
Who does not know this one star, Vy Canis Majoris Had occupied the position as the biggest star ever found. but now the VY star Canis Majoris shifts to the ninth position in the order of the biggest stars. The biggest star is currently held by UY Scuti.
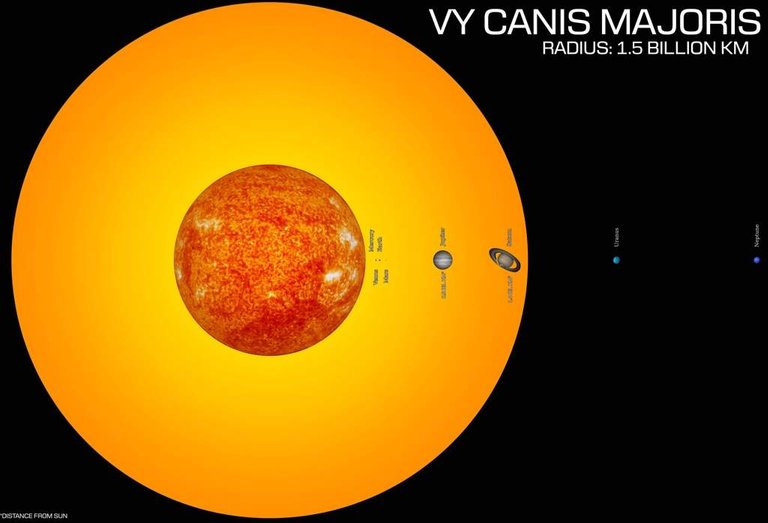
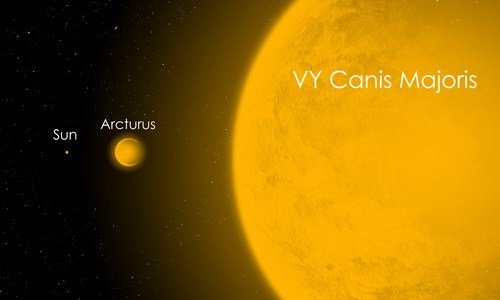
VY Canis Majoris (VY CMa) is a red Hypergiant star located in the constellation Canis Major. This star has radius of 1800 to 2100 times the radius of the Sun, (8.4-9.8 AU (astronomical unit), 1.5315 × 10 9 km, or 0.85 × 10 9 mi), VY CMa is one of the most radiant stars ever known. The star is located about 1.5 kiloparsec (4900 light years, 4.6 × 10 16 km, or 2.9 × 10 16 miles) from the earth. Unlike most other hypergiant stars with multiple star systems, VY CMa is a single star. VY CMa is categorized as a semi-regular variable star. VY CMa has an average density of 0.000005 to 0.000010 kg / m 3.
Professor Roberta M. Humphreys of the University of Minnesota estimates the CMY VY radius is 1800 to 2100 times the radius of the Sun. To illustrate, if the Sun is replaced by VY CMa, its radius can extend beyond the orbit of Saturn. Light takes more than 2.7 hours to travel around the VY CMa, compared to 14.5 seconds for the Sun. To fill the VY CMa volume, it takes 7 × 10 15 Earth.
If the Earth is represented by a ball with a diameter of 1 cm, the Sun is represented by a sphere of 109 cm in diameter, with a distance of between 117 meters. On this scale, VY Canis Majoris has a diameter of approximately 2.3 kilometers.
VY CMa has a surface temperature of about 3200 ° C (5800 F). The temperature of the sun is still hotter than this star which reaches 5505 ° C (9941 ° F). The measurement of the luminosity of these stars varies considerably, from 250,000 to 500,000 times more than the sun.
VY CMa is in the Milky Way galaxy, has been detected by astronomers currently undergoing a dramatic "weight loss", an event that preceded the end of the star's life: dying!
Astronomers from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) use the Very Large Telescope (VLT) to see the area around the VY star CMa and discover that each year this massive star loses mass to 30 Earth masses. They use the SPHERE instrument, which has the ability to direct imaging, in order to get detailed information about the material released by this dying star.
Hypergiant stars like VY CMa tend to lose material in the form of dust and gas on a large scale. The dust and gas are visible on the VY CMa image above, in the form of colorful nebula around the star. The nebula will continue to be created until an unavoidable hypernova explosion. Theoretically, the hypernova will cause a gamma-ray burst that can damage the contents of the nearest solar system (2-5 light years). However, the explosion of VY CMa is expected too far to affect Earth.
According to astronomers, this nebula is created from the starlight that spews out the dust, in the same way as the wind pushes the sail of the boat.
"A massive star with a short life," said Peter Scicluna, lead author of the scientific paper, published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. When these supermassive stars are close to death, they will lose a lot of mass.
Dust and gas ejected by stars like VY Canis Majoris play an important role in "recycling" in the Milky Way galaxy. This dust and gas will spread to the interstellar medium, becoming a new material that can create new stars and planets from the next generation.
Reference :
- http://www.rozenek.com/vy-canis-majoris-too-small-4u/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VY_Canis_Majoris
- http://www.cosmosup.com/hypergiant-red-star-vy-canis-majoris-is-going-to-die-soon/
- http://www.iflscience.com/space/dying-hypergiant-star-losing-30-earths-worth-mass-every-year/


Hi, I found some acronyms/abbreviations in this post. This is how they expand:
Get free upvotes your post https://mysteemup.club