
Preview: This post is all about the modern advancement of technology used in treating diseases such as cancer. I hope everyone will leraned a lot after all and be always guided by the precautions along the way.
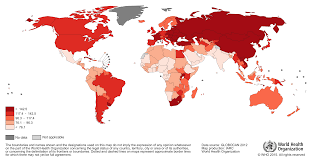
One of the serious burden disease in the world as of today that claimed and victimized a lot of people worldwide is cancer. Cancer is a major burden of disease worldwide. Each year, tens of millions of people are diagnosed with cancer around the world, and more than half of the patients eventually die from it. In many countries, cancer ranks the second most common cause of death following cardiovascular diseases. With significant improvement in treatment and prevention of cardiovascular diseases, cancer has or will soon become the number one killer in many parts of the world. As elderly people are most susceptible to cancer and population aging continues in many countries, cancer will remain a major health problem around the globe.
What is Cancer?
.jpeg)
According to medical study today, cancer is defined as a class of diseases characterized by out-of-control cell growth. There are over 100 different types of cancer, and each is classified by the type of cell that is initially affected.
Cancer harms the body when altered cells divide uncontrollably to form lumps or masses of tissue called tumors (except in the case of leukemia where cancer prohibits normal blood function by abnormal cell division in the blood stream). Tumors can grow and interfere with the digestive, nervous, and circulatory systems, and they can release hormones that alter body function. Tumors that stay in one spot and demonstrate limited growth are generally considered to be benign.
.jpeg)
Cancer can be the result of a genetic predisposition that is inherited from family members. It is possible to be born with certain genetic mutations or a fault in a gene that makes one statistically more likely to develop cancer later in life.
Cancer and other medical factors
As we age, there is an increase in the number of possible cancer-causing mutations in our DNA. This makes age an important risk factor for cancer. Several viruses have also been linked to cancer such as: human papillomavirus (a cause of cervical cancer), hepatitis B and C (causes of liver cancer), and Epstein-Barr virus (a cause of some childhood cancers). Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) - and anything else that suppresses or weakens the immune system - inhibits the body's ability to fight infections.
Facts about Cancer
.jpeg)
Study reveals the important reality and facts of cancer and everyone must be attentive about this
•More than 575,000 people die of cancer, and more than 1.5 million people are diagnosed with cancer per year in the US.
.jpeg)
•Cancer is considered to be one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
.jpeg)
•The financial costs of cancer in the US per year are an estimated $263.8 billion in medical costs and lost productivity.
•African Americans are more likely to die of cancer than people of any other race or ethnicity.
.jpeg)
•It is believed that cancer risk can be reduced by avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol intake, limiting UV ray exposure from the sun and tanning beds and maintaining a healthy diet, level of fitness and seeking regular medical care.
Screening can locate cervical cancer, colorectal cancer and breast cancer at an early, treatable stage.
•Vaccines such as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine assists in preventing some cervical, vaginal, vulvar, and oral cancers. A vaccine for hepatitis B can reduce liver cancer risk.
•According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the numbers of new cancer cases is expected to rise by about 70% over the next 20 years.
•The most common sites of cancer among men are lung, prostate, colon, rectum, stomach and liver.
.jpeg)
•The most common sites of cancer among women are breast, colon, rectum, lung, cervix and stomach.

LASER AS TREATMENT
.jpeg)
Laser stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Laser light is different from regular light. The light from the sun or from a light bulb has many different wavelengths and spreads out in all directions. Laser light, on the other hand, has a single wavelength and can be focused in a very narrow beam. This makes it both powerful and precise.
Lasers can be used instead of blades (scalpels) for very careful surgical work, such as repairing a damaged retina in the eye or cutting body tissue. They can also be used to heat and destroy small areas (such as some tumors), or to activate light-sensitive drugs.
Types of lasers
Lasers are named for the liquid, gas, solid, or electronic substance that’s used to create the light. Many types of lasers are used to treat medical problems, and new ones are being tested all the time. The main types of lasers currently being used in cancer treatment include:
•Carbon dioxide (CO2)
•Argon
•Neodymium: yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG)
Doctors and other health professionals who use these lasers need special training in how to operate and safely handle them.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers
The CO2 laser can cut or vaporize (dissolve) tissue with fairly little bleeding. It does very little damage to the surrounding or deep tissue. This type of laser is sometimes used to treat pre-cancers and some early-stage cancers.
.jpeg)
Argon lasers
The argon laser, like the CO2 laser, only goes a short distance into tissue. It’s useful in treating skin problems and in treating some types of eye tumors. It’s sometimes used during colonoscopies (tests to look for colon cancer) to remove polyps before they become cancer. It also can be used with light-sensitive drugs to kill cancer cells in a treatment known as photodynamic therapy (PDT).
.jpeg)
Nd:YAG (Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet) lasers
Light from this laser can go deeper into tissue than light from other types of lasers, and it can make blood clot quickly. Nd:YAG lasers can be used through thin flexible tubes called endoscopes to get to hard-to-reach parts inside the body, such as the esophagus (swallowing tube) or the large intestine (colon). This light can also travel through optical fibers (thin, clear tubes), which can be bent, put into a tumor and then heated to destroy the cancer.
.jpeg)
TREATING CANCER WITH LASER
Lasers can be used in 2 main ways to treat cancer:
•To shrink or destroy a tumor with heat
.jpeg)
•To activate a chemical – known as a photosensitizing agent – that kills only the cancer cells. (This is called photodynamic therapy or PDT.)
Though lasers can be used alone, they are often used with other cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation.
