The University of Delft pushed the limits of datastorage to the level of atoms. Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) was used to push around chlorine atoms over a raster of copper atoms. The team of researchers was inspired by the QR code system. The technique is not expected to hit the market anytime soon, but it is still a neat little trick to watch:
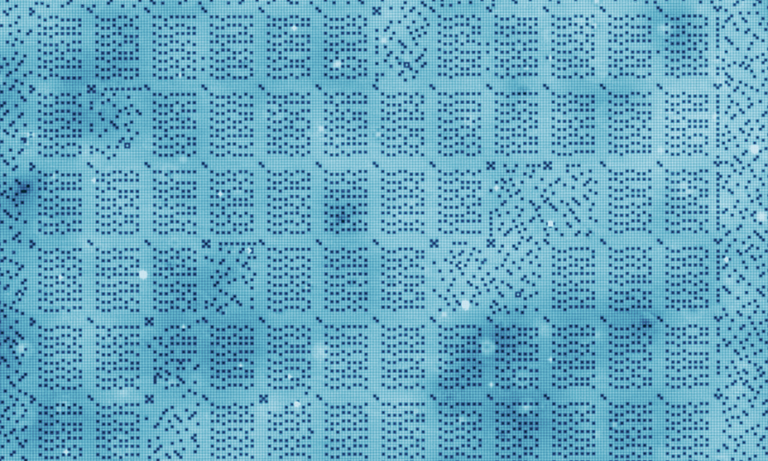
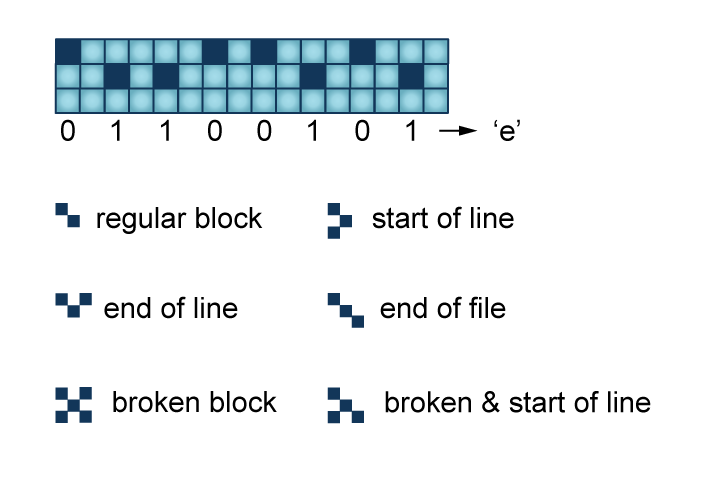
The video supplied by the university of Delft is very explanatory:
Published article:
A kilobyte rewritable atomic memory, Nature Nanotechnology, dx.doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2016.131