resistor,variable resistor and light dependent resistor.
Let's briefly discuss the three types,
- Fixed value resistor :-this is a resistor cannot be changed as it is set at a specific value.
- Variable resistor:- this is a resistor that its value can be adjusted.
- Light-dependent resistor:- this is a resistor that has a resistance that changes with the light intensity that falls upon it. It is also called photoresistor.
References
Electronic tutorial-DC circuit theory
Elprocus- Ac and Dc
The sub-topic I will be writing about in my next posts are listed below.
- Ohm's law
- Series and parallel circuits
- Voltage and current divider rule.
- DC circuit analysis
This is really great. Nice work on the Tutorial. I was also hoping you would explain Ohm's law which I think you will explain in your next post. Thanks for sharing 💗
Ohm's law posted.
Good
Thanks bro for remembering me.. Dont worry I will write on it on my next post.
Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by Hayzeed from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, theprophet0, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
your tutorial was detailed
would love a tutorial on electrical circuit theory 2, detailing on parallel and serial resistor circuit and network port connection.