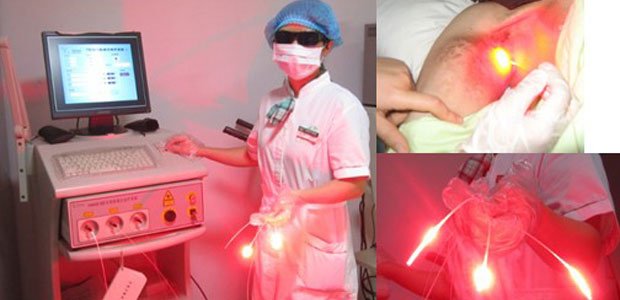
** Other aspects and fields of LASER **
Lasers are also being looked at to treat or prevent side effects of common cancer treatments. For instance, low-level laser therapy (LLLT) might be helpful in treating the arm swelling (lymphedema) that can result from breast surgery. Some studies are also looking at LLLT for preventing or treating severe mouth sores caused by chemotherapy. Other lasers used in medicine.
Shrinking or destroying tumors directly
The CO2 and Nd:YAG lasers are used to shrink or destroy tumors. They can be used with thin, flexible tubes called endoscopes that let doctors see and work inside certain parts of the body that could not be reached except by major surgery. Using an endoscope also helps the laser beam accurately hit its target.
.jpeg)
In the medical fields,Lasers are used this way to treat many kinds of cancer. Here are some examples:
•In the colon and rectum (large intestine), lasers can be used to remove polyps, which are small growths that might become cancer.
.jpeg)
•Lasers can be used to treat certain skin pre-cancers and cancers, as well as pre-cancers or very early cancers of the cervix and surrounding areas.
.jpeg)
•Lasers can sometimes be used to treat cancer that has spread to the lungs from other areas, as well as cancer that is causing a blockage in the airway.
.jpeg)
•In certain cases, small cancers of the head and neck may be treated with lasers.
.jpeg)
•A type of laser treatment called laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT) can be used to treat some types of tumors, such as certain tumors in the liver. It uses heat to help shrink tumors by damaging cells or depriving them of the things they need to live (like oxygen and food).
.jpeg)
Photodynamic therapy
.jpeg)
For most types of photodynamic therapy (PDT), a special drug called a photosensitizing agent is put into the bloodstream. Over time it is absorbed by body tissues. The drug stays in cancer cells for a longer time than in normal cells.
Photosensitizing agents are turned on or activated by certain types of light. For example, an argon laser can be used in PDT. When cancer cells that contain the photosensitizing agent are exposed to light from this laser, it causes the chemical reaction that kills the cancer cells. Light exposure must be carefully timed so that it’s used when most of the agent has left healthy cells, but is still in the cancer cells.
PDT is sometimes used to treat cancers and pre-cancers of the esophagus (swallowing tube), and certain kinds of lung cancer that can be reached with endoscopes.
PDT is also being looked at for use in other cancers, such as those of the brain and prostate. Researchers also are looking at different kinds of lasers and new photosensitizer drugs that might work even better.
Benefits and limitations of laser treatment
.jpeg)
Lasers have some benefits and drawbacks compared with standard surgical tools. Each person’s case is different, so it’s important to discuss the pros and cons of laser therapy with your doctor to decide if it might be right for you.
Lasers have some advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) compared with standard surgical tools.
Positive aspects of laser treatment

•Laser are more accurate and exact than blades (scalpels). For instance, the tissue near a laser cut (incision) is not affected since there is little contact with skin or other tissue.
.jpeg)
•The heat produced by lasers helps clean (sterilize) the edges of the body tissue that it’s cutting, reducing the risk of infection.
.jpeg)
•Since laser heat seals blood vessels, there is less bleeding, swelling, pain, or scarring.
.jpeg)
•Operating time may be shorter.
•Laser surgery may mean less cutting and damage to healthy tissues (it can be less invasive). For example, with fiber optics, laser light can be directed to parts of the body through very small cuts (incisions) without having to make a large incision.
.png)
•More procedures may be done in outpatient settings.
•Healing time is often shorter.
.jpeg)
Limitations of laser treatment
•Fewer doctors and nurses are trained to use lasers.
.png)
There are lot of doctors and nurses in our socity but why is it that only few are trained?this is a problem to be solved quickly.
•Laser equipment costs a lot of money and is bulky compared with the usual surgical tools used. But advances in technology are slowly helping reduce their cost and size.
.jpeg)
•Strict safety precautions must be followed in the operating room when lasers are used. For example, the entire surgical team and the patient must wear eye protection.
.png)
•The effects of some laser treatments may not last long, so they might need to be repeated. And sometimes the laser cannot remove all of the tumor in one treatment, so treatments may need to be repeated.
.jpeg)
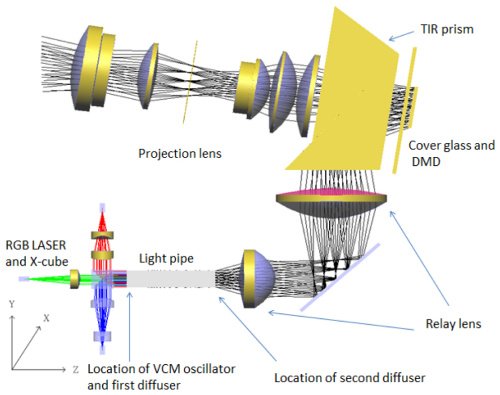
Below is the schematic diagram for different laser diodes set-up in medical industry:
.jpeg)
I know that life on earth is not permanent,what matters most is that we all enjoy our moment together with the people who truly loves us the most and no matter what will happen they are also here for us,that's our family. Take care of your health because it is our individual wealth.
Thank you so much!
.jpeg)
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/lasers-in-cancer-treatment.html
.