There is no doubt that, in order to start a construction project, it is necessary to have a structural project that explains what the client wants to build, with what he has imagined, as well as his needs so that it can become a reality.

Source
So, in order to materialize these ideas, a set of elements are needed, which are:
1. Plans
The plans are an indispensable and fundamental instrument for any type of construction or project. They are the representation of a graphic, detailed and scaled form of a real object. In the execution of a project they help to standardize measures.
Types of plans:
- Survey plans
They show the main physical characteristics of the land (buildings, rivers, roads) as well as height information between the geographical features of the land (mountains, valleys, etc).
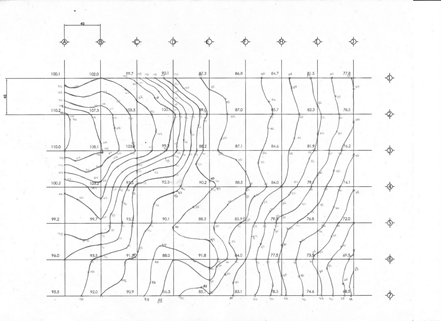
Source
- Foundation plans
These plans are fundamental because they show the foundations of a construction whose purpose is the support of the structure or construction, guaranteeing stability and avoiding damage to both structural and non-structural materials.
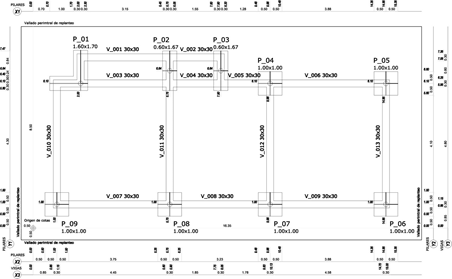
Source
- Facilities drawings
Electrical: This is the whole electrical installation of the construction such as: Connections, transformers, circuits, electrical boxes, points of light, plugs, etc.
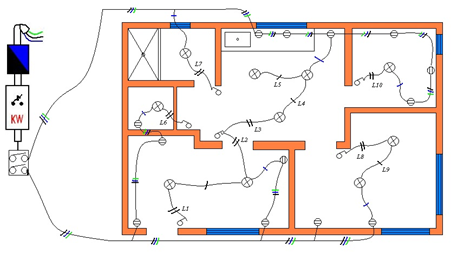
Source
Sanitary: In the sanitary installation the plumbing and sanitation plans of the building must be included: Supply and distribution of water (cold and hot), internal installations of sewage, external installations for rainwater and wastewater, distribution and location for sanitary devices and cooking.
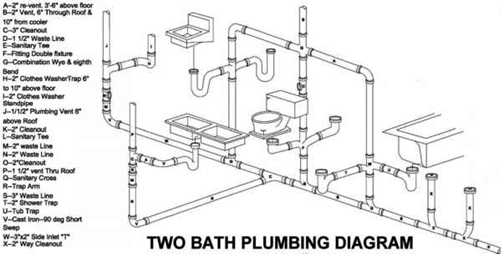
Source
Gas installation: This shows the gas installation of the building: stopcocks, vents, pressure, meters and connections.
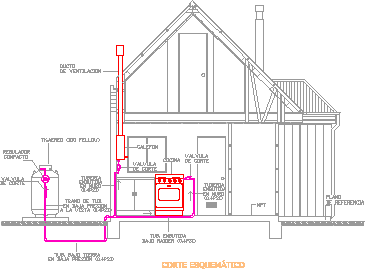
Source
- Cutting plans of sections
This represents a projection of the building or construction in vertical or horizontal direction. It is used to clarify or explain elements that are not sufficiently clear in the plans of floors and facades.
-Longitudinal section.
-Cross section.
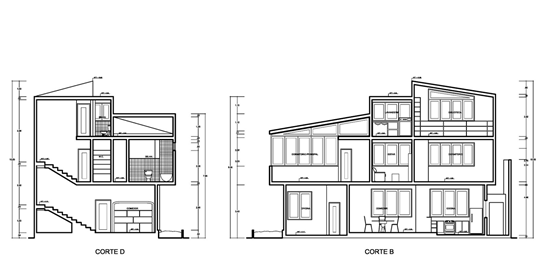
Source
- Plan of plants:
It represents the general distribution of the building, locations of the different spaces or environments, furnishing of the spaces, marking of areas, delimitation of spaces and carpentry (wood and metal).

