
Third Generation (3G) mobile devices and services will transform wireless communications into on-line, real-time connectivity. In 1980's the first generation (1G) mobile phones are consists of Analog models. Then after 10 years the Second generation (2G) mobile phones are entered into the world with Digital networks. This leads to new wireless data and internet services all-round the world since 1991 onwards. But this wireless growth and internet growth which is of great demand in later days. This leads to the next generation development(i.e 3G). So, the communication industry's they plan to implement 3G wireless technology for facing the great demand in market. In 2002, the third generation(3G) technology introduced in market with simultaneous use of speech and data services. Among this 3g, a new high speed(gigabit) internet providing technology 4G(fourth generation) touches the world with mobile WiMAX technology in 2006.Finally, In this paper we have to share and explore our ideas in current and future trends of wireless technologies.
Existing Mobile Networks
First Generation Wireless Technology
.jpg)
In first generation mobile communication networks are based on analog signaling. They are commonly called as AMPS(Analog Mobile Phone Systems). Analog systems are basically circuit switched technology and designed only for voice not data.
Second Generation Wireless Technology

The second generation mobile communication networks are based on low digital data signaling. At present, the most user rated 2G wireless technology is known as GSM(Global System for Mobile Communications). GSM technology is a combination of CDMA and FDMA. In addition to GSM, a similar technology, called PDC(Personal Digital Communication). PDC technology based fully on TDMA. Both, GSM and other TDMA based systems have become the leader of 2G wireless technologies. The special features of CDMA technology are clear voice quality without background noise, fewer dropped calls, enhanced security, greater reliability as well as network capacity. As stated earlier, 2G network is based on circuit-switched technology, it can expanded its application to more advanced voice services called Line Identification. 2G wireless networks handles some data services such as FAX, SMS at the data rate of upto 9.6 kbps. At the same time, it is not suitable for web browsing and multimedia applications.
Second Generation (2G+) Wireless Technology
As stated in a previous section, the virtual explosion of Internet usage has had a tremendous impact on the demand for advanced wireless data communication services. However, the effective data rate of 2G circuit-switched wireless systems is relatively slow -- too slow for today's Internet. As a result, GSM, PDC and other TDMA-based mobile system providers and carriers have developed 2G+ technology that is packet-based and increases the data communication speeds to as high as 384kbps. These 2G+ systems are based on the following technologies: High Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution (EDGE) technologies.
PACKET: It's a digital networking communication methods that groups all transmitted data regardless of content, type or structure into suitable sized blocks. packets send the data in the process of buffering and queueing.
HSCSD is one step towards 3G wideband mobile data networks. This circuit-switched technology improves the data rates up to 57.6kbps.

.jpg)
GPRS technology is packet-based and designed to work in parallel with the 2G GSM, PDC and TDMA systems that are used for voice communications over a data speed upto 115kbps. The data is packetized and transported over Public Land Mobile Networks (PLMN) using an IP backbone so that mobile users can access services on the Internet, such as SMTP/POP-based e-mail, FTP and HTTP-based Web services.
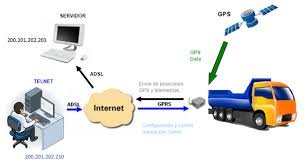
EDGE technology is a standard that has been specified to enhance the throughput per timeslot for both HSCSD and GPRS. The enhancement of HSCSD is called ECSD, whereas the enhancement of GPRS is called EGPRS. In ECSD, the maximum data rate will not increase from 64 kbps due to the restrictions in the A interface, but the data rate per timeslot will triple. Similarly, in EGPRS, the data rate per timeslot will triple and the peak throughput, including all eight timeslots in the radio interface, will exceed 384 kbps.

