
Docker is an open source tool, designed to create, deploy and run applications easily and quickly by using containers. It packages, provisions and runs containers independent of the OS. It is developed in Go language.
Containers allows packaging an application with all the libraries, configuration files and dependencies as one single image. This helps the developers to be rest assured that the application will run on any other machine regardless of settings that the machine might have that could differ from the machine used for writing and testing the code.
Docker use kernel of the host system on which the applications are running. It shares the services of underlying operating system. This gives a significant performance boost and reduces the size of application.
Docker was created to work on Linux platforms. However, non-linux operating systems like Microsoft Windows and Apple OS X are also supported. Versions for Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure is also available.
Features
- Easy and faster delivery of application
- Deploy and scale easily
- Increase Productivity
- Applicatin isolation
- Easier management
In this tutorial, let us see how to install community version of Docker from its repository as well as from its package, on CentOS.
Requirements
- Minimum version of CentOS 7
- The
centos-extrasrepository must be enabled. This repository is enabled by default, but if you have disabled it, you need to re-enable it. - The
overlay2storage driver is recommended.
Installation From Repository
- Install required packages : yum-utils, device-mapper-persistent-data and lvm2.
yum-utilsprovides theyum-config-managerutility anddevice-mapper-persistent-dataandlvm2are required by thedevicemapperstorage driver needed by Docker.
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2

- Add the stable Docker repository.
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo

- Install the community version of Docker, docker-ce.
yum install -y docker-ce

- Start Docker service.
systemctl start docker
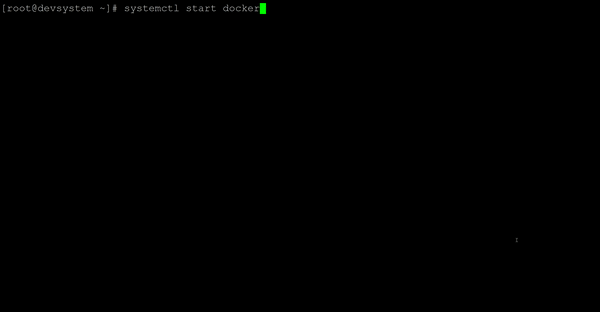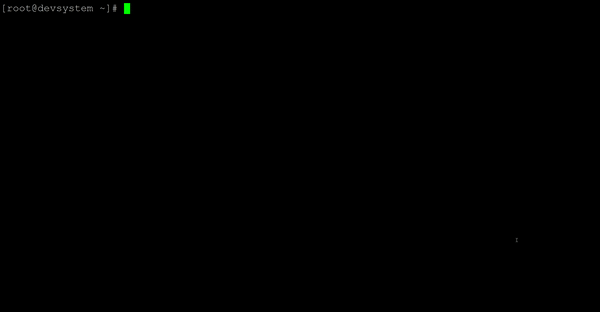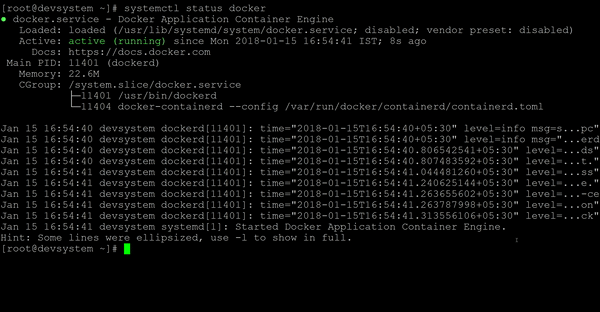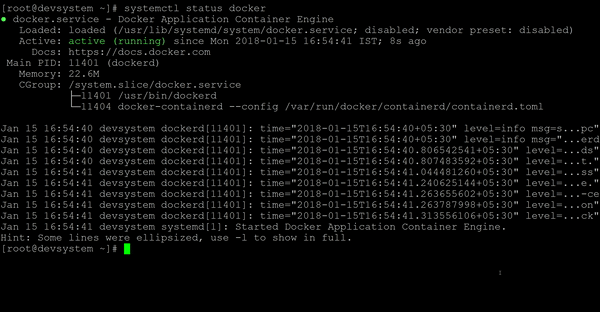
- Verify that the Docker service has started. The service should be in
runningstate.
systemctl status docker
- Verify that docker is installed correctly by running the
hello-worldimage.
docker run hello-world

- Check the version of docker.
docker --version

Installation from Package
- We'll download Docker's RPM using
wget. Ifwgetis not availble, install it using yum.
yum install -y wget

.rpmfile for the needed Docker version using wget. (Since I need Docker version 17.12.0-ce in have downloadeddocker-ce-17.12.0.ce-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm)Stable Docker's RPM package for CentOS is available at https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/ . Goto this link and download the
wget https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/docker-ce-17.12.0.ce-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm
- Install the downloaded RPM using yum.
yum localinstall docker-ce-17.12.0.ce-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm

- Start the Docker service.
systemctl start docker
- Verify that the Docker service has started. The service should be in
runningstate.
systemctl status docker

- Verify that docker is installed correctly by running the
hello-worldimage.
docker run hello-world

- Check the version of docker.
docker --version

If you have any questions or comments, I'd would love to hear from you in comment section.
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
@originalworks
Nice post @rohancmr
Your contribution cannot be approved because it does not follow the Utopian Rules.
You can contact us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]