What Will I Learn?
In this tutorial
- You will learn to embed a steem-js bot into an AWS Lambda
- You will learn to configure an AWS Lambda to be triggered periodically
- You will learn to protect your Steem key with KMS
Requirements
To follow this tutorial you need
- node.js installed
- an Amazon AWS account
- AWS CLI installed and configured for your account
Difficulty
Intermediate
Tutorial Contents
This tutorial will show how to create a steem-js bot, that runs as AWS Lambda. The bot will be triggered periodically. Further this tutorial will show how you encrypt your Steem key with KMS, such that it is not necessary to include it as plain text in the bot's source code.
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Lambda executes your code only when needed and scales automatically, from a few requests per day to thousands per second.
(from the AWS Documentation)
Why AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda functions are the only AWS service that offers a free contingent, even after the first 12 months (where Amazon offers a limited set of its AWS services for free). Every month up to one million Lambda calls are included with up to 400.000 GB/s per month. The second metric is a bit confusing, basically it it means that the overall runtime of your Lambda multiplied with its memory consumption must be less than 400.000 GB/s per month to stay within the free contingent. The lowest available memory tier is 128 MB. This is sufficient for a typical steem-js bot, such that it may run up to 3.2 million seconds per month. Hence if one execution of a bot run takes less about 3 seconds we are bound by the one million free calls per month, such that the bot may run more than 1000 times per hour, which should be totally sufficient for most applications.
Long story short, you don't need to pay for a dedicated server, if you run your bot as AWS Lambda function.
Project setup
Setup a new node project and add steem-js as dependency with
npm init
npm install steem --save-dev
Be sure to select index.js as main entry point.
I separate the project into three source files: bot.js that includes all the logic for the bot, index.jswith the extra logic for the AWS Lambda, and app.js to test the bot locally.
Implementation of the bot
The bot itself is pretty simple, as this is not the main focus of the tutorial. It's purpose is to look for new posts in utopian-io and to vote for the first tutorial it finds. The key required for the vote is passed as parameter to the bot function, while other settings are directly configurable in bot.js. The full source code of bot.js is shown below.
"use strict";
const steem = require("steem");
/* settings */
var my_account = "nafestw";
var vote_weight = 10000;
module.exports = function(wif) {
steem.api.getDiscussionsByCreated(
{ tag: "utopian-io", limit: 100 },
(err, result) => {
// filter everything but tutorials
let candidates = result.filter(res => {
if (!res.json_metadata) return false;
return res.json_metadata.indexOf('"type":"tutorial') !== -1;
});
if (candidates.length > 0) {
let target = candidates[0];
// vote for the first one
steem.broadcast.vote(
wif,
my_account,
target.author,
target.permlink,
vote_weight,
function(err, result) {
if (err) console.log(err);
else console.log(result);
}
);
}
}
);
};
The implementation of app.js is trivial and just calls the function exported by bot.js with the Steem key:
"use strict";
const bot = require("./bot");
var wif = "ENTER_STEEM_KEY_HERE";
bot(wif);
Encryption of the Steem key
As state above, it is not a good practice to include your key in plain text in source code that is uploaded to a server. AWS provides an encryption mechanisms to solve this, such that an encrypted version of the key can be stored with the Lambda function.
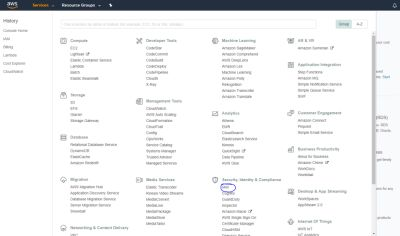
Create a Role
Log into the AWS Management console and select IAM under "Security, Identity & Compliance". First you need to setup a role. This role will be needed for the key and to create the Lambda function:
- Select Roles -> Create Role.
- Select Lambda and press Next
- Select AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole and press Next
- Enter a name for the role: steem_bot_role
Create the encryption key
On the left, select the last point: "Encryption Keys". Now it's necessary to select the region, which will also be the region you will use for your Lambda later. You can find all regions that support Lambdas here. Next, select "Create Key", enter an alias for the key and select next step. Adding tags is optional and can be skipped by selecting "Next Step". Next select the users that may administer the new key. Now, for the usage permissions, select the role created before. Review your settings and press Finish. The next page shows the Key ID required for encryption in the next step.
The encrypt your Steem key, go to the command line and encrypt your key with
aws kms encrypt --key-id <kms_key_id> --plaintext "<YOUR_STEEM_KEY>" --query CiphertextBlob --output text | base64 -D > encrypted_secret
Replace <kms_key_id> with the key id from the AWS management console and <YOUR_STEEM_KEY> with your Steem key. The aws kms encrypt command outputs the encrpyted string in base64 encoding. To decrypt it, it must be in binary form. Hence it is piped to base64 -D and written to the file encrypted_secret which should be stored next to the bot's source code.
