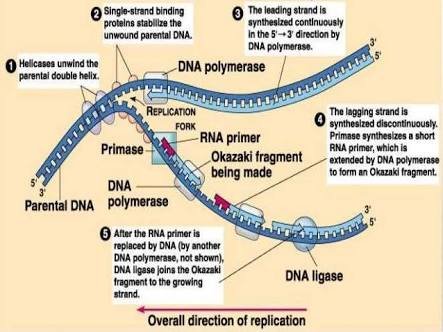
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two similar replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. It happens in all living organism and its the basis for biological inheritance.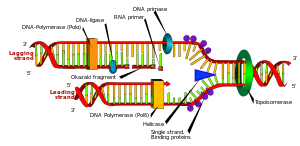
DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. In replicating, the strand are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a basis for the production of its counterpart, this process is called semi-conservative replication.
In a cell, the DNA replication starts at particular locations, or origins of replication, in the genome. Unwinding of DNA at the origin and synthesis of new strands results in the replication of forks growing bi-directionally from the origin. Some proteins are associated with the replication of forks to help inthe initiation and continuation of DNA synthesis. Most famously, DNA polymerase synthesizes the new strands by adding nucleotides that compliment each strand. DNA replication happens during the S-stage of interphase..jpg)
DNA replication can also be perfomed artificially i.e outside a cell. DNA polymerases isolated from cells and artificial DNA primers can be used to initiate DNA synthesis at known sequences in a template DNA molecule. A common laboratory technique known as the polimerase chain reaction (PCR) clinically applies such artificial synthesis to amplify a specific target DNA fragment from a pool of DNA, DNA carries the information feom the parent.
Bereh gam