Hey Steemians,
Today, I’ll be sharing a whole new approach to kill or inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria. From centuries we have been suffering from several microbial infections and researchers are trying really hard to find a way to inhibit the pathogenic bacteria. All the antibiotics we prepare to inhibit them are again overcome by a new modified strain. Every time they develop resistance to these chemically produced molecules. Several other biological and chemical molecules are also being used to inhibit the growth of these pathogenic bacteria, but still there are many bacterial infections which are having a large impact on the human health and sometime being deadly too.
Image Source (Image is in Public Domain)
Nanotechnology has great promise to the human world and there are reports which claim to be effective on the bacterial infection. These are mainly either a metal nanoparticle, a surfactant made particle or a liposome based molecules but all these are either specific to a strain or a broad range. But some of the time they either are lacking the delivery method or the polymer used in the study is toxic to the host body or faces the destabilization of the molecule in the environment. These nanoscale particles of size around 100nm arrange themselves in layers and forming a molecule with combined property.
Nanocomposites
It’s a multiphase or multilayer material combined by the nano sized particle with an objective of producing a composite with combined properties of all the components. Nanocomposites are based on a principle of mixtures gives an averaged properties. The whole idea to develop such material is to utilize these nano sized building blocks to create a new material with an unmatched flexibility and physical strength. There are many polymer based, ceramic based, metal based nanocomposites are present. Nature has also these nanocomposites in the form of bones and the organism containing shells. These composites are not only used in the material study but also have a wide application in the biological sciences. There are many nanoparticles which have inherent property of inhibiting bacteria like silver nanoparticles, Carbon Nanotubes (CNT), Graphene nanotubes, tellurium nanoparticle etc. and on mixing the inhibitory proteins with these nanoparticle will enhance the activity. Different proteins or enzymes can be loaded into these nanocomposites with having property of the polymer and the protein. Most of time the polymer utilized is being used for the protection and covering of the protein molecule which makes it stable and active. There are enzymes from different source which are toxic to the microbial population or have a bactericidal property are can be used to form a composite with some nanoparticle to have these bactericidal property.Considering the health of the populations visiting the hospitals or workers working over there are prone to carry certain infections. These infections are mainly induced by the microbial populations growing in such conditions and producing the biofilm to adhere to the surfaces. These biofilm producing bacteria are really a threat and are responsible for causing number of infectious diseases. Better to use equipment’s which are made to be infection free, which won’t allow the bacteria to adhere to the surface and nanotechnology has a solution and advanced material for such purpose. Here is one study which shows the use of a bacteriophage enzyme with a silica based nanoparticle can act as an antimicrobial agent and inhibit the microbial population (1).
Image Source (Image is in Public Domain)
Immobilized endolysines can act Listericidal (A Case Study)
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram positive bacterium which is pathogenic in nature, causes listerosis. It is responsible for food borne disease. Listeria is facultative anaerobe and can survive and divide at 0 °C; as a result of this it can survive and flourish in cold stored foods. It was very first described by Murray as Bacterium monocytogenes in 1924 due to its characteristic monocytosis; later in 1927 it was renamed as Listeria monocytogenes by Harvey Pirie (2). Listeria infection in man was confirmed for the first time in 1929 by Nyfeldt, in sample taken from his three patients with an infection of mononucleosis-like disease (3).
Like other bacteria listeria is also resistant to antibiotic and disinfectant. To understand this characteristic of Listeria scientist have studied it in the presence of antibiotics. Kallipolitis group had done work on Listeria sRNA which regulates its virulence. Listeria always have a notice of its environment, a minor change in its environmental conditions and it adapts in accordance to the surrounding. Small RNA (sRNA) is known to help bacteria to adapt to new environment or for the virulence of pathogenic bacteria. These RNA molecules help listeria to combat the host immune response. Like for entering in the host Listeria makes use of protein LapB, but once it is inside the cell RNA down regulates its production which helps it to bypass host immune system. These RNA molecules also help Listeria to sustain in presence of antibiotics. Most of the antibiotics attack the cell membrane of bacteria, so when bacteria senses rupturing of membrane these sRNA molecules become active and stops the rupturing of membrane (4). Listeria is also resistant to disinfectants, Stephan group from University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna has shown that in dairy to maintain the pathogen free environment they used disinfectant but it was ineffective on Listeria. The disinfectant they used was benzalkonium chloride; they found that transposon Tn6188 was responsible for this tolerance against benzalkonium chloride (5). In one of my earlier post I have talked about phage therapy, so phages can be used to kill Listeria. Jonathan S. Dordick group from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute used enzyme from phages to make nanocomposites to fight against Listeria. They used Endolysin to kill Listeria.Endolysin are phage encoded enzymes that break down bacterial peptidoglycan at the terminal stage of the phage reproduction cycle.
Ply500 has been characterized as cell lytic enzyme against Listeria, it consists of enzymatically active domain (EAD) linked to a cell-wall-binding domain (CBD). This enzyme resembles a structure of chair in which one alpha helix and three antiparallel beta-strands makes the seat structure and two more alpha helix and another alpha helix together forms backrest. The enzymatic active domain is at N-terminal which acts on bacterial cell wall and cell-wall binding domain forms C-terminal; this part targets the enzyme specifically to its substrate in the bacterial cell wall envelope (6).
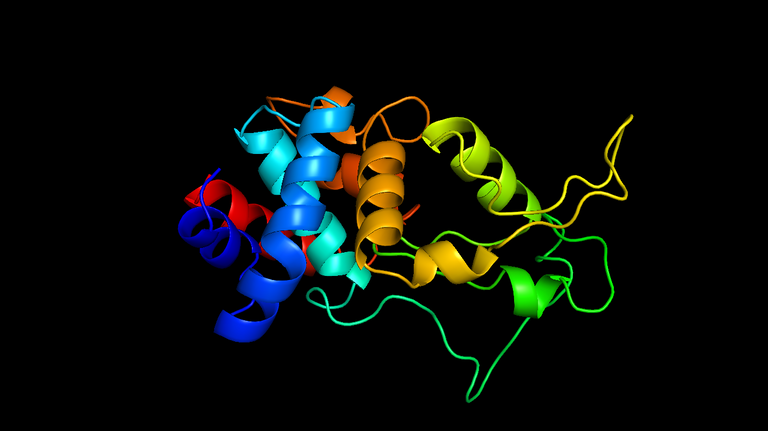
For the purpose of making it nanocomposites they conjugated Ply500 with silica nanoparticles, silica was used for this study as it marked as GRAS (Generally recognized as safe) by US FDA. In one of their earlier studied they have shown that protein attachment on curvy surface is more stable than smooth surface (7). So for this purpose they first functionalized the Silica nanoparticles using cyanide and methacrylate group. To check for the proper attachment of functional group on the nanoparticle they did titration with benzylamine to find the attachment. After functionalization, they attached protein with the silica nanoparticle. To form the sheet like structure there was need of polymerization, so to fulfill this condition they polymerized Ply500-SNP conjugates containing methacrylate group with HEMA and polyethylene glycol dimethylacrylate (PEGDMA), as cross linker, in presence of ammonium persulphate and TEMED as initiator.
Next to check the efficiency of this conjugate they carried out on more experiment. Readymade foods which are generally stored at low temperature to maintain its life gets infected Listeria or sometimes the machine or cold storage equipment gets contaminated because of Listeria. So for the study they used film of both pHEMA and Ply500-SNP and allowed the growth of culture for 48 hours. After 48 hours they found that no Listeria was found on PL500-SNP coating whereas cell growth was found on control that is pHEMA films.Another problem which they tried to solve in this paper was to develop a packaging material which can reduce Listeria attack during storing condition. For this study they thought of using starch as it is used in many packaging industry and sprayed on food. In their lab they constructed a fusion protein using mannose binding protein (MBP) and Ply500, but during experiment they found that due to large size of MBP it was causing steric hindrance which in proper attachment to the bacterial cell wall. To tackle this problem they linked MBP and Ply500 by using 10 amino acid sequences, after this they again studied the listericidal effect of this fusion protein compared with only MBP, the results showed that MBP-Ply500 fusion protein was also helpful in reducing listeria attack (8).
