Greetings Steemians, it’s good to have you here again. Today I would like to discuss about SCADA systems and its many applications in the industry.
My first encounter with the SCADA systems was during an internship at an automation academy in Ibadan Nigeria. Pumps, lightings, machines, and other devices meters away in the factory were switched on/off with just a click and monitored from what looks like a computer screen. At that time I was fascinated and curious about what the underlying principle of operation could be. Maybe you have also wondered how industrial machines and processes are remotely controlled and monitored. For instance, how electric power utility companies take sections of power grid offline or online or how cross-border oil and gas pipelines are monitored. The answer lies in the application of SCADA. Let us find out how

SCADA system automation (Picture by Hhdgomez- wikicommon CC BY S.A 4.0)
So, What is SCADA?
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. SCADA is a concept in control engineering employed for monitoring, controlling, acquiring and analyzing real-time data of industrial equipment and process. They are used in virtually every industrial process in the world. SCADA system at its most basic consist of hardware and software elements that are interconnected through communication network for real time data acquisition.
Any application that gets data about a system in order to control that system is a SCADA application.
For instance, a fire –alarm protection system that detects potential fire risks such as smoke, heat etc., triggers the buzzers and sirens to notify the people in that surrounding and then displays the location of the smoke on its supervisory panel can be considered as a simple SCADA application. This is because, in this scenario, data has been acquired (detecting the risk) and processed (displaying the location and alerting the people) to control the situation. So we can say that SCADA is just an application and not a certain technology.
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
To start with, let us talk about the essential components that make up a SCADA system so that we can have a basic understanding before we join the pieces together to explain how it works.
Essential components of a SCADA system
- Human Machine Interface (HMI)
HMI is mainly used for process visualization and control. This has a graphical user interface (GUI) just like a computer screen or an automated teller machine (ATM) screen where users can interact directly with machines or control the devices. It could be a computer or a small GUI device.
The HMI presents the data acquired from the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or Remote Terminal Units (RTUs). Its screen displays the graphical representation or drawing of the equipment/processes to be monitored in a kind of flow diagram as shown in the picture.
The graphic representations provided by these drawing programs can be very simple or extremely complex, depending upon the makeup of the network and the level of detail desired.
This graphic representation is drawn using the sophisticated SCADA/HMI software such as SIMATIC WinCC. The software has inbuilt representations for many common industrial elements such as pumps, electric motor, valves, contactors, boilers etc. Just like in an android app with clickable buttons, these elements are made clickable and that is how they can be remotely controlled when integrated with the PLC.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)/Remote Telemetry Unit (RTUs)
PLCs are mainly used to control automated systems in industries. As its name implies, it continuously monitors the state of input devices e.g. sensors and make decisions based upon a custom program (logic) to control the state of the output devices.
Typically, PLCs support numerous analog and digital inputs (e.g. sensors) and outputs (e.g. relays and actuators for pump, valve, and hydraulic cylinder operational control)
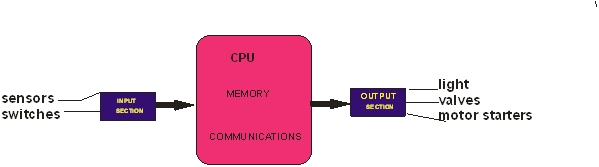
Image created by me @ibk-gabriel
A PLC consists of two main sections namely: the input/output (I/O) and the CPU. As shown above, Input elements such as sensors, smart devices, switches are connected to the input section of the PLC. The data provided by the input elements is processed by the CPU and the corresponding action based on the logic programmed into the memory chip of the PLC is sent to the output element.
For instance, the picture below is one of the SCADA projects I worked on using PLC
It is a model of an intelligent traffic light system. The sensor sends signal to the PLC whenever there is a car approaching. The sensor is directly wired to the input section of the PLC. The PLC in turn sends signal to the appropriate pilot lamp (green, yellow, or red) at the side where the car is approaching. The lamps are used to represent traffic lights and they are all wired to the output section of the PLC.
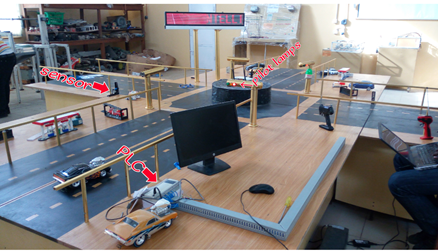
Image captured and edited by me @ibk-gabriel
You may want to ask how the PLC knows the appropriate lamp to activate. This is based on the logic stored in its memory chip. The logic is achieved through PLC programming. PLCs are programmed using SCADA software on a PC. They are connected through an Ethernet, RS-232, and RS-422 or RS-485 cables to a PC. There are many PLC programming techniques but the ladder technique is mostly used. The CPU is a combination of memory chip, microprocessor and other integrated circuits to control logic, monitoring and communication.
RTUs also perform basically the same function as a PLC.
It communicates with an array of object such as factory machines, HMIs, sensors and then route the information from those objects to computers with SCADA software.
