Cloning is the procedure of creating the exact replica of an organism. You might want to pause and think that this definition is synonymous with reproduction. Let me specify the definition then: Cloning is the procedure of creating the precise GENETIC replica of an organism. In the sense that the original organism and the clone, share exactly the same features. No distinctions whatsoever.
This process occurs naturally in most cases. A clone is an organism that has the exact gene copy of another organism. Common examples are Identical twins and triplets, who sometimes, are clones of themselves or their parents. When you take out the leaf of a plant and plant it somewhere else it grows to the exact same copy of the mother plant.
FACTORY MANUAL
Interestingly, our body is like a giant robot with billions of workers, named Cells, following a set of instructional manuals called DNA - Deoxyribonucleic Acid. This Acid, as the name implies, is found in the nucleus of the cell and is the major factor in any cloning process. Natural cloning is not a new thing in the world as the DNA has, often times created perfect clones such as the case with the Identical twins or triplets. Note, that not all Identical twins are clones but all clones are Identical. Some twins may be identical in the looks department but end up not being clones at all. This is because there may be certain features that one possesses that the other does not.
Not all identical twins are clones but all clones are identical
For example, let’s say a woman is delivered of Identical twins. Initially, both babies look strikingly alike, cry alike etc. but as they grow up they start having slightly different features; One’s voice is deeper than the other, one has a broader chest while the other is not so buff, One’s eye color is chestnut while the other has hazelnut splashed with blue, the list could go on. These little variations are what differentiate them from clones. This is due to the simple fact that clones have no variations or differences whatsoever.
DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID - DNA
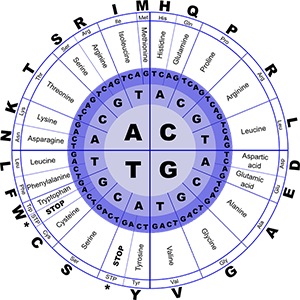
The DNA is coded information found in almost every species of living things. It has the ability to copy itself; this explains why we are not so different from our predecessors. The DNA of an organism can be located in two places, mainly in the nucleus and then in the mitochondria.
Coded information in the DNA is made up of four distinct chemical bases. These are;
Adenine
Guanine
Cytosine
Thymine
The DNA of a human being is 99% similar to the DNA of another human being but is different compared to another animal’s own DNA. Just about 1% of the information in the DNA is responsible for the different physical properties that distinguish one human being from another. These differences are just a result of the various arrangements of the chemicals listed above. These four chemical bases are arranged in a certain way that is different from the DNA arrangement of other living things. Similar to the way alphabetical letters combine in different pairs to form different words and sentences – U.S. National Library of Medicine.
For a species to continue to survive their DNA must be copied by their offspring’s - and so it is because living things must survive and reproduce. It is observed to happen in bacteria, insects, plants and animals as they reproduce asexually.
GENES
Genes are a series of different DNA arrangements that act as instructions for the creation of proteins in the body. It is the basic unit of hereditary replication. What I mean is, the smallest pair of DNA structure that can be passed on to the offspring is called a gene.
Every offspring always have two pairs of each gene this is because they inherit one of them from both their parents. Just as it is with DNA, most of the genes in a living organism are 99%. The same when compared with another living organism from the same species. Just 1% is found to have little difference in the serial arrangement of their DNA base-chemicals.
DOLLY WAS A LITTLE LAMB
After years of thorough research and experiments in Roslin Institute in Edinburg, the United Kingdom, the first mammalian animal ever to be successfully cloned was born and she was named Dolly-that was in the year 1996. Unfortunately, Cloned animals age faster and Dolly died six years after she was given birth to. She died in 2003 and is presently in the National Museums of England, Edinburg. Since then, several other mammals and plants have been cloned.

