Good day to my dear steemians, thanks for visiting my blog, it is my pleasure to express my observation on farm animals today, I observed that animals found on the farm were healthy while some were unhealthy. I began to think what can lead to the ones that unhealthy or illness and discovered that some of these animals were infected by microorganisms like bacteria, parasites, virus, fungi etc.
Below are some of the questions, what is a pest?, What is diseases?, What are factors that cause livestock diseases?, What is the Mode of Transmission of Farm Animals Diseases?, What are the Symptoms of Farm Animals Diseases?. Don’t be disturbed, all these questions will be discussed below.
Pest and Diseases of livestock are very important economic factors in livestock development and production. They can cause ill-health and reduce productivity in farm animals. Gains in any animal production venture depend on how far these pests and diseases are prevented or controlled. With a good understanding of some of the common pests and diseases of farm animals, it is possible to prevent or control their occurrences and increase the productivity of farm animals.
What is pest?
A pest or parasite is an organism that lives on another without conferring any gain or advantage on its host. They live on and obtain their food or nutrients requirements from the body tissues of another living organism usually referred to as the HOST.
What is diseases?
A disease is defined as any change in the normal function or well-being of farm animals caused by another organism. It is an illness, unhealthy or abnormal condition in the body of farm animals. A disease is any impairment of normal body functioning that is impairment of the normal State of health of the body of a man, animal or even plant. A disease can be infectious or contagious.
What are the Classification of Livestock Diseases?
On the basis of factors that cause livestock diseases, the following types of diseases are widely recognized.
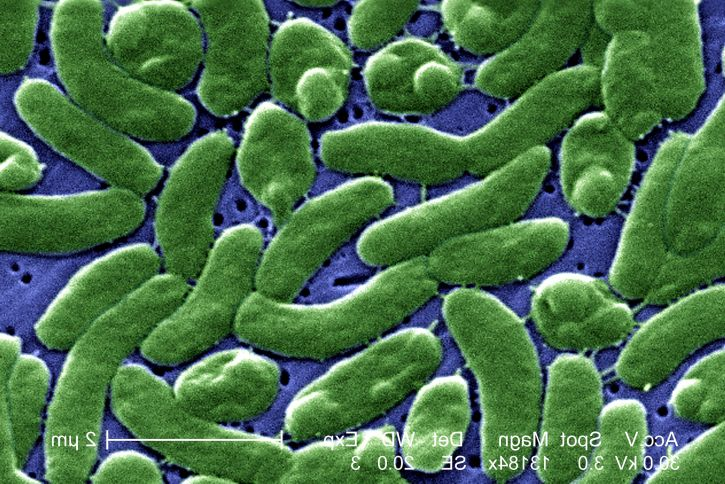image credit:pixnio.com:])
[: Pixnio.com under CCO](https://pixnio.com/science/microscopy-images/vibrio-related-diseases/depicts-a-grouping-of-vibrio-vulnificus-bacteria)
- Bacteria Diseases
These are diseases caused by bacteria. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms ranging from 0.002mm to 0.005mm in diameter. They are found virtually everywhere. Examples of bacterial diseases of farm animals include anthrax, mastitis, brucellosis and contagious abortion in ruminants, pigs etc.
2.Viral Diseases
These are diseases caused by viruses. Viruses are extremely small microorganisms which can survive only inside living cells. They are much smaller than bacteria. Examples of viral diseases of livestock are foot and mouth diseases, Newcastle diseases and birth flu.
3.Fungi Diseases
These are diseases caused by fungi. Fungi are lower plants which do not contain chlorophyll. They reproduce by spores and live by absorbing nutrients from organic matter. Examples of fungi diseases are ringworm and brooder pneumonia.
4.Metazoan Diseases
Diseases caused by parasites are known as metazoan diseases. Those parasites which live externally on their hosts are called Ectoparasites. Examples are live lice, ticks, and mites. Those which live internally in their hosts are called Endoparasitesare liver flukes, roundworms, and tapeworms.
5.Protozoan Diseases
These are diseases caused by a protozoan. The protozoan is a single-called majorly microscopic and mostly water-dwelling organisms which live independently or on colonies. They feed on organic compounds. Examples of protozoa diseases of livestock are trypanosomiasis, babesiosis, and coccidiosis.
What is the Mode of Transmission of Farm Animals Diseases?
There is some common mode of transmission of disease-causing organisms among farm animals. These include;
Contact between infected and non- infected animals.
Discharges and fluids from infected animals.
Contamination of feed and water with the pathogen of the disease by infected animals.
Saliva droplets from infected animals.
Air-borne diseases
Insect vectors such as tsetse flies that transmit trypanosomes, ticks and mites.
image credit:pixnio.com:])
[: Pixnio.com under CCO](http://www.whiteman.af.mil/News/Features/Display/Article/325776/keeping-stray-animals-to-a-minimum/)
What are the Symptoms of Farm Animals Diseases?
The Symptoms are the signs or indications of the presence of an abnormal condition in an animal. Animals infected with a disease usually show some specific symptoms which can be observed through abnormal changes in the functioning of their body. For example, malaria, typhoid etc.
The following sign is indications that an animal is sick:
There may be a loss of appetite and reduced feed utilization.
Water may be running down from its nose, mouth, or eyes.
There may be swellings on some parts of the body.
The Rise in body temperature (high fever).
Loss of hair from the animal body.
Loss of weight.
Stained blood.
Enlarge udder
Abortion
Death.
What are the Effect of Disease on Farm Animals.?
The effect of diseases on farm Animals include the following;
1.Loss of Appetites: Disease condition in farm animals can cause loss of appetite and consequently reduced feed intake.
2.Loss of body weight: The low feed intake due to lack of appetite can result in loss of body weight in sick farm animals.
3.Reduced Productivity: Diseases and pests can affect the growth, development, and health of farm animals. This will result in substantial reduction in the quantity and quality of milk, egg, meat, and other products obtained from such diseased animals.
4.Death of Animals: The presence of disease often leads to the death of farm animals. Economic losses as a result of high rate of mortality could be severe. E.g, Gumboro disease outbreak leads to loss of thousands of young chicks in a large poultry farm.
5.Endangering Human Health: Disease which afflicts livestock can indirectly endanger the health of human being. This is because disease organisms can be transmitted through animal product meant for human consumption. For examples, Trichian worm (Trichinella spiralis) can live in pig and certain others animals.
Someone eating improperly cooked pork infected with this worm can consume the larva which will later develop into the adult worm in the person. The worms will negatively affect the person’s health.
- Disease and pest control is a key consideration in the husbandry of animals and the management of livestock operations. This control consumes resources in terms of time and money which could have been better employed.
CONCLUSION: The pest is a wide range of diseases or vectors that affect the well being of animals. Pest and Diseases are very important economic factors in livestock development and production. The control of such diseases can the reduce their occurrences and increase the productivity of farm animals.
References
image credit:pixnio.com:])
image credit:pixnio.com:])