Geographic Information System (GIS) connects Geography with data. A geographic information system is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographical data. Rooted in the science of geography, GIS integrates many types of data. It analyzes spatial location and organizes layers of information into visualizations using maps and 3D scenes.
Geographic Information System comes down to just 4 simple ideas:
- Create geographic data
- Manage it.
- Analyze it.
- Display it on a map.
Types of GIS
There are two basic types of GIS data:
- Raster
- Vector
Raster Data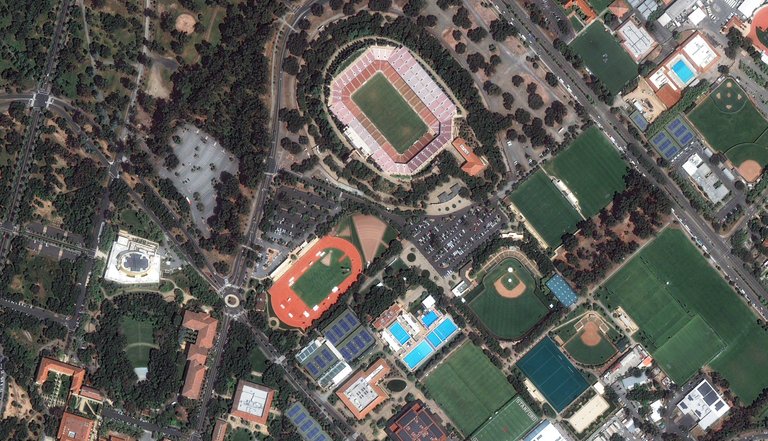 [Image Source]
[Image Source]
Raster is called imagery data, like satellite imagery. Satellites orbit the planet over and over taking photos as they cross the surface and send the pictures back down to earth to analyze. We also use airplanes, helicopters and drones to get a closer look at things like land cover and elevation.
Vector Data
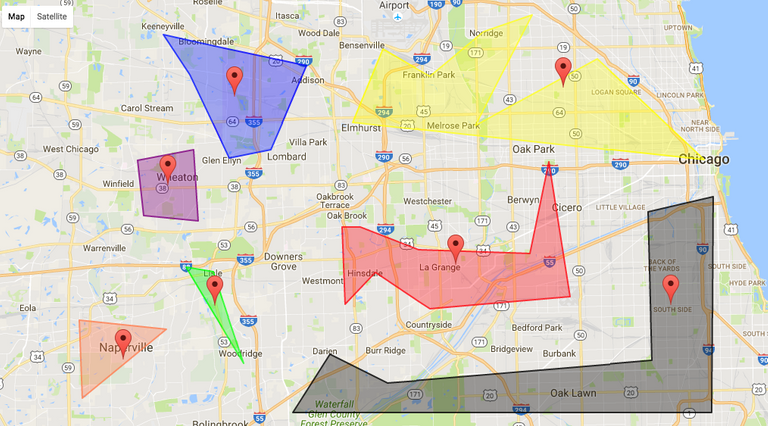 [Image Source]
[Image Source]
Vector data about people, places, parks, zoos any information with a latitude, longitude, street address or even zip code can be mapped and analyzed using points line and polygons and GIS tools.
Uses of GIS
GIS benefits organizations of all sizes and in almost every industry. GIS can be used as tool in both problem solving and decision making processes, as well as for visualization of data in a spatial environment. Geospatial data can be analyzed to determine:
- Mapping where things are
- Mapping quantities
- Mapping densities
- Finding what is inside
- Finding what is nearby
- Mapping change
Hundreds of thousands of organizations in virtually every field are using GIS to make maps that communicate, perform analysis, share information, and solve complex problems around the world. This is changing the way the world works.

STEEM.com.bd Discord Channel.Congratulations! This post has been upvoted by @bdcommunity. It is a curation and support project for Bangladeshi content creators. Please join us at the