"Dolly face closeup" by Toni Barros, from São Paulo, Brasil, with Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license.
Dolly was formed by taking a cell from the udder of her six-year-old mother and having the DNA of another animal, of the same species, injected into it. Basically what was done in the lab was that: the scientists took the egg cell of an organism, in this case, Dolly’s mother, and after removing the DNA from that cell, implanted the DNA from a totally different egg cell of another animal into the now DNA-free egg cell of Dolly’s mother. Note that the process of first emptying the former egg cell of its original DNA is done carefully with a very thin needle before the process of implantation begins. They carefully extracted the DNA copy of the animal that was to be cloned and placed it in the DNA-free egg cell previously collected. The last process is incubation and this could be natural i.e. biological birth or artificial i.e. incubation. However, in the case of Dolly, the egg cell was inserted into the surrogate sheep’s ovum.
Biology deals with all the complexities of living things; life is a big deal and scientists have a lot of complexities to flip through.
The success of dolly was due to a long try of 434 experiments done by profound scientists. At that last experiment the embryo formed successfully and was then inserted into the ovum of a sheep that underwent normal pregnancy. The project was led by a two British scientists Keith Campbell Sir Ian Wilmut. Dolly lived in Scotland all her life until she died in 2003 at the age of six. Born in July 1996, her existence was a secret until 22 February 1997, when she was introduced to the world. The first animal we cloned where frogs. Don’t get confused with the last statement; Dolly was the first MAMMAL to be cloned whereas frogs where the first ANIMALS to be cloned.
Cloning can bring a lot of benefits to medical science and what’s so fascinating to write about is that; modern technology can be used to create these cloning processes in the lab. This means that cloning is not restricted to sexual reproduction alone. It can be done asexually.
The idea of cloning is therefore not a new phenomenon in our Biological Sciences. Scientists have been cloning living things for a long time. Although it is right to say that we do not know a lot but we do know some things, and what we do know is what we have found a way to uses for our benefit - like drug testing.
The modern cloning technology has allowed the cloning of animals; an Asian carp was successfully cloned in 1963, the mouse called Cumulina, 1997, Noto and Kaga two cloned cows in Japan during the ‘90s. Then there was Mira, a goat cloned in 1998, a family of pigs, the monkey – Tetris, the cat, the rat, Prometea the horse, etc.
Cell Cloning
To understand cell cloning we need to know more about cells. The cell (from a Latin word meaning small room) is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently.
Cells carry out the instructions from the information stored in the DNA. They are responsible for the shape of our physical form. Every single detail relating to how you will look is carried out by your cells. The cells help to break down food eaten by you; it does this to convert food nutrients into energy and other things useful to it.
Cell cloning is the process of producing multiple copies of cells from a single mother cell. We are all made up of cells, bits and bits of tiny little living organisms. Layers upon layers of trillions and trillions of them make up your entire body. This means that if we can replicate cells, we can replicate our body; all this can be done without reproduction.
HUMAN CLONING

"Cloning diagram english" coverted to SVG by Belkorin, modified and translated by Wikibob with Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
Reproductive cloning is probably the most popular type of cloning. The reason I think it is the most popular type of cloning is that we see this type of cloning every day, introduced by nature in instances where we have identical twins or children who look like replicas of their parents or just one of the parents. This is not the type of cloning that bothers people so much. We interpret the term ‘’human cloning’’ not as the reproduction of genes through natural processes but as the artificial reproduction of human cells and tissue to recreate the features of another human being or organ.
THERAPEUTIC CLONING
This type of cloning has nothing to do with recreating a human being from scratch as most people imagine. Instead, it majorly involves the process of recreating specific cells in other to make someone feel or look better. The key point is to know that they are creating an embryo (the very first rudiments of biological life in humans) and using it to recreate cells. To perform a therapeutic cloning, the method used is called: Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT).
Here’s how it works
What happens is that they take the cell from the body of a person - every cell has a nucleus, this is where the DNA instructions stay - and extract the nucleus with the DNA in it and place it inside an empty egg cell. It then becomes an embryo. This is the hardest part. Sometimes, the scientists go through hundreds of failed experiments before they finally succeed in forming an embryo. The last process is done by releasing shock charges until the embryo starts to grow. You should note that all of these things are done in extremely controlled environments.
The embryo is the key! Every organ that we have as biological agents came from the embryo. It is like a printer because it contains stem cells. These stem cells are cells which can grow to any other type of cell. This explains how we can have different organs in our body instead of just one whole organ. This can be used in the recreation of organs for transplant and replacing of dead cells.
STEM CELLS
Stem cells are very important in the lives of biological organisms. This is because they have the ability to become any other organ and that is why they are the pillars of human cloning.
Stem cells are gotten from two main sources which include:
⦁ Embryonic stem cells
⦁ Somatic stem cells
Embryonic Stem
Embryonic stem cells are cells that appear few days after the embryo has been formed. These cells give rise to every organ in a developing organism. This means they are the stem cells responsible for development in the body. The embryo is the first stage of life for a fetus. This knowledge has become the bedrock of somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Somatic stem
Somatic stem cells or adult stem cells are also very important for biological life. Both stem cells have pretty much the same abilities but are found in different locations and at different times inside the body. However, this stem cell handles the repair of damaged organs and helps in processes like skin repair from an injury or burn.
REFLECTIONS
Having thoroughly understood the concept of cloning, one might begin to ask; ‘Could this be the long sought-after an experience where you actually get to converse with what is technically yourself? And literally, see yourself from ‘’another’s’’ eyes?’
Given time, and the go-ahead to continue with the Somatic stem research on human cloning, this experience might just come true!
Thank you for reading!