The following protocols which that are used on the GPRS networks infrastructure,
Sub-Network Convergence Protocol Logical Link Control (LLC)
Base Station System- Protocol
GPRS tunnel protocol (GPRS TP)
GPRS Mobility Management Network Service
BSSAP+
SCCP, MTP3,MTP
Mobile Application Part(MAP).
.jpg)
Third Generation (3G) Wireless Networks
The most important feature of this generation technology is ability to unify the existing cellular Standards CDMA, GSM and TDMA in a single network. The following three interface modes will prove the above result CDMA, CDMA2000 and Universal Wireless Communication (UWC-136) interfaces.
.
Wideband CDMA (W-CDMA) is compatible with the current 2G GSM networks prevalent in Europe and parts of Asia. W-CDMA will require bandwidth of between 5Mhz and 10 Mhz, making it a suitable platform for higher capacity applications. It can be overlaid onto existing GSM, TDMA (IS-36) and IS95 networks. Subscribers are likely to access 3G wireless services initially via dual band terminal devices. W-CDMA networks will be used for high-capacity applications and 2G digital wireless systems will be used for voice calls.
The second radio interface is CDMA2000 which is backward compatible with the second generation CDMA IS-95 standard predominantly used in US.
The third radio interface, Universal Wireless Communications � UWC-136, also called IS-136HS, was proposed by the TIA and designed to comply with ANSI-136, the North American TDMA standard.
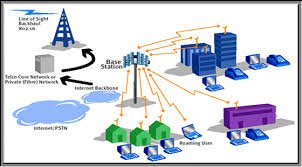
3G wireless Networks consists of Radio Access and Network (RAN) and Core Network. The core network consists of a packet-switched domain, which includes 3G SGSNs and GGSNs, which provide the same functionality that they provide in a GPRS system, and a circuit-switched Domain, which includes 3G MSC for switching of voice calls. Charging for services and access is done through the Charging Gateway Function (CGF), which is also part of the core network. RAN functionality is independent from the core network functionality. The access network provides a core network technology independent access for mobile terminals to different types of core networks and network services. Either core network domain can access any appropriate RAN service; e.g. it should be possible to access a �speech� radio access bearer from the packet switched domain.
The following protocol which that was using in the 3G technology they are
Global Mobility Management (GMM) : protocol that includes attach, detach, security, and routing area update functionality.
Node B Application Part (NBAP) : provides procedures for paging distribution, broadcast system information and management of dedicated and logical resources.
Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) : maps higher level characteristics onto the characteristics of the underlying radio-interface protocols. PDCP also provides protocol transparency for higher layer protocols.
Radio Link Control (RLC) : provides a logical link control over the radio interface.
Medium Access Control (MAC) : controls the access signaling (request and grant) procedures for the radio channel.
Radio resource Control (RRC) : manages the allocation and maintenance of radio communication paths.
Radio Access Network Application Protocol (RANAP) : encapsulates higher layer signaling. Manages the signaling and GTP connections between RNC and 3G-SGSN, and signaling and circuit-switched connections between RNC and 3G MSC.
Radio Network Service Application Part (RNSAP) : provides the communication between RNCs.
GPRS Tunnel Protocol (GTP) : protocol that tunnels the protocol data units through the IP backbone by adding routing information. GTP operates on top of TCP/UDP over IP.
Mobile Application Part (MAP) : supports signaling between SGSN/GGSN and
HLR/AuC/EIR. AAL2 Signaling (Q.2630.1, Q.2150.1, Q.2150.2, AAL2 SSSAR, and AAL2 CPS): protocols suite used to transfer voice over ATM backbone using ATM adaptation layer 2.
Sigtran (SCTP, M3UA): protocols suite used to transfer SCN signaling protocols over IP network.

Fourth Generation (4G) wireless Networks
Based on the study, 4G mobile technology is in a determining and standardization stage. Although 4G wireless technology offers higher data rates and the ability to roam across multiple heterogeneous wireless networks, several issues require further research and development. Since 4G is still in the cloud of the sensible standards creation, ITU and IEEE form several task forces to work on the possible completion for the 4G mobile standards as well. 3GPP LTE is an evolution standard from UMTS, and WiMAX is another candidate from IEEE.
Fourth Generation Technologies
• 4G Mobile Technologies
• 3GPP Long Term Evolution
• WiMAX, WiBro, Software
• Defined Radio
• Open Architecture
These technologies have different characteristics and try to meet 4G characteristics to become a leading technology in the future market. Under these circumstances, this paper will present about the current trends and its underlying technologies to implement the 4G mobile technology. This paper also shows some of the possible scenarios that will benefit the 4th generation technology.
.jpg)
Increasing Positions of Broadband in 4G
• Asymmetric Digital Subscriber(ADSL)
• Optical Fiber Access Systems
• Offices or Home LANs
Features of 4G
• Low cost compared to 3G
• Coverage of Wide Area -> Maintain a service area during the transition of new system from existing system.
• ImprovingI Efficiency and Services
• Making use of new spectrum opportunities
• Better Integration with other open standards
Fourth Generation(4G) Standards
IEEE 802.16 -> Standard Protocol Using in WiMAX
IEEE 802.16e -> Standard Used for Roaming and Sharing
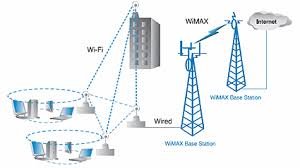
IEEE 802.20 -> Standard Protocol Used for Replacing low Compatability in WiMAX to High Compatability.
In the present world, 3G technologies are growing more to overcome the 2G technologies mainly in mobile networks. For example, recently India's second tele-communications network BSNL launches its 3G services all over india during the half of this year. In this 3G service Video Conferencing Calls, Mobile Broadband of High speed upto 120kbps, Mobile TV etcs�.. are very effective and efficient in BSNL. As well as, Korean leading Mobile company SAMSUNG planned to launch its WiMAX mobile phones in India to be soon. The research says, at the end of 2010 North America, Europe and Asian countries are expected to grow upto 2500 Million subscribers totally. Among all, a new technology of Fourth Generation(4G) is still in cloud of the sensible standard creation to beat 3G. Finally, in this paper, we share and explore our ideas in Future Wireless networks (3G&4G).

The evolution of wireless tech, from 1G to 4G, transformed connectivity. What is LTE Network https://www.uctel.co.uk/blog/4g-vs-lte-understanding-the-difference-between-4g-and-lte ? LTE (Long-Term Evolution) enhances 4G with faster speeds and seamless data handling, supporting HD streaming, VoIP, and IoT. It ensures efficient integration across diverse devices, making it vital for modern mobile ecosystems. Future innovations promise even greater possibilities!