Magma is formed when the fusion of the rocky substance that forms the planet gradually occurs. Most rocks are composed of minerals, with different melting points and chemical-physical relationships of great complexity. The great pressure that exists in the bowels of the Earth determines that the solid components soften.
The temperatures within the liquid complex of magma are very high. They are in the range that goes from 700 to 1300 degrees Celsius. In general, the composition of this substance is associated with certain environments, which include the so-called subduction zones, that is, continental areas, oceanic ridges and hot spots of the planet. Magmas are formed only in these special circumstances.
Volcanic magma is a combination of molten rock and volatile and solid compounds, which is found within the surface of the earth. This mixture may also contain suspended crystals, dissolved gases and gas bubbles. Sometimes magma builds up in the chambers of a volcano and feeds it, although it can also be squeezed between adjacent rocks or out.

Processes of formation and evolution of magmas.
Formation of a magma
The origin of the magma is located in the changes of the variables that govern the stability of the minerals of a rock: temperature, pressure and composition.
Evolution of a magma
A magma tends to ascend due to its lower density, occupying a space that we call magma chamber. The ascent is made by the injection of magma into the cracks and subsequent fall of blocks of the roof of the chamber.
In this ascending path, the magma varies its composition by several processes:
Magmatic differentiation: Minerals
formed in the magma can be separated
(by gravity, by currents etc) of the part
melted The residual magma becomes impoverished in
the chemical eleMagmatic Assimilation: Magma, in its
rise, integrates rocks inside the
walls of the magmatic chamber and, at
melt them, incorporate their elements.Mix of magmas: The successive generation
of magmas can cause them to mix
magmas of different compositions.
WHY THERE IS RED ROCK INCANDESCENT SO FAR FROM THE PLANET NUCLEUS?
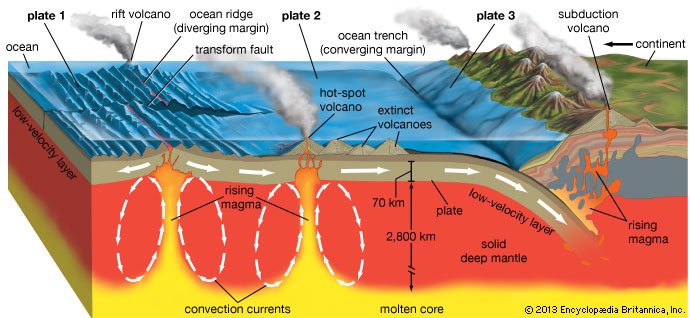
The Asthenosphere is an area of plastic consistency that lies just below the Lithosphere. Its plasticity is due to the fact that the temperature sometimes exceeds 1,500 ° C, but at the same time, the pressure is so huge that the melted rock can not move freely as it would if it were a liquid. The high temperature of this zone is an effect, both of the enormous pressures due to the weight of the lithosphere that is above, and the fact that this area is in constant motion, with entire kilometers of rock moving and rubbing against each other. The enormous pressures and friction to which the rock of this area is subjected form a layer of "plastic" rocks that is in constant movement.
In some areas, especially where one plate collides with another, the asthenosphere forms thicker pockets that can end up being pushed up. When this happens, the magma rises a few kilometers and when finding cracks through which to surface, a volcano ends up forming. Even magma bags can be formed much higher still, where the continental plates collide or overlap each other, creating areas of higher friction (image on the right).
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magma
this research is mine I only put that content because it seemed essential for people to learn and I could source it and everything and still it came out
@cheetah