Call the bot function from the Lambda handler
Using AWS Lambdas to execute your code requires that it is encapsulated in a handler function. This function must be exported to exports.handler and receives three parameters (event, context, callback), which we ignore, because we don't need them. On default AWS Lambda expects export.handler to be defined in index.js (you can change that in the AWS management console).
The encrypted key is loaded from file and decrypted with kms.decrypt before it is passed to the bot function. The full implementation of index.js is:
"use strict";
const bot = require("./bot");
var fs = require("fs");
var AWS = require("aws-sdk");
var kms = new AWS.KMS({ region: "us-west-2" });
var secretPath = "./encrypted_secret";
var encryptedSecret = fs.readFileSync(secretPath);
var params = {
CiphertextBlob: encryptedSecret
};
exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => {
kms.decrypt(params, function(err, data) {
if (err) console.log(err, err.stack);
else {
let wif = data["Plaintext"].toString();
bot(wif);
}
});
};
Deploy the Lambda
To deploy the Lambda, all code and assets (as encrypted_secret) including the node_modules folder must be added to a ZIP file. (Smaller Lambdas without extra dependencies can be edited online). If you have the ZIP file ready, go to the AWS Management Console and select Lambda and then Create function. In the following form keep "Author from scratch" selected, enter a name for the function, keep the NodeJS Runtime, and choose the steem_bot_role that has been created before. Then press "Create Function".
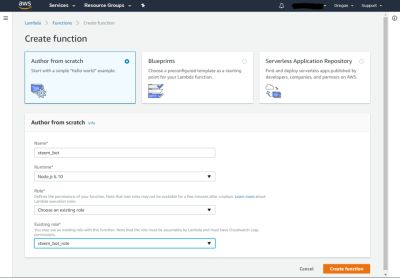
In the section "Function code", select "Upload .ZIP file" as "Code Entry Type", press "Upload" and select the ZIP file with your bot's code.

Finally, it is necessary to add a trigger for the Lambda function. The steem_bot should be triggered periodically, so select CloudWatch Events and "Create New rule" for a new rule. The rule must be named and a expression for the actual schedule must be specified. The simplest rules are in the form rate(5 minutes), which runs the Lambda function every five minutes. If everything is entered, press Add.
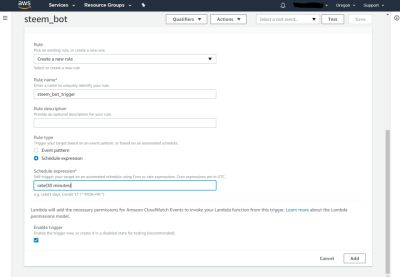
Amazon AWS Lambdas are terminated after a configurable timeout, which is three seconds on default. Depending on what your bot does, you may need to adapt this setting. You can find it on the lamba's page further below under "Basic Settings".
That's it. If you press Save on the top right, the ZIP file is uploaded and your Lambda is saved. You can test it immediately by selecting "Test" or just wait for its first automatic invocation. If something doesn't work as expected, you can extend your Lambda's code with console.log() statements, which are accessible through the monitoring functions of AWS Lambda.
This concludes the tutorial on running a steem-js bot as AWS Lambda function.
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
Unfortunatly this solution is not totally free, I found out that the KMS key is billed with 1$/month. 20.000 key usages/month are free (should be sufficient for a bot). Further you have to pay for incoming and outgoing traffic, if your free tier expired. So monitor the costs with the ASW management console, if you choose this solution.
@nafestw, I always try to support who contribute to open source project, upvote you.
Discord Channel50SP | 100SP | 250SP | 500SP | 1000SP | 5000SP | custom amount.You got a 8.89% upvote from @whalebuilder courtesy of @nafestw. Join @whalebuilder family at our . Don't let your precious stake(SP) go stale...Make it do more so you have to do less. Deligate it to @whalebuilder by clicking on one of the ready to delegate links:
Thank you for the contribution. It has been approved.
like your work
You can contact us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Hey @nafestw I am @utopian-io. I have just upvoted you!
Achievements
Suggestions
Get Noticed!
Community-Driven Witness!
I am the first and only Steem Community-Driven Witness. Participate on Discord. Lets GROW TOGETHER!
Up-vote this comment to grow my power and help Open Source contributions like this one. Want to chat? Join me on Discord https://discord.gg/Pc8HG9x
Congratulations @nafestw! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on any badge to view your own Board of Honor on SteemitBoard.
For more information about SteemitBoard, click here
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP