
Before proceeding to today's discussion on our last post we talked about ecological population, its climax and characteristics, we all know succession is usually a process of progressive and orderly which can occur in a natural habitat like the sea shores and abandoned farmlands.if you missed out on the first post don't worry here is the link:
Outcome of succession
The following are the outcome or results of succession;
- Replacement by complex organisms which simpler organisms which start the succession are usually replaced by more complex ones in an evolutionary trend sequence.
- Changes in the physical environment changes in the physical environment are attained from the structural changes of the species and the activities in the community.Fast replacement as some species make conditions favorable for other, they in turn create unfavorable conditions for themselves, thereby increasing the process of replacement.
- Attainment of equilibrium point equilibrium point is attained through the colonization of the abandoned farmland by a wide variety of organisms that are just the same with a neighboring habitat. Climax community form the final stage the final outcome of succession is the climax or stable community.
Primary Succession starts on bare surfaces which have not previously borne vegetation. It usually starts with lower organisms and takes a longer time to reach a climax community. Examples of primary succession are found in ponds, vegetation on rocks, mangrove forest, estuary etc.
Factors which can give rise to primary bare surfaces include: Erosion & Extreme drought,Deposition of sand dunes & Volcanic ash, Mining or construction activities & Hurricanes, Landslides & Earthquakes, Emergence of bare surfaces & Thunderstorms
While Secondary Succession starts on already colonized surface. It may start with fairly complex organisms and it takes a shorter time or duration to reach a climax community. Examples of secondary succession are found in abandoned farmlands and grasslands.
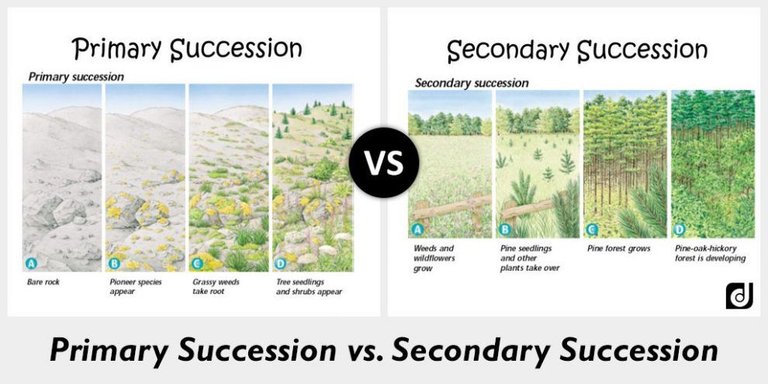
Differences between Primary and Secondary Succession
Primary Succession
- It starts on a bare surface,It is slower or it takes longer time to reach a climax communityand starts with lower organisms.
Secondary Succession
- It starts on already colonized surface,shorter time to reach a climax community,and with a fairly complex organisms.
Major communities in a plant Succession
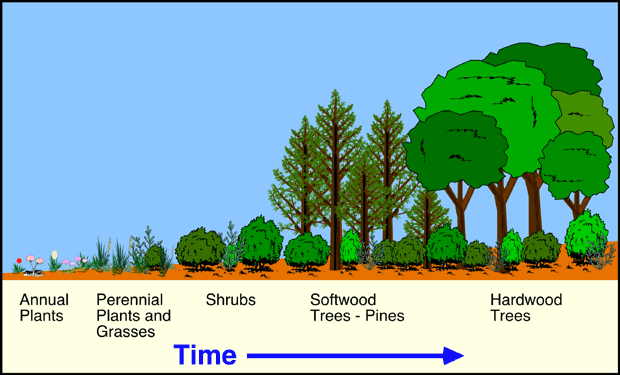
There are three major communities in a plant succession these include: Pioneers or early colonizers: Pioneers or early colonizers include the first group of plants in a succession. They are small, lower plants and highly drought-resistant organisms. They require minimum space, substratum or nutrients,. They are highly adapted to growing on bare surfaces, e.g. Algae, lichens, mosses and liverworts. Also the second one is Developmental, intermediate or transitory communities: These are series of communities which follow the pioneers with each succeeding communities more complex than the one it replaced. They are less opened than the pioneers. They have more diverse species with greater numbers of individuals per species. Examples are herbivorous plants such as talinum, Ageratum, Imperata cylindrical, Cyanotus and Sida acuta. And the last but the least is Climax community: This is the terminal plant succession or stable community which establishes equilibrium with ecological conditions within the locality. They are the most complex in the series of communities in a succession. It has the greatest species diversity and greater species population diversity. It has bigger life forms, e.g. trees and shrubs.
Process of Succession in Estuary (An Example of Primary Succession)
The process of succession can be observed or studied in lakes, ponds or estuary. An estuary is the mouth of a river where it enters the ocean or sea. The estuary has a high salt content and flooding due to tides that take place. The first groups of plants to colonize this salty and muddy habitat are the red mangroves. The red mangroves produce seedlings which germinate on the parent plant before dropping in the mud. They continue to grow in it resulting in the production of stilt roots. These roots fix them firmly into the, mud. The banks of the river mouth are raised with the accumulation of plants and animal remains and the mangrove trees develop strong roots. After this stage, the white mangroves trees replace the red mangroves. These white mangroves grow on the more stable and higher ground. The white mangrove trees now form open forest with some herbs which grow among its pneumatophores. Dead parts of plants and animals accumulate and the white mangrove give way collection of different trees, shrubs, herbs, grasses, ferns and epiphytes. As a result of increased accumulation of the remains of these floras, a normal forest fauna and flora soon emerge to give a stable forest community. The first group of animals that colonized the mangrove swamp is the flying insects, later followed by water birds which feed on them. Other animals include crabs, snails, worms etc. In the white mangrove and the forest proper, animals commonly found are squirrels, monkey’s rats and birds. The process of succession in estuary is illustrated below.
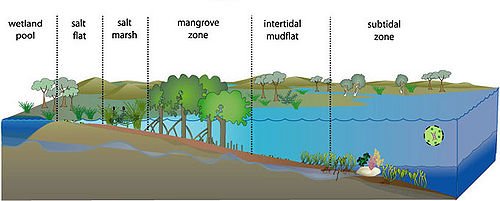
Plant community (Producers) Red mangrove White mangrove Grasses shrubs Tall trees (Forest)
Animal community(Consumers) Water birds, insects, worms, crabs Squirrels, rats, snakes, monkeys, birds
SUMMARY
Process of succession in Abandoned Farmland (An example of secondary succession) In an abandoned farmland, nutrients remain from the destruction of the old farm. The initial pioneers or colonizers are insect eggs, larvae, worms, seeds of plants, underground stems etc. The second stage of succession will now involve the germination and growth of more grasses. The hatching of eggs of insects and other species. The vegetation can now support more animals such as rats and other rodents, snakes and reptiles. The third stage succession results in the herbs being displace by shrubs and increases in the diversity of species. In the fourth stage, more trees grow and species diversity includes birds, snakes, reptiles, and monkeys etc. which live in different strata of the habitat. The population and activities of detritus feeders now increase and climax vegetation is reached. The animal community will now include herbivores, carnivores and detritus feeders which are involved in a complex food web.
Thank you for reading.
REFERENCES
Being A SteemStem Member