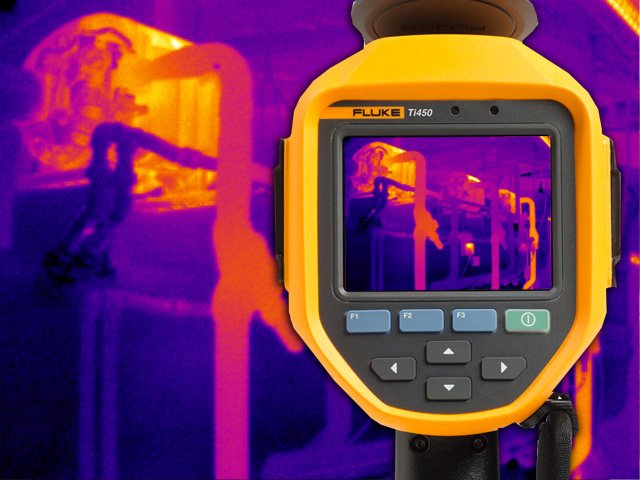
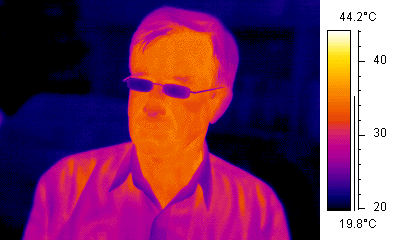
Infrared thermography.
Infrared thermography is a technology that has existed for many years but needs an impulse since its level of implantation is still very low despite the fact that it could be applied in many fields.
In the case of energy efficiency, infrared thermography is a fundamental diagnostic tool. Its use in energy audits of buildings, facilities, etc., is increasingly frequent. It allows the technician to detect and evaluate energy losses with great ease and it serves as support to write the reports and transmit to the owner, in a very visual way, the situation. So both can decide what improvements to make.
It is a technique that allows, at distances and without any contact, to measure and visualize surface temperatures with precision, this technique allows to produce visual images from the infrared spectrum (invisible to our eyes) that emit objects due to their thermal condition.
Source

Importance of temperature.
Temperature is a fundamental variable in any situation, both in everyday life and at an industrial level.
Source

Source

Benefits of infrared thermography
- Warm-up detection due to unbalance, overload, low power factor and harmonic distortion.
- Current detection in ground connections.
- Inspection of transformers, banks of capacitors and banks of batteries.
- Detection of connections overheated.
- Detection of defects in insulators.
Inspection of breakers, switches, transfers, fuses, cut-out, sectioning units and kpf.
Source

Source

Thermal radiation.
Thermal radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The bodies emit thermal radiation as a consequence of their temperature. The transmission of heat by radiation is carried out by emission and absorption of thermal radiation. All bodies emit and absorb thermal radiation at the same time.
Since all objects have a temperature, they all emit thermal radiation. The higher the temperature, the greater the amount of thermal radiation will be emitted.
All bodies, whatever their temperature, emit energy continuously from their surface. This energy is called radiant energy and is transported by electromagnetic waves for this reason the radiant energy can be transmitted even in a vacuum.
Source
Electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the energy distribution of the set of electromagnetic waves.
The electromagnetic spectrum extends from the radiation of shorter wavelengths, such as gamma rays and X-rays, passing through ultraviolet light, visible light, and infrared rays, to electromagnetic waves of longer wavelength, such as radio waves. It is believed that the limit for the smallest possible wavelength is the Planck length while the maximum limit would be the size of the Universe although formally the electromagnetic spectrum is infinite and continuous.
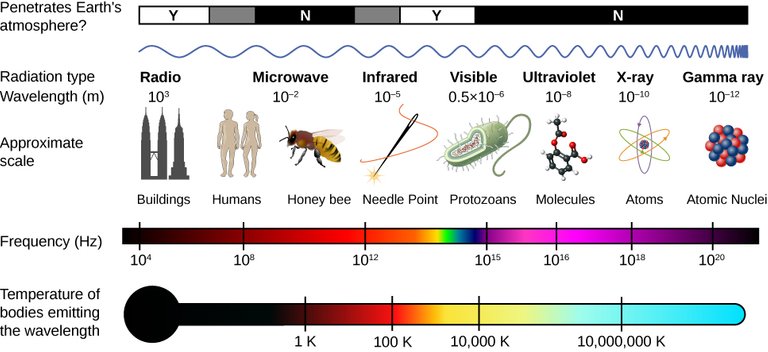
Range of electromagnetic wavelengths
Source
References:
- http://www.infrared.avio.co.jp/en/products/ir-thermo/what-thermo.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4168422/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/thermal-radiation
- Basic infrared thermography principles, Wayne Ruddock
Nice post. :) Need more exposure? If you want get followers, upvote and resteem https://steemit.com/dsound/@mrnastykilla/dimension-switch-green-void
thank you friend :)
I would love to have a thermo imager at work.