Source of image of pixabay
The heart is the engine of the circulatory system, it is placed in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs and lightly displaced towards the left side, in adult man it weighs approximately 300 grs. Inside the heart there are four compartments: two Superiors who are the auricles and two low ones that are the ventricles.
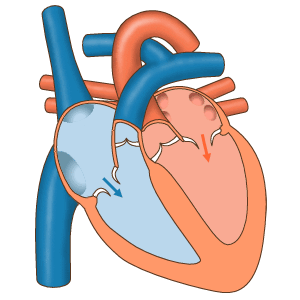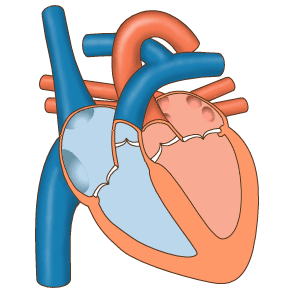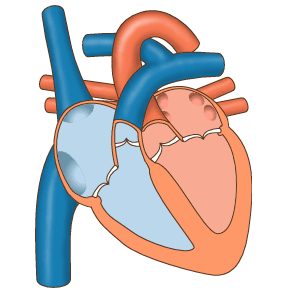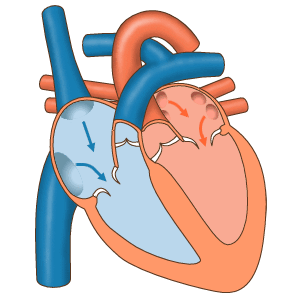
Vascular flow across the cardiac cameras, source image gif, of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: josiño.
The right auricle receives the blood of the whole body, except of the lungs across three veins (Superior digs vein, vein digs low and coronary bosom), the venous blood for the left ventricle, which is pumped up to the lungs, to where pulmonary turn of the arteries comes. From the lungs, cuatros pulmonary veins empty the blood become oxygenated in the left auricle, from where it flows to the left ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood across the aorta towards all the parts of the body, excluded the lungs.
The walls of the heart are formed by three layers, which of out inside are: epicardio, myocardium and endocardio, the muscular fibers of the myocardium are the causers of the contraction of the heart. To be able to carry out the function of pumping, the ventricles on all the lefthanders, it has the very thick muscular walls, with a very developed myocardium.
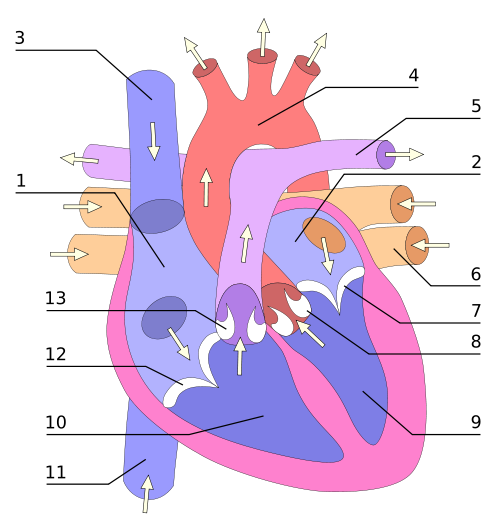
Frontal sight of a human heart. The white arrows indicate the normal flow of the blood. 1. Right auricle; 2. Left auricle; 3. Superior digs vein; 4. Artery aorta; 5. Pulmonary, left and right arteries; 6. Pulmonary veins; 7. Valve mitral; 8. Aortic valve; 9. Left ventricle; 10. Right ventricle; 11. Vein digs low; 12. Valve tricúspide; 13. Pulmonary valve, source of image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author en:User:Wapcaplet.
The structure of the heart, we have cuatros cavities so that those of the right side do not communicate with those of the left side, he avoids the miscellany of the venous blood, which is poor in oxygen with the arterial blood and system of independent circulation allows the existence of two, that are the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation, the pulmonary circulation is the one that takes place from the right ventricle, up to the lungs and from these left side comes even the auricles by means of the pulmonary veins. The systematical circulation is the one that distributes the blood become oxygenated by all the textiles, he gathers the products of waste and takes across the veins his wine-cellars, up to the right auricle.
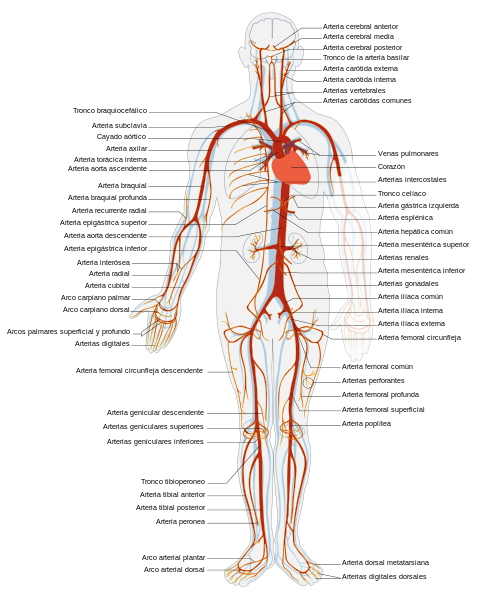
The blood circulates along the arteries to raised pressure and speed, to be able to support the pressures that are generated inside the arteries, also his walls are reinforced by smooth musculature and elastic fibers. As the arteries move away from the heart, they go branching out until glasses form the thinnest, the arteriolas who communicate with microscopic glasses endoteliales and the capillaries, in regarding the capillaries they are permeable to certain substances, which distributes to the textiles oxygen and nutrientes, likewise receive cellular products of waste of the metabolism.
