ai.jpg)
Machine learning is a field of computer science that gives computer systems the ability to "learn" (i.e., progressively improve performance on a specific task) with data, without being explicitly programmed.
The name machine learning was coined in 1959 by Arthur Samuel.Evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence,[3] machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data such algorithms overcome following strictly static program instructions by making data-driven predictions or decisions, through building a model from sample inputs. Machine learning is employed in a range of computing tasks where designing and programming explicit algorithms with good performance is difficult or infeasible; example applications include email filtering, detection of network intruders or malicious insiders working towards a data breach, optical character recognition (OCR),learning to rank, and computer vision.
THEORY;
- Pattern recognition
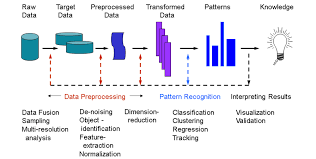
this is a branch of machine learning that focuses on the recognition of patterns and regularities in data, although it is in some cases considered to be nearly synonymous with machine learning. Pattern recognition systems are in many cases trained from labeled "training" data (supervised learning), but when no labeled data are available other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns (unsupervised learning).
The terms pattern recognition, machine learning, data mining and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) are hard to separate, as they largely overlap in their scope. Machine learning is the common term for supervised learning methods[dubious – discuss] and originates from artificial intelligence, whereas KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and stronger connection to business use. Pattern recognition has its origins in engineering, and the term is popular in the context of computer vision: a leading computer vision conference is named Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. In pattern recognition, there may be a higher interest to formalize, explain and visualize the pattern, while machine learning traditionally focuses on maximizing the recognition rates. Yet, all of these domains have evolved substantially from their roots in artificial intelligence, engineering and statistics, and they've become increasingly similar by integrating developments and ideas from each other.
- Computational Learning Theory
In computer science, computational learning theory (or just learning theory) is a subfield of Artificial Intelligence devoted to studying the design and analysis of machine learning algorithms.
.jpg)
Theoretical results in machine learning mainly deal with a type of inductive learning called supervised learning. In supervised learning, an algorithm is given samples that are labeled in some useful way. For example, the samples might be descriptions of mushrooms, and the labels could be whether or not the mushrooms are edible. The algorithm takes these previously labeled samples and uses them to induce a classifier. This classifier is a function that assigns labels to samples including samples that have never been previously seen by the algorithm. The goal of the supervised learning algorithm is to optimize some measure of performance such as minimizing the number of mistakes made on new samples.
- Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI, also machine intelligence, MI) is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence (NI) displayed by humans and other animals. In computer science AI research is defined as the study of "intelligent agents.
any device that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chance of successfully achieving its goals. Colloquially, the term "artificial intelligence" is applied when a machine mimics "cognitive" functions that humans associate with other human minds, such as "learning" and "problem solving".[
The scope of AI is disputed: as machines become increasingly capable, tasks considered as requiring "intelligence" are often removed from the definition, a phenomenon known as the AI effect, leading to the quip, "AI is whatever hasn't been done yet. For instance, optical character recognition is frequently excluded from "artificial intelligence", having become a routine technology. Capabilities generally classified as AI as of 2017 include successfully understanding human speech, competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and Go, autonomous cars, intelligent routing in content delivery network and military simulations.
Artificial intelligence was founded as an academic discipline in 1956, and in the years since has experienced several waves of optimism, followed by disappointment and the loss of funding (known as an "AI winter"), followed by new approaches, success and renewed funding.For most of its history, AI research has been divided into subfields that often fail to communicate with each other. These sub-fields are based on technical considerations, such as particular goals (e.g. "robotics" or "machine learning"),the use of particular tools ("logic" or "neural networks"), or deep philosophical differences. Sub fields have also been based on social factors (particular institutions or the work of particular researchers).
IMPORTANCE OF MACHINE LEARNGING;
The traditional problems (or goals) of machine learning include reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, learning, natural language processing, perception and the ability to move and manipulate objects. the general intelligence is among the field's long-term goals.Approaches include statistical methods, computational intelligence, and traditional symbolic AI. Many tools are used in machine learning, including versions of search and mathematical optimization, neural networks and methods based on statistics, probability and economics. The field draws upon computer science, mathematics, psychology, linguistics, philosophy and many others.
The field was founded on the claim that human intelligence "can be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it".[18] This raises philosophical arguments about the nature of the mind and the ethics of creating artificial beings endowed with human-like intelligence, issues which have been explored by myth, fiction and philosophy since antiquity.Some people also consider machine learning to be a danger to humanity if it progresses unabatedly. Others believe that , unlike previous technological revolutions, will create a risk of mass unemployment.
In the twenty-first century, the techniques have experienced a resurgence following concurrent advances in computer power, large amounts of data, and theoretical understanding; and AI techniques have become an essential part of the technology industry, helping to solve many challenging problems in computer science.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Machine_learning
Not indicating that the content you copy/paste is not your original work could be seen as plagiarism.
Some tips to share content and add value:
Repeated plagiarized posts are considered spam. Spam is discouraged by the community, and may result in action from the cheetah bot.
Creative Commons: If you are posting content under a Creative Commons license, please attribute and link according to the specific license. If you are posting content under CC0 or Public Domain please consider noting that at the end of your post.
If you are actually the original author, please do reply to let us know!
Thank You!
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence
Awesome!
I did not read the entire text yet, but I will.
Do you plan to also go a little more into detail by programming a machine learning software? I would like to learn it from scratch.
yes! that would be in the part 2 of the article