Pregnancy is defined by literature as "a physiological state detectable from an early time, always depending on the diagnostic method we use".
This gravid period begins from the moment of the implantation of the zygote in the womb of the now-pregnant woman, until the moment of birth.
We consider as "pregnancy" the whole physiological process that the woman goes through, manifested in biological, hormonal and morphological changes, to be able to provide nutrition, protection and an adequate development to the fetus inside the uterus.

This is not to be confused with gestation, which refers to these processes of adaptation, but only evidenced in the fetus.
During the 38 weeks since fertilization, these modifications will gradually become evident, which will not begin with the biometrics of women, but with hormonal changes that allow us to guide a much more precise diagnosis at an early gestational age.
Now, it's easy to consider the basic ideas that society has about pregnancy; when we think about it at the slightest indication of the following signs or symptoms:
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
- Sudden mood swings.
- Unusual cravings for certain foods.
- Sudden growth of the breasts.
Some, even, are more mystical when speaking of certain "signs" like the songs of birds, or evidence in the hips or hair of women, to sentence them as pregnant.

However, modern embryology doesn't conform to the rudimentary fables of old people. And although many of the aforementioned signs may correspond to pregnancy, they are not accurate indications of the same because they may have multifactorial etiologies independent of pregnancy.
For this reason, and to avoid confusion or old wives’ tales, literature has decided to differentiate these "evidences" according to the degree of probability or certainty in three: presumptive signs, probability signs and signs of certainty.
This is why I have decided to present you:
5 Pregnancy Diagnostics
1. Amenorrhea
Mentioned before, it is probably the most important presumptive sign of all. But yes, you read it well: presumptive. This is because the cessation of menstruation in a healthy woman, of reproductive age and sexually active with regular and predictable menstrual cycles, suggests a pregnancy very directly.

This can be evidenced at least two weeks after fertilization.
However, pregnancy is not the only cause of amenorrhea.
There are physical diseases such as ovarian tumors, endocrine or hormonal disorders, certain traumas, anorexia, and even stress or anxiety, that can produce it. In fact, this sign becomes even more complicated when the menstrual cycles of the woman are irregular, being then that the delay must be at least 2 months to consider it as a presumptive sign.
2. Chadwick-Jacquemier Sign
The hormonal alteration also brings with it certain morphological modifications that produce this other presumptive sign. It consists in the increase of the vascularization of the vagina and the cervix by the action of progesterone, producing a violaceous color in these structures, so that we can visualize the mucosa of these areas as having a slight bluish hue.
It's important to mention that, as in this sign, there are some hyperpigmentations also in areas such as the line alba or the face of women, producing the signs called pregnancy line and the Gravidaric Chloasma.
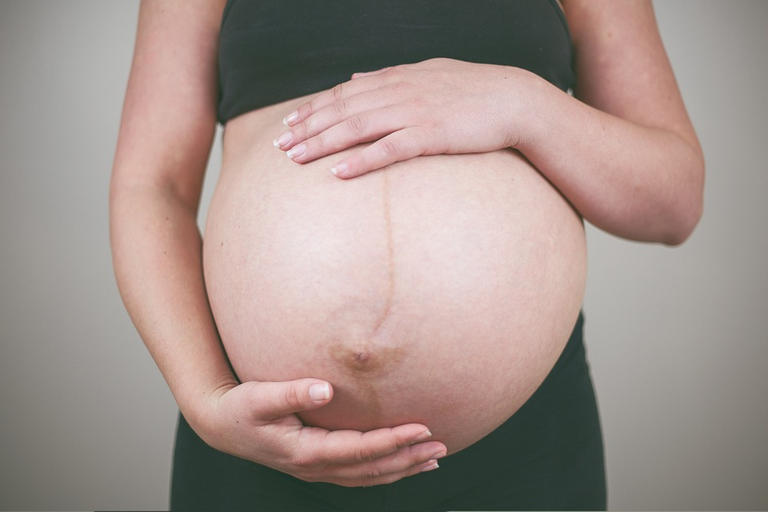 Pregnancy Line
Pregnancy Line 3. Shapes of the Uterus
These morphological changes increase until certain signs are developed that will be typical of a probable pregnancy because, unlike the previous ones that could be due to the use of oral contraceptives or hormonal changes, these changes are more stylized and typical of a gestational development.
These signs consist mostly of changes in the structure of the uterus, so they will be perceived through the use of semiological maneuvers that allow palpating and distinguishing certain forms, softening, asymmetry or firmness of a uterus adapted to accommodate the fetus.

Some of these signs are:
- Sign of Noble-Budín.
- Sign of Hegar I and II.
- Piskacek sign.
- Goodell sign.
- Branxton Hicks contractions
4. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin.
The most reliable, fast and accessible probabilistic diagnostic method in the world.

It consists of the determination of a hormone in blood or urine of the hormone hCG, which is produced initially by the syncytiotrophoblast in a very early period of pregnancy, being detectable even at six days after ovulation.
This is the basis of home pregnancy tests.
As accurate as the reactivity of these hormones is to different tests, it is still considered a probable sign for two main reasons:
It is not the only hormone increased during pregnancy and, in addition, the alpha fractions of this hormone have a great deal of similarity with luteinizing hormones, follicle stimulating hormone and thyrotropin, so there is a certain degree of probable error in these tests.
Although it may show a true positive to pregnancy, it does not guarantee in any way the vitality of the fetus inside the uterus. Even if it is an abortion, this hormone would still be present 21 days after the curettage.
5. Signs of certainty
They are two in essence, which guarantee not only pregnancy, but also the vitality of the fetus. These consist of tests that demonstrate the presence of embryonic structures in women through ultrasound and other techniques.
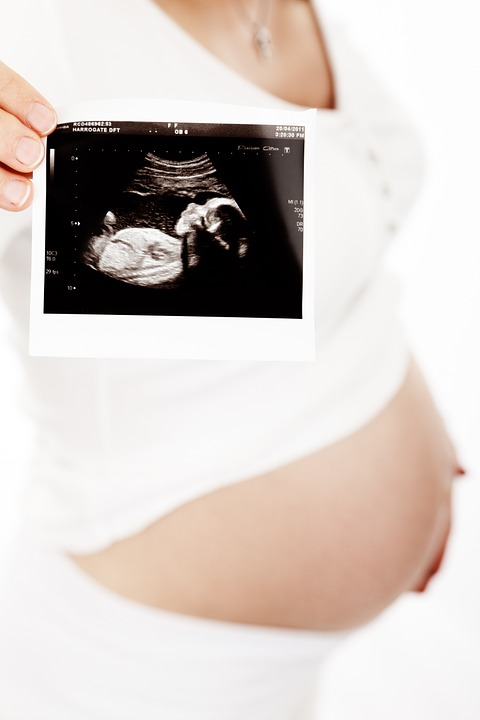
Doppler ultrasound, a special fetoscopy or auscultation, allows us to identify cardiac pulsations different from those of the mother, between 110 and 170 beats per minute, which will be evident since weeks 9 and 10.
Likewise, it will be possible to demonstrate embryonic structures (anatomical parts and yolk sac) after the second half of pregnancy, by bidimensional or three-dimensional transabdominal ultrasound.
It's for this reason that we can conclude that the most precocious and accurate test of pregnancy is ultrasound.
References of the original research in Spanish
DESCHAMPS, Y. P., 1979 Embarazo Maternidad en Adolescentes, Ed. Herder, Barcelona.
MCG Health System (octubre de 2007).«Glosario - Embarazo y Nacimiento». Health Information > Embarazo y Parto. Elgueta V, Patricia (2005).
«Diagnóstico del Embarazo». Universidad de Chile - Facultad de Medicina, Escuela de Obstetricia. Archivado desde el original el 22 de febrero de 2007.
Juan Aller y Gustavo Pagés - Fundación Aller para Estudios de Fertilidad (enero de 2007).
«Diagnóstico de Embarazo». Archivado desde el original el 23 de abril de 2007. Víctor M. Espinosa de los Reyes Sánchez; Sergio Azcárate Sánchez Santos.
«Cambios fisiológicos durante el embarazo». Programa de Actualización Continua para Ginecología y Obstetricia. libro 1 (Vigilancia prenatal): 18. Archivado desde el original el 16 de marzo de 2008.
KidsHealth.org (marzo de 2006). Calendario semanal del embarazo. Editado por Elana Pearl Ben-Joseph y The Nemours Foundation.
ALL IMAGES ARE EXTRACTED FROM PIXABAY.
THEY ARE FREE FOR COMMERCIAL AND CREATIVE USE.
Special thanks to @mike961 for the translation!
THEY ARE FREE FOR COMMERCIAL AND CREATIVE USE.
Congratulations @korotkov! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness and get one more award and increased upvotes!
Congratulations @korotkov! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!