Source
- Plan of finishes and details
In this plan are specified the finishes and details that each component of the building will take, materials used in floors, ceilings, doors, windows, furniture, stairs, exteriors; For example: paints, veneers, pavements, insulators, some hardware etc.
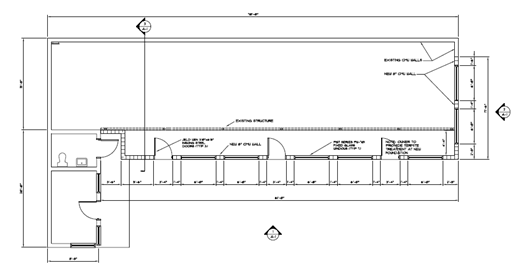
Source
2. Workshop plans
It is a plane of an object or mechanism to be manufactured that has all the necessary measurements and specifications to be able to manufacture said object. It explains in detail the diameter of the holes of the screws, with the clear indication of the form or method as they should be done, the class and diameter of the screws is also indicated. The shape and dimensions of the welded joints, preparation of edges, procedures and position of the weld, the characteristics of the material of contribution and order of execution if this is necessary. Indications of special methods or treatments that should be given to a particular item.
In addition, it contains the necessary dimensions to clearly define all the elements of the structure, which are generally given in mm (millimeters).
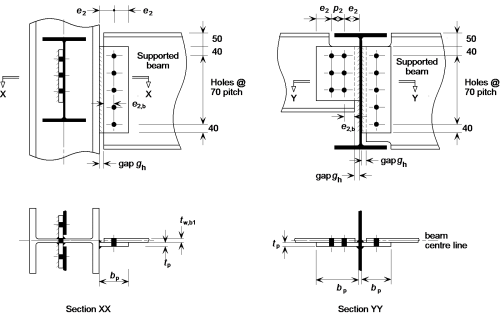
Source
3. Descriptive memory / calculation
It is the document where the final solution chosen is reported, giving ideas on: operation, materials to be used, approximate costs, the reasons for choosing that solution among all possible, etc.
The information must contain a calculation memory is as follows:
a) Structural calculations, actions and solicitations, and quality parameters of the materials.
b) Structural Descriptive Memory, which includes the sources of information used for the project and the scope of the responsibility assumed by the designer.
c) Objective and scope, system of units, regulations and codes used, technical specifications of the materials, soil properties, description of the structural system and foundations, design solicitations, load combinations, analysis and design considerations, analysis results and design.
4. Lists of materials
Analysis and detailed listing of the materials and equipment necessary to carry out a project.
5. Technical specifications
A technical specification is a document that defines a series of requirements that a product or assembly must meet or exceed.
6. Copy of the soil study
The study of soil allows to know the physical and mechanical characteristics of the soil, that is to say the humidity, the depth, the type of foundation most suitable for the work to be built and the settlements of the structure in relation to the weight that will support.

Source
What does background check and form check mean?
A form check consists of verifying whether or not there is an error related to the level of organization, legibility, concordance in the plans or any document. It occurs when in the background, in the matter, it is correct, but not in the form of posing it. Its respective control must be carried out. (Scale, format, lace, style of presentation, legibility, etc.)
A background check consists of verifying whether or not there is coherence in the content, concordance between what you want to do with those that you have captured, in other words, errors from the conception of the idea. It must be corrected as soon as possible. (Complete and correct information, correspondence between plans, technical specifications and construction aids)
Good post...useful information...
thank you!!!
maracuchitaaa éxitos
graaaaaaaaacias! saludos