Structure of Bacterial cell
A bacterial cell has many components.Some of these are external and others are internal to the cell wall.Capsules, slime layer, flagella and pilli are the external components.Some structures are present only in certain species.
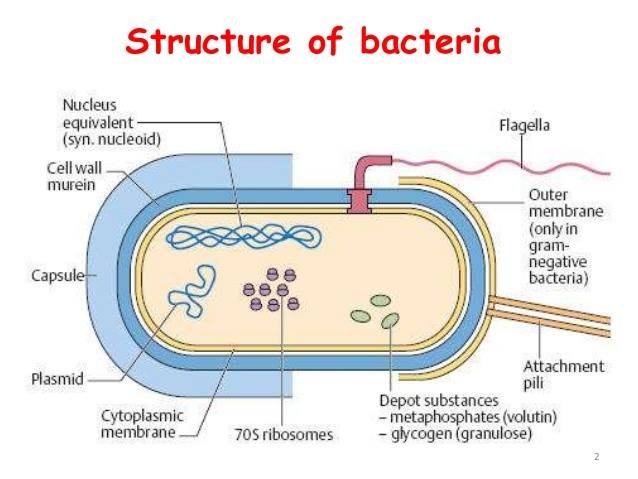
- Capsule and Slime layer
secreted by the cell wall of the bacteria.In some cases this layer may diffuse and known as slime layer.The capsules are made of polysaccharides while a few capsules are polypeptides.The capsule has a glue-like nature that help the bacteria to adhere to their substrate or unite to form colonies.It also provide protection against antibiotics. - Flagella
The organ of locomotion in bacteria are flagella.These are hair-like, helical cytoplasmic appendages.The flagella may be present at one or both ends of the bacterial cell and in some cases they are present along the sides or all around the bacterium. - Pilli
Pilli are also present on the cell surface of the bacteria.These are present in non-motile species.These are hollow, filamentous and rod like known as pilli or fimbriae.These are made by a protein which is called pillin.They are involved in attachment from cell to cell.They are also involved in mating during sexual reproduction. - The Cell Wall
Beneath the capsule cell wall is present.It is a rigid structure that gives shape to the cell.The cell wall is necessary for bacterial growth and development.Without cell wall a cell can’t grow and its division is not occurs. - Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria
The bacteria are divided into two forms on the basis of cell wall characteristics.These are Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.Gram-positive bacteria that can not be stained with Gram’s stain.While the Gram-negative bacteria that do not stain with Gram’s stain.They are differentiated on the basis of cell wall.The cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria are thinner than the Gram-positive bacteria.The composition of both almost similar.They consists of an insoluble, porous network formed of peptidoglycan, also called murein.It is a sac-like macromolecules consisting of parallel polysaccharide chain cross-linked in a regular fashion by short peptidoglycans in their cell walls than Gram-negative bacteria.In gram-negayive bacteria, the murein layer is coated on the outside wiyh a smooth, soft lipid layer which protect them against antibacterial enzymes(lysozyme). - Cytoplasmic Membrane
It is present beneath the cell wall and surrounds the living matter of the bacterial cell.It is semi-permeable membrane and composed of phospholipid about 20 to 30 percent and protein is about 60 to 70 percent.The phospholipids form a bilayer in which most proteins are embedded.It also involve in ATP production and attachment for the bacterial DNA. - Specialized Membrane
These are the infoldings that form complex internal structures and also increase its surface area.Two important specialized membranes which are given below.
(a) .Mesosomes
These are cell surface membrane infoldings which are associated with DNA during cell division, and also involved during the separation of the daughter cell of DNA after the replication and form new cell wall between the daughter cells.
(b)Photosynthetic Membranes
Some bacteria are able to produce or prepare their own food by photosynthesis due to the presence of photosynthetic pigments.In photosynthetic bacteria a tubular or sheet-like infoldings are produced by cytoplasmic membrane. Thses are resemble thylakoids in cyanobacteria(Blue green algae).The pigment present in the bacteria is known as bacteriochlorophyll.These are sites of photosynthesis. - The Cytoplasm
The cell material bounded by the cytoplasmic membrane which is called cytoplasm.It can be divided into two parts, a liquid part rich in nuclear material known as cytosol and a part rich in proteins called ribosomes.
(a) Cytosol
The portion of cytoplasm rich in nuclear material , is cytosol.It contains concentrated solution of inorganic acids, proteins, peptides, nitrogenous bases, amino acids, vitamins, enzymes, coenzymes which provides a chemical environment for metabolic and cellular activities.
(b)Ribosomes
Ribosomes are basically involved in the formation of proteins.These are the RNA-proteins bodies that lie freely in the cytoplasm mostly.Each ribosome made of two subunits, a 50S and a 30S subunit formed of equal amount of RNA and protein.They are smaller in size than the ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells and sediment at 70 Svedberg units(70S).
(C)Nucleoid-Bacterial Chromosomes
The bacterial chromosomes consists of DNA molecule formed of about 5*106 base pairs and about 1mm in length.A small portion of proteins is associated with it.The bacterial chromosome is primitive and usually referred as nucleoid.
In most bacteria, the DNA is concentrated as a mass of fibers and the region of the cytoplasm containing it stains less than surrounding cytoplasm.It is called nucleoid region or nuclear body.In Escherichia coli, thenbacterial chromosome is in the form of a ring of double-straded DNA molecule. - Plasmids
Plasmids are extra chromosomal circular DNA molecules.Ther are much smaller rings of DNA.Each plasmid consists of few genes and is capable of self-replicating independent of main chromosome.There are certain palsmids which provide protection to cell against antibiotics or disinfectants.They produce enzymes which destroy these substances.Some help in cleaning oil oil spills and producing protein from petroleum.
There are some plasmids that are capable of integrating into the bacterial DNA chromosome, they are known as episomes. - Spores and Cysts
Some bacteria produce resistant spores around their bodies either within the cell called as endospores and external to cell known as exospores, for example in Bacillus and clostridium spp.These can provide protection against heat, desiccation and radiation and help to overcome unfavourable growth conditions.When the condition become favourable, the spores germinate to form new cell.
In some bacteria, for example Azotobacter, whole cell develops into a thick-waleed resistant bidy called cyst.
11.Gas Vacuole
Some aquatic bacteria form gas vacuoles that provide buoyancy.These are hollow, rigid cylinders with a protein boundary impermeable to water, however dissolved gases can penetrate the boundary.
nice information are you a doctor???
please vote and share
yes
Congratulations @mameen745! You have completed the following achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
SteemitBoard World Cup Contest - Russia vs Croatia
Participate in the SteemitBoard World Cup Contest!
Collect World Cup badges and win free SBD
Support the Gold Sponsors of the contest: @good-karma and @lukestokes