REFERENCES:
- Wikipedia | Cloning
- Interesting Engineering | Cloned
- BIO | Therapeutic Cloning
- Wikipedia | Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer



Being A SteemStem Member
Remember that even if the DNA sequence are identical in a cloned animals (or people) it will not necessarily lead to identical phenotypes. This is due to environmental or epigenetic effects. This is why identical twins with the same genotype are not really identical. Another great example is CC (carbon copy) the cloned cat and her "clone" (Rainbow) shown here in these pictures (right and left respectively) and CC and her surrogate mother below.
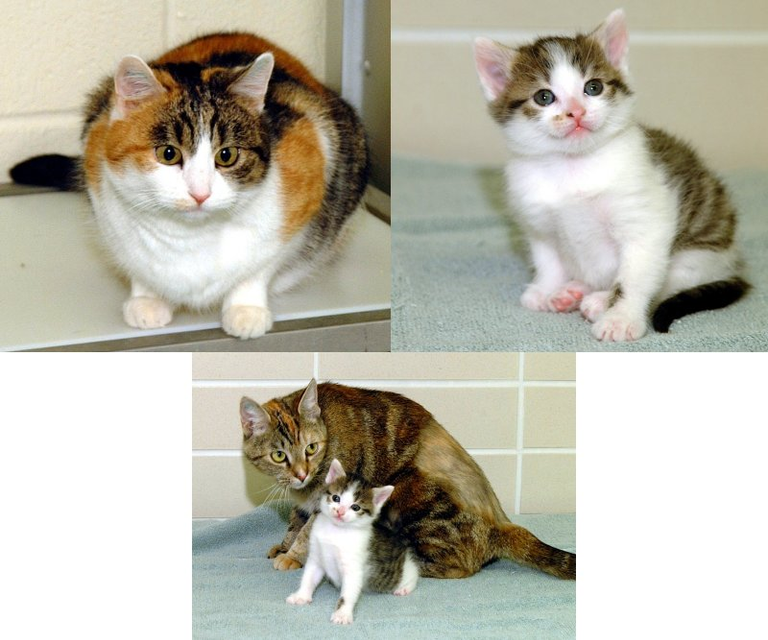

image source
As you can see CC the cloned cat looks quite different from her clone. Although the genetic material is identical in each cat, the X chromosomes (which have the coat colour genes) are inactivated randomly giving rise to the difference in appearance.
Love genetics!
Cheers!
ian
This is phenomenal
You're absolutely right, phenotypes can be influenced be certain environmental conditions.
This case is very interesting, I'll definitely look into it. Thanks for sharing.
I am really looking forward to transferring my consciousness to another young clone of me. Just so I can live as long as I want when this body of me gets too old to sustain me. Muhahahaha!!!!
That concept has being severely explore in Hollywood movies, but in reality no known cases has been recorded.
But hey, it could be possible before that body of yours get old
I worry that there will be people of exactly the same features and they would not be differentiated from each other. What would happen then? BTW an excellent article by you
There are already people of the very similar features - twins, and a way of differentiation is names. Plus they tend to have different personalities. I'd like to think that will be similar to human clones
I see a certain evil in this piece of technology.!!
Evil is largely dependent on the context. Is anyone getting hurt with this technology - no, will the technology save lives - certainly yes...
Where is the evil in that?
You may need to double check your pictures, they aren't CC0 (dolly is CC2.0, cloning diagram is CC3.0)
I will give an example attribution for the dolly photo:
"Dolly face closeup" by Toni Barros, from São Paulo, Brasil, with Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license.
To copy this attribution I have it here:
"<a href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Dolly_face_closeup.jpg">Dolly face closeup</a>" by <a href="https://www.flickr.com/people/12793495@N05">Toni Barros, from São Paulo, Brasil,</a> with Creative Commons</a> <a href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/deed.en">Attribution-Share Alike 2.0 Generic license.</a>"[image name with link to source]" by [author with link to author] with [license and link to license]
Thanks for the feedback,
Much appreciated
One or more of your photos is breaking some form of copyright or it is not sourced, whether it be that the photos require proper attribution or are licensed in such a way that they are not free to use. For more information, check out this post here on steemstem copyright standards.
Sincerely,
@kryzsec
I watched a documentary where they cloned a horse, it wasn't exactly the same, they had several phenotype differences and also different personalities which were developed according to their breeding. At this moment, the "perfect" cloning is not yet available, but we are heading to the future, and it will be very helpful to clone animals. Also in the future, scientists are expecting to "recreate" people that already died by using their DNA, this sounds very crazy, but maybe we will be able to see Michael Jackson dancing thriller again in some years.
You're absolutely right, the 'perfect' clones are not yet available, genetics is still advancing.
Now I don't know how I feel about recreating dead people from their DNA, it kinda sounds like zombification. Even if it'll all goes according to plan, seeing Michael Jackson again, will create a whole range of emotional responses from people. Many won't be thrilled.
But it will be great to see how things play out at the end.