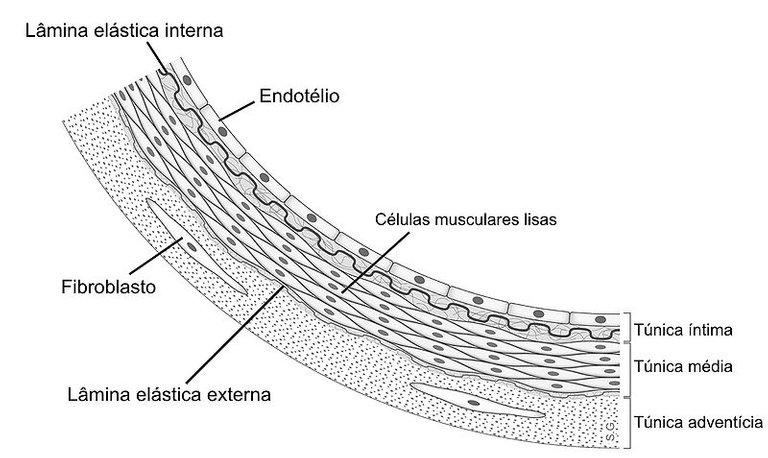
Histology of the arterial wall, source image of domain of Wikimedia Commons, Author: Rhcastilhos
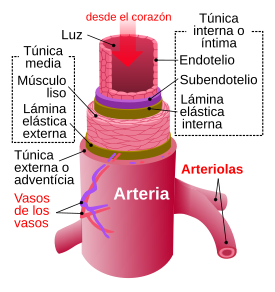
Transverse section of an artery, source image of domain of Wikimedia Commons, Author: Kelvinsong
From the capillaries the blood I tried already in oxygens and with a lot of substances of waste, which happens to the vénulas and of this one to the veins, for which it flows at low speed and pressure up to the heart. At level of embryology the circulatory system is the first functional system of the embryo of a vertebrate, the fetal heart shows activity from the third week of the embryonic development.
The Formation of the heart starts in the primitive line of the embryo dividing the cells cardiogénicas of the mesodermo, the transformation of the mesodermo in textile cardiogénico depends on some proteins produced by the endodermo, between them the protein morfogénica bony (BMP) and the factor of growth fibroblástico 8 (FGF-8). In the 5.th week the cardiac frequency of the embryo is between 60-80 latidos/min, it rises progressively up to reaching in the 10.th week 180-200 latidos/min.
Big contribution that they announced on this system realized it William Harvey, who described and popularized the modern concept of the circulatory system and the functions of arteries and veins in the XVIIth century, although the Spanish Miguel Servet described the pulmonary circulation a quarter of century before Harvey was born, he wrote it in a book of Theology (Christianismi Restitutio, published in 1553), which was considered to be a heresy and led him to the bonfire. Consequently, almost all the copies of the same one were burned except three, which were discovered decades later.
In resume can say that the heart is the engine of the circulatory system, ventricle is composed by two auricles and two, the blood comes for the vein top wine-cellar, the vein digs low and the coronary bosom goes on to the left ventricle and to the lung across the pulmonary arteries of the lung it returns to the left auricle, from where there flows the left ventricle, which gets drunk across aorta towards the whole body. Cuatros valves prevents the ebb of the blood: the tricúspide, the mitral and two semispots, also we have the structure of the heart there allows the existence of two system of pulmonary circulation and the systematical circulation of blood become oxygenated by the textiles and turned to the heart by means of vénulas and veins.

The circulatory system: why does my heart beat? for Sue Barraclough - 2008.
Biology: the life in the ground - Page 550 for Teresa Audesirk, Gerald Audesirk, Bruce E. Byers - 2003.
The Circulatory Device for Conrad J. Storad - 2006.

Source 1
Source 2
...and so on.
Plagiarism is the copying & pasting of others work without giving credit to the original author or artist. Plagiarized posts are considered spam.
Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
More information and tips on sharing content.
If you believe this comment is in error, please contact us in #disputes on Discord
I think you meant atria, not auricles. Auricles are ear like compartment arising from each atrium. It's designed to increase the maximum capacity of both atria to receive blood.
There are some words which I'm not familiar with from your article, for example, what is cuatroz? Are you direct-translating this from another language?
This long sentence is both confusing and not making any sense. Ventricles are composed of two auricles and two? You obviously forgot to check this or like I said before, you were direct-translating by using Google translate or something. I would say, that is not a good idea.
Thanks for you corrections I understand it and understand it for future publications