- Communication Infrastructures: These are used to establish communication between PLCs and the HMI. This connectivity can be through wired e.g. fiber optic cable or wireless (satellite, radio) networks using different communication protocols.
JOINING THE PIECES TOGETHER
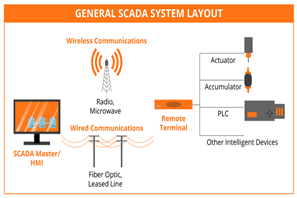
A SCADA system performs four main functions namely data acquisition, data presentation, control and networked data communication.
As shown in this diagram, the field elements such as sensors, breakers etc. are connected to the RTUs/PLC. The PLC gathers data (data acquisition) from these field elements in real time and gives corresponding actions (control) based on the logic in its memory. The whole process is visualized (data presentation) and can also be controlled in real time from the HMI because the PLC is connected through wired or wireless (communication) network to the HMI.
DRAWBACKS
SCADA platforms provide vast benefits and are widely adopted for short distance as well as outside-the-fence applications (water waste, electric power system, cross-border oil and gas). However, there are some challenges associated with the outside-the-fence applications due to the long distance of communication. Power and communications issues are the major limitations encountered when linking SCADA system components in one remote location to the other. PLCs needs to be uninterruptedly powered so as to communicate in real-time with the HMI at the viewer’s end but it can be difficult to get the PLC connected to a fixed source of power in a remote location. Instead batteries are used but they need to be replaced periodically when depleted.
Another challenge is the vulnerability of SCADA components in remote locations to theft, vandalism and cyber warfare. SCADA systems in remote locations are mostly left unattended and are therefore prone to attacks and viruses especially those installed near human settlements.
APPLICATIONS
SCADA systems are widely used in many modern industries to automate and keep track of several processes in real time. Some of which are listed below:
Power Systems: Monitoring is key in the generation, transmission and distribution of electric power and that is why SCADA systems find great implementation in this area. For example, between power generating station and the final consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. The substations are built to step up or step down the voltage or perform several other important functions such as load shedding, fault analysis, protection of transmission systems etc. as occasion warrants. Therefore a substation is an important link between the point of generating and consuming. Despite their importance, they are mostly left unattended or sometimes with minimum technical personnel; courtesy of SCADA applications. With the aid of SCADA systems, substations are monitored and the data acquired in real time can be sent to the master station server.
Transportation: SCADA systems are also employed in intelligent traffic light systems to monitor and control the traffic lights.
Oil and Gas transport: SCADA systems are employed in the oil and gas industry for controlling and monitoring pipelines and pump stations electrical elements, leak detection and several other important functions. Vandalization of pipelines is a huge concern in this sector, but with the aid of SCADA systems, it can be reduced to bare minimum.
Manufacturing: SCADA system is used in manufacturing industries for monitoring automation processes e.g. counting and regulating the numbers of products on a conveyor belt. They are also used for quality control and fault diagnoses. Overhauling of machines becomes quite easy with SCADA as faulty and unreliable parts of the machines can be easily identified from the HMI. Monitoring hundreds of processes in an industry can be an overwhelming and herculean task. But with SCADA, the task becomes simplified and the data from these processes can even be logged for future purposes.
The list is numerous. SCADA systems find application anywhere supervision, real-time data acquisition and presentation as well as remote control are needed especially where human control is difficult.
CONCLUSION
Like a river without boundary, SCADA systems flow across many industrial sectors. The importance of SCADA systems cannot be overemphasized. The SCADA platforms provide numerous benefits and it is safe to conclude that SCADA applications are the pillars upon which industrial automation thrives. I hope this article has supplied you with sufficient information to grasp what a SCADA system entails.
Thank you for reading
REFERENCES
- Introduction to SCADA systems
- What is SCADA
- SCADA
- Programmable Logic Controller
- Shaw, T., "Energy Infrastructure Cyber Security: Pipelines—A Step-by-Step Guide for Keeping Pipeline Infrastructure Safe From All Cyber Attacks," Oil & Gas Journal Research Center, 2009.
hereblogIf you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord . If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this by @stemng for more details.



I witnessed something like this at the power plant i visited late last year. They had these system they were using to monitor and control everything that goes on regards power generation there.
This is an awesome article about it. Well done.
Yes, it is used in virtually every modern industry. Thank you for reading
You are welcome.
SCADA is not so popular in Nigeria though, we like doing things the old way. The way it has always been done.
Yes. But many big companies in Nigeria use it
I encountered something like this too when we visited the WARTSILLA plant in. Large generators are switched on and off only by a click from the engine control room.
Nice write up sir
The Human-Machine interface is a component of the SCADA! That's really cool. Thanks for this info. I've learnt something new.
Nice piece
Thank you for reading. I am glad you found it informative
Yeah Yeah, I saw this on my visit to WARTSILA Power Plant as well. It's nice to be finally reading about it.
Thanks for the opportunity
Thank you for reading
You're welcomed