
Whether you're an avid gamer who is extremely cautious and mindful of your computer specs, or a casual computer user, you've heard the term RAM before. It's an essential part of the computer.
One of the biggest things you've heard when it comes to RAM is probably "Just add more RAM, and it'll speed up your computer!"

Is this true? Does RAM actually have a purpose in increasing computer speed? What does it actually do?
Well I hope to summarize and simplify this in the 2nd installment of Simplifying Computers! A quick note before continuing on is this is NOT going to go over the history of RAM. I believe that it is not needed within the context of explaining its purpose and how it functions within the context of a PC.
Difficulty level: 3.5/5
What is RAM? - The Basics
Meaning: RAM stands for "Random Access Memory".
Purpose: RAM is used to specifically allow current data (via the applications, games, and programs used in the PC/device) to be quickly accessible by the CPU. Think of RAM as short-term memory storage! The memory stored within the RAM will only be kept as long as the computer is running; so, if someone turns off their PC, all the memory within the RAM is lost. When a user turns their PC on again, RAM will be activated and have the files retrieved from the computer's hard drive or solid state drive.
Random Access Memory will not run out of memory because of this process. It can store up all its entire capacity during a computer session; but, it will not run out since it is temporarily used up.
Types of RAM
There are two main types of RAM:
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM) - basically requires power to continue functioning and doing its job. DRAM is more compact and dense; in other words, within its small size, it can pack more memory than SRAM could at the same capacity.
- Static RAM (SRAM) - a predecessor to DRAM. It does not need electricity and power to function; however, it is more expensive, requiring bigger, bulkier materials to be effective.
SRAM is significantly faster than DRAM since it has more transistors - SRAM typically has 4-6, while DRAM has only 1 - meaning the SRAM would require no refresh cycles. In this case, SRAM can be used for cache memory (another topic!)
Within the sector of each type of RAM, there are specific names of RAM that are used in today's PC builds. They will not be mentioned for the sake of simplicity; but, you can check out the specific names on your own. I definitely recommend it!
How does DRAM work?
Since DRAM is used in modern computers, we will explain its function and process.
DRAM has 1 transistor and 1 capacitor. 1 transistor plus 1 capacitor equals 1 memory cell. One memory cell is one bit of data. If you want to know what each one specifically does on its own, I suggest reading up Basic Electronic Components! It will explain it much better than I can :p
The capacitor's role is to hold the data - whether it be a one or a zero (binary). A capacitor is extremely limited in its holding capacity, however. Think of a toddler attempting to carry a three pounds of sand in a bucket. It is almost certain that the toddler will lose its grip and drop some - if not all - the sand in the bucket. Remember this analogy as I explain the capacitor.
Capacitor's are capable of holding electrons, or data. In binary, there are two numbers: 1 and 0. Data is in binary form when it comes to storing memory in the RAM. When data is at 1 in binary, that is equivalent to a capacitor holding a bucket full of electrons up to the brim. When the data is a 0 in binary, the capacitor's electrons are emptied.
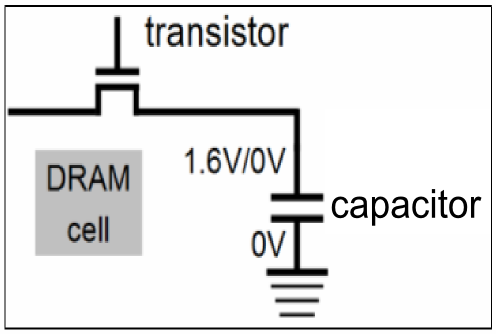
This is where the analogy explained earlier comes in. The capacitor (the toddler) is not capable of holding its electrons for long, and will be emptied within seconds (dropping the sand in the bucket) simply because that is how it functions; hence, dynamic random access memory.
To compensate, the CPU contains a memory controller that recharges all the capacitor's that are holding a 1, which represents the data they are holding. The memory controller will quickly read the capacitor's charge (via the transistor) and recharge all the capacitor's that are holding a 1 before it leaks or discharges. This entire process is done in nanoseconds, and is done thousands of times per second! Amazing how this whole thing works.
This is where Dynamic comes from. A capacitor must be dynamically reminded of its state, or else it will forget, and data will be potentially lost or corrupted.
The transistor's function is to toggle between allowing memory control read from the capacitor, or change the state of the capacitor (binary). Think of this as a gate to the house. The house is the capacitor, which holds valuable data/collections of items and information. If a request is sent from memory control to access and read the capacitor's information, it must go through the transistor. The same goes for writing on the capacitor (aka changing its state).
A Quick Explanation on How SRAM Works
SRAM is completely different, since it does not need to be dynamically reminded of a capacitor's state.
SRAM uses around 4-6 transistors for each memory cell, and it does not have a capacitor in each cell like DRAM does.
It is typically used for cache memory, as mentioned.
Where is RAM located?
RAM is located on your computer's motherboard. Within the motherboard, there will be specific RAM slots to place your RAM in. Usually there are two to four slots, depending on the type and build of your PC. There is a specific procedure that you must follow, but it is extremely easy to replace and remove your RAM.

Why do we need RAM? Can't we put everything in the Hard Drive/Solid State Drive?
As mentioned, RAM is extremely important in keeping a processor running efficiently. It would be extremely slow and tiring for the processor to go to a Hard Drive/Solid State Drive, search for the Boot system for the OS and applications and mandatory programs, and run them. No one would want to be waiting for a long boot time. Processors have a big job, and so it does need help from other areas of the motherboard. There is so much data that goes around in one short computer session, and so having a specific location for memory allows the processor to easily navigate and use the necessary programs, applications, and files needed for a successful boot.
Does Better RAM Equal Better Computer Speed?
No. It does not directly improve your computer speed.
However, it does allow you to multi-task a lot more smoothly and efficiently. Since you have a bigger capacity to hold volatile memory within your RAM, you have the ability to open more applications, programs, and activities without diminishing overall performance.
It would be recommended to gauge your day to day computer usage, and see if you need a bit more RAM to compensate for your computer-related activities.
Conclusion
There you have it! A simple explanation of how RAM works in your computer! I hope you learned something new today.
I would like to say that this is just the beginning. This post does not cover everything you need to know about random access memory because there are so much variations and types. I just covered the surface level. Now it's on you to dig deeper and learn more about the world of computers, particularly RAM and its further uses. Don't be afraid to Google something or ask from peers or experts in this area. We are all learners at the end of the day, so I encourage you to learn!
Also, if I made any technical mistakes with my explanations, please do not hesitate to let me know! I'd be more than happy to change it, and discuss the matter with you further.