
What is Mixin Network?
Mixin Network is an open-source and decentralized web3 platform bringing speed and scalability to the blockchain. The Network allows blockchains to gain free and lightning fast peer-to-peer digital assets transactions, with enhanced privacy and unlimited extensibility.
Mixin's distributed ledger is an open ledger collectively maintained by 25 mainnet nodes. All deposits, withdrawals, and transfers are recorded on this distributed ledger, and each record contains asset type (BTC, ETH, BNB, EOS etc.), transfer amount, and other information.
Foundation:
Founded in Japan by Cedric Fung in 2013, Mixin network was launched on February 28, 2019. As of April 2023, it holds more than 2800 digital assets with top 100 assets totaling market value of +1 Billion dollars with 25 full nodes.
Mixin Consensus:
Mixin uses PoS + aBFT-DAG as consensus algorithm with block confirmation in less than 1 second with a min. of 7 full nodes and 50 at most. Security enhancement is done with the Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). Data modeling & structuring is done through DAG technology (Direct Acrylic Graph). The network supports 48 public blockchains, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Avalanche, Solana, EOS and more, using Sidechain technology for Cross-chain.
The core of Mixin Network is the Mixin Kernel, a fast asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerant directed acyclic graph (aBFT-DAG) to handle unspent transaction outputs within limited Kernel Nodes.
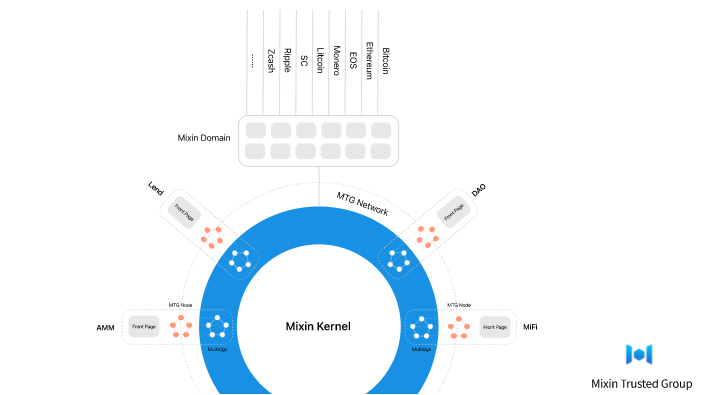
Governance:
Mixin uses the XIN token for security and governance of the network. One must pledge at least 10,000 XIN to establish initial trust and join the network as a full node. It’s also used for network decision making, dApp resources and API calls. The maximum supply is 1 000 000.
XIN token utility:
- Collateral for participating in full-node bookkeeping to obtain mining reward and excess transaction fee.
- Collateral for being a light node to supervise full-node bookkeeping and arrange automatic voting.
- Collateral for participating in the management of the domain assets, and jointly manage assets with nodes.
- Voting to participate in community governance, such as voting to determine the amount of punishment for malicious nodes, what chains to accept, kernel specifications, or some strategies in the upgrade process, etc.
- Creating a Dapp requires a one-time consumption of XIN and cost is determined by the resources that the dApp claims to consume.
In the next article (Part 2) of the Mixin Network overview, we will cover Mixin key features and dApp ecosystem.
Posted using ThiagoRe.com