[ESP]
¡Hola, comunidad de apasionados por la electrónica! 🚀
Hoy exploraremos un concepto clave en el mundo eléctrico y electrónico: la Ley de Potencia. Esta ley nos permite entender cómo se mide la energía utilizada en un circuito y cómo calcular el consumo de nuestros dispositivos. ¡Acompáñame en esta explicación! 📡⚙️

🔎 ¿Qué es la Potencia Eléctrica?
La potencia eléctrica (P) es la cantidad de energía que un circuito consume o genera en un determinado tiempo. Se mide en vatios (W) y nos indica cuánta energía se transforma en luz, calor o movimiento en un sistema eléctrico.
La fórmula básica de la Ley de Potencia es:
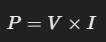
Donde:
🔹 P = Potencia en vatios (W)
🔹 V = Voltaje en voltios (V)
🔹 I = Corriente en amperios (A)
🔢 Ejemplo Práctico
Supongamos que tenemos un LED de 5V que consume 20mA de corriente. Para calcular la potencia consumida:
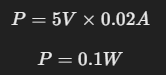
Este LED consume 0.1 vatios de potencia, lo que es una cantidad muy pequeña en comparación con, por ejemplo, una bombilla incandescente de 60W.
🔄 Relación con la Ley de Ohm
Si recordamos la Ley de Ohm:
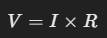
Podemos combinarla con la Ley de Potencia y obtener otras dos formas útiles:
1️⃣ Usando resistencia y corriente:
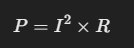
2️⃣ Usando resistencia y voltaje:
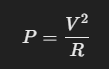
Estas fórmulas nos ayudan a calcular la potencia sin necesidad de conocer todos los valores del circuito.
🔥 Diferencia entre Potencia en Corriente Alterna y Corriente Continua
En corriente continua (CC), la potencia se calcula directamente con P = V × I.
En corriente alterna (CA), hay que considerar el factor de potencia (cos φ), ya que la corriente puede estar desfasada con respecto al voltaje. La fórmula completa es:
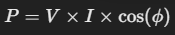
Esto es importante en sistemas eléctricos industriales, donde el factor de potencia influye en la eficiencia de los equipos.
🏗️ Aplicaciones de la Ley de Potencia
✔️ Dimensionamiento de fuentes de alimentación (evita sobrecargar la fuente).
✔️ Cálculo del consumo eléctrico (para saber cuánta energía usan nuestros dispositivos).
✔️ Diseño de circuitos de potencia (como reguladores de voltaje o sistemas de iluminación).
✔️ Optimización de eficiencia energética (evitar pérdidas innecesarias de energía).
📢 Conclusión
La Ley de Potencia es fundamental en la electrónica y electricidad, ya que nos permite calcular el consumo energético y diseñar sistemas eficientes. Saber cómo aplicarla nos ayuda a optimizar circuitos y reducir el desperdicio de energía.
💡 ¿Tienes dudas o quieres que haga un ejemplo con Arduino? ¡Déjamelo en los comentarios! 💬📲
🔋 ¿Qué otros conceptos eléctricos te gustaría explorar? ¡Házmelo saber y seguimos aprendiendo juntos! 🚀⚡
[ENG]
Hello, community of electronics enthusiasts! 🚀
Today we will explore a key concept in the electrical and electronic world: the Power Law. This law allows us to understand how the energy used in a circuit is measured and how to calculate the consumption of our devices. Join me in this explanation! 📡⚙️

🔎 What is Electrical Power?
Electrical power (P) is the amount of energy that a circuit consumes or generates in a given time. It is measured in watts (W) and tells us how much energy is transformed into light, heat or movement in an electrical system.
The basic formula for the Power Law is:
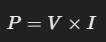
Where:
🔹 P = Power in watts (W)
🔹 V = Voltage in volts (V)
🔹 I = Current in amps (A)
🔢 Practical Example
Suppose we have a 5V LED that consumes 20mA of current. To calculate the power consumption:
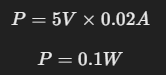
This LED consumes 0.1 watts of power, which is a very small amount compared to, for example, a 60W incandescent bulb.
🔄 Relationship with Ohm's Law
If we remember Ohm's Law:
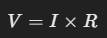
We can combine it with the Power Law and obtain two other useful forms:
1️⃣ Using resistance and current:
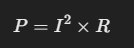
2️⃣ Using resistance and voltage:
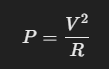
These formulas help us calculate the power without needing to know all the circuit values.
🔥 Difference between Power in Alternating Current and Direct Current
In direct current (DC), the power is calculated directly with P = V × I.
In alternating current (AC), the power factor (cos φ) must be considered, since the current may be out of phase with respect to the voltage. The full formula is:
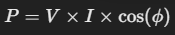
This is important in industrial electrical systems, where the power factor influences the efficiency of the equipment.
🏗️ Applications of the Power Law
✔️ Sizing of power supplies (avoid overloading the source).
✔️ Calculating electrical consumption (to know how much energy our devices use).
✔️ Designing power circuits (such as voltage regulators or lighting systems).
✔️ Optimizing energy efficiency (avoiding unnecessary energy losses).
📢 Conclusion
The Power Law is fundamental in electronics and electricity, as it allows us to calculate energy consumption and design efficient systems. Knowing how to apply it helps us optimize circuits and reduce energy waste.
💡 Do you have questions or want me to do an example with Arduino? Leave it in the comments! 💬📲
🔋 What other electrical concepts would you like to explore? Let me know and we'll keep learning together! 🚀⚡