Conclusion
Nanocomposites shows a broad range of application from strengthening a material to providing it biomedical advantage and here I have tried to focus on a small part of it in the field of microbes. These composites can be used to solve some of the problem related to food storage and increasing the shelf life of stored food. For treatment of listerosis many antibiotics are being used but they are ineffective due to the defense mechanism of Listeria. So to kill them Endolysin are used coated on silica nanoparticles. And further to make a packaging material they used MBP to design a fusion protein and this fusion protein can be used in developing anti-listeria packaging material or can be used as spray or coated on food to increase its life. Despite of its success in the microbial field there are still lots of thing to be explore and enhance its function, like how the toxicity life can be enhance for the material.
References
Matharu et. al., 2018 Nanocomposites: Suitable Alternatives as Antimicrobial Agents.
Peterkin et. al., 1991 Listeria monocytogenes, a Food-Borne Pathogen. 55(3);476-511.
Kilinger et. al., 1996 Listeria monocytogenes and Listeric Infections. 30(2);1-74.
Asuri et. al., 2007 Enhanced stability of enzymes adsorbed onto nanoparticles. 7(4);1675-1678.
Solanki et. al., 2013 Enzyme-Based Listericidal Nanocomposites. 1584.
Hope you enjoyed reading it, Please upvote and follow my page for further reads on such topics. Feel free to comment.




Awesome example of antimicrobials that deviate away from traditional antibiotics. I'm guessing these kinds of nanoparticles still have a ways before they're routinely used for food storage, but the science is very cool and promising.
I can tell you, it's also an active area of research to prevent biofouling on membranes, particularly those used for desalination via reverse osmosis.
One of the most interesting ones is biomimetic and is based on the nanostructures found on dragonfly wings.
Yeah, they hold much more promises than this.
Thanks for the comment :)
yeah, certainly it is.......yeah, they are still to pass several checkpoints to be approved for the daily use as these particles are containing polymers.Thanks for the comment @tking77798
Another great read, @vinamra! It is certainly exciting to see how this develops to a broader appeal, and if it will end up being as good as we think it can be.
The Nanotechnology has so much for us.....
May be in the coming articles I'll be sharing more on these enzyme containing nanoparticles which are stimuli responsive.Thanks @valth
Cool, I'm looking forward to reading about it :)
Muy interesante el tema. Me pregunto ¿No mutaran las bacterias para desarrollar resistencia a este nuevo tipo de ataque? Saludos/Very interesting the subject. I wonder, will not the bacteria mutate to develop resistance to this new type of attack? Greetings.
Sí, estos nanocompuestos atacan la superficie y la enzima rompe la membrana celular, algo que los microbios no pueden evitar.
Gracias por el comentario
Hola @vinamra. Gracias por atender mi inquietud. Saludos.
Your article is very useful, silver nanoparticles have proven effective in controlling bacteria, and as I read earlier this technique has eliminated more than 630 species of bacteria, and according to a scientific study conducted by Miguel Jose Yacaman and researchers from the University of Texas; silver nanoparticles have proved effective in eliminating HIV-1 virus, so I wonder why this technique was not circulated to eliminate aids arround the world?
i have another question, To what extent does Listeria virus pose a risk to humans?
Thanks for the comment @benainouna
Well, I haven't heard of this. But I can tell you AIDS virus is not something which can be killed easily. As most of the viruses change or modify their envelope protein with new strains and as the AgNPs attacks the surface it can help but the coat protein is really tough to break through. I also have to see this not sure of treating HIV with nanoparticles. First of all, Listeria is a gram-positive bacteria and is mostly known to contaminate the food items, and its infections are disastrous.@vinamra thank you for answering, and about treating HIV They said they had experimented and were effective, but work and research were still going on. I have benefited greatly from your article and from your discussion, thank you very much and I will wait for your next articles. :)
Congratulations